Few people know that we do not get enough folic acid from food. And it is very necessary for the female body. So during pregnancy planning it is prescribed to many women. I just decided to accept it for general strengthening body.
Why is it needed at all? folic acid? And why is it taken together with vitamins B6 and B12?
- Folic acid is a growth factor - it is necessary for the body to produce cells of the skin, mucous membranes, and hair. In addition to participating in the creation of fetal cells, folic acid takes part in the formation of all blood cells. In addition, it provides good mood, participating in the exchange of biologically active substances serotonin and adrenaline, which play an important role in the state of the nervous system.
- Vitamin B12 and folic acid are related vitamins, so taking them together is recommended. A lack of vitamin B12 leads to the development of partial or secondary folic acid deficiency.
- Vitamin B6 participates in the transformation of amino acids, the metabolism of tryptophan, lipids and nucleic acids, participates in maintaining the immune response, in the processes of inhibition and excitation in the central nervous system, promotes normal formation of red blood cells.
Reception features: 1 tablet 1 time per day is a very convenient regimen. The package contains 40 tablets (that is, my course of treatment was 40 days). After taking it you don’t feel sick, no undesirable symptoms are observed)
And now the most interesting part: Effect. During the treatment, my hair began to grow rapidly! For me this is borderline fantastic; usually hair grows very slowly. The condition of my nails has improved, growth has accelerated (but I don’t complain about them anyway). There were no changes to the skin. But there is another positive effect - the pain in the lower abdomen during critical days(I didn’t even have to take painkillers).

Dosage form
pills
Compound
1 tablet ( daily intake) contains: Folic acid 600 mcg, Vitamin B6 6 mg, Vitamin B12 5 mcg.
pharmachologic effect
Folic acid is a growth factor - it is necessary for the body to produce skin cells, mucous membranes, and hair. For a woman planning a pregnancy, folic acid is the most important vitamin, since it is she who is responsible for the formation of the fetus and cell growth. In the early stages of pregnancy, even a short-term deficiency of folic acid is fraught with the development of defects in the nervous system in the fetus.
In addition to participating in the creation of fetal cells, folic acid takes part in the formation of all blood cells. In addition, it provides a good mood by participating in the exchange of biologically active substances serotonin and adrenaline, which play an important role in the state of the nervous system.
Vitamin B12 and folic acid are related vitamins, so taking them together is recommended. Lack of vitamin B12 leads to the development of partial or secondary folic acid deficiency.
Vitamin B6 is involved in the transformation of amino acids, the metabolism of tryptophan, lipids and nucleic acids, participates in maintaining the immune response, in the processes of inhibition and excitation in the central nervous system, and promotes the normal formation of red blood cells. Helps maintain normal level homocysteine in the blood. Insufficient intake of vitamin B6 is accompanied by increased fatigue, depression, nervousness, and deterioration of skin condition.
Folic acid can be called the “motherhood vitamin”. For a woman planning a pregnancy, folic acid is the most important vitamin, since it is responsible for the formation of the fetus and its proper development. If there is insufficient amount of folic acid in female body there is a high probability of accompanying pregnancy with various deviations in the development of the baby.
It is important to take folic acid for young women, as it regulates the flow of menstrual cycle and prevents the development of osteoporosis. In addition, folic acid has an estrogen-like effect and can slow down the onset of menopause and even reduce unpleasant symptoms after it occurs.
Folic acid is also necessary for normal functioning circulatory system, the vessels and capillaries were healthy and strong.
Selling Features
Without a license
Indications
For women's health and beauty
Contraindications
Persons with individual intolerance to the components of the product, pregnant or breastfeeding women. It is recommended to consult a doctor before use.
Normal shape with full functions. This is why vitamin B 12 is often called antianemic factor .
Name and forms of vitamin B 12
Vitamin B 12 is common name two chemical variants of the cobalamin molecule with vitamin activity. These variants of the molecule are called vitamers and are, in fact, varieties of the same substance, differing from each other in spatial orientation. Vitamin B 12 consists of two vitamers - cyanocobalamin And Hydroxycobalamin. The names of both vitamers are the names of vitamin B 12. However, at present, the name cyanocobalamin is usually used to designate vitamin B 12, since it is in this form that the human body enters most of of this substance.In addition, there are two more active forms vitamin B 12 ( methylcobalamin And deoxyadenosylcobalamin
), which are formed from cyanocobalamin and hydroxycobalamin in the human body. It is in active forms that vitamin B 12 performs its physiological functions. The names of active forms are practically not used to designate vitamin B 12.
Why is vitamin B 12 needed - physiological role
Vitamin B 12 in the human body has the following physiological effects:1. Ensures the formation of normal shaped red blood cells with full functions.
2. Prevents the destruction of red blood cells.
3. Provides coverage of nerve fibers with the myelin sheath, necessary for transmitting impulses and protecting the structure from negative impact external factors.
4. Prevents fatty degeneration of the liver, spleen, heart and other organs.
The listed physiological effects are provided at the molecular level, at which vitamin B 12 activates and supports certain biochemical transformations. At first glance, it is difficult to imagine, but in fact, every biochemical transformation in the body that occurs at the molecular level has its own “physiological” reflection in the form of an effect at the level of organs and tissues. Let's consider how vitamin B 12 provides its physiological effects at the molecular level.
Active forms of vitamin B 12 provide normal work enzymes from the class of reductases, which, in turn, convert folic acid into tetrahydrofolic acid. And tetrahydrofolic acid activates the process of cell division and, therefore, ensures the normal process of regeneration of organs and tissues, maintaining them in a young and fully functioning state. Activation of cell division is especially important for rapidly renewing tissues, such as blood cells, mucous membranes, epidermis, etc. It is thanks to the influence of vitamin B 12 that these tissues are maintained in a normal state.
In addition, cobalamin’s ability to activate cell division can prevent megaloblastic. The fact is that with a deficiency of vitamin B 12, the precursor cells of red blood cells grow, but do not divide, as a result of which giant red blood cells (megaloblasts) are formed in small quantities. Such red blood cells contain little hemoglobin and cannot penetrate small vessels due to their size, resulting in megaloblastic anemia. Vitamin B 12 stimulates the timely division of progenitor cells, resulting in the formation a large number of normal red blood cells containing hemoglobin in sufficient concentration.
The formation of the myelin sheath on nerve fibers is impossible without a sufficient amount of vitamin B12, since its active form ensures the conversion of methylmalonic acid into succinic acid, which is necessary structural component myelin. If vitamin B 12 is not enough, then succinic acid is not formed in the required quantity, as a result of which nerve fiber remains demyelinated. The absence of myelin leads to impaired sensitivity, poor conduction of impulses from the brain to the muscles and back, resulting in numbness of the limbs, tingling, a feeling of “pins and needles” and other symptoms of nerve fiber degeneration.
Prevention of fatty degeneration various organs is provided due to the ability of vitamin B 12 to activate the conversion of homocysteine to methionine. Methionine, in turn, is necessary for the process of removing excess fat by the liver.
Absorption and excretion of vitamin B 12
 Vitamin B 12 is normally absorbed into the blood from the small intestine. However, absorption of this vitamin is possible only in the presence of a small protein compound called Castle's intrinsic factor
and is produced by stomach cells. If internal factor If there is no castla, then vitamin B 12 supplied with food or in tablet form will not be able to be absorbed into the bloodstream and the person will develop a deficiency. Since Castle factor is produced by stomach cells, when it various pathologies The absorption of vitamin B12 may be impaired. However, recent studies have shown that in high dosages (more than 200 mcg per day), vitamin B 12 can be absorbed into the blood without connection with the Castle factor. But such dosages of the vitamin can only be achieved by regularly taking cyanocobalamin tablets.
Vitamin B 12 is normally absorbed into the blood from the small intestine. However, absorption of this vitamin is possible only in the presence of a small protein compound called Castle's intrinsic factor
and is produced by stomach cells. If internal factor If there is no castla, then vitamin B 12 supplied with food or in tablet form will not be able to be absorbed into the bloodstream and the person will develop a deficiency. Since Castle factor is produced by stomach cells, when it various pathologies The absorption of vitamin B12 may be impaired. However, recent studies have shown that in high dosages (more than 200 mcg per day), vitamin B 12 can be absorbed into the blood without connection with the Castle factor. But such dosages of the vitamin can only be achieved by regularly taking cyanocobalamin tablets. In general, the absorption of cobalamin into the blood from food occurs in the following successive stages:
1.
Formation of the Castle factor + cobalamin complex;
2.
Arrival of the complex in small intestine and its passage through the wall into the portal vein of the liver;
3.
Disintegration of the complex and release of vitamin B 12;
4.
Transfer of free vitamin B 12 to all organs.
In organ cells, vitamin B 12 is converted into active forms - methylcobalamin and deoxyadenosylcobalamin, in which it exerts its physiological effects. After performing the functions, the active forms of vitamin B 12 are again transferred into the blood and delivered to the liver and kidneys, from where they are excreted in urine and feces.
Vitamin B 12 can accumulate in the liver, creating a depot that lasts a person for about 3 to 4 years.
Lack of vitamin B 12 - symptoms
With a lack of vitamin B 12 in the body, a person develops the following diseases or clinical symptoms:- Megaloblastic anemia;
- Increased fatigue;
- Funicular myelosis (degeneration of areas of the spinal cord);
- Paresthesia (feeling of goosebumps, tingling on the skin, etc.);
- Paralysis accompanied by dysfunction of the pelvic organs;
- Dry tongue, colored bright red, on the surface of which tingling and burning may be felt;
- Decreased or complete absence of appetite;
- Unpleasant smell bodies;
- Ahilia (zero acidity of gastric juice);
- Erosion on the mucous membranes of various organs (mouth, throat, nose, bronchi, intestines, vagina, etc.);
- Heaviness when walking;
- Yellowing of the skin;
- Shortness of breath and laceration heartbeat during physical activity;
- Patchy hair loss;
- Ulceration of the corners of the mouth;
- Glossitis (inflammation of the tongue);
- Seborrheic dermatitis on certain areas of the skin of the body and face, especially near the nose or mouth;
- Inflammation and itching of the skin in the genital area in men and women;
- Redness, itching, burning and sensitivity of the eyes to light;
- Darkening of vision;
- Formation;
- Personality degradation.
Vitamin B 12 deficiency: causes, symptoms, consequences - video
Vitamin B 12 – which foods contain it?
 Vitamin B 12 is the only compound with vitamin activity that is not synthesized by plants and animals. This vitamin is produced only by microorganisms and must enter the human body from outside as part of food. A small amount of vitamin B 12, which is synthesized in the large intestine by its own microflora, is not absorbed because it cannot rise to the overlying parts of the intestine, where this compound is absorbed into the bloodstream.
Vitamin B 12 is the only compound with vitamin activity that is not synthesized by plants and animals. This vitamin is produced only by microorganisms and must enter the human body from outside as part of food. A small amount of vitamin B 12, which is synthesized in the large intestine by its own microflora, is not absorbed because it cannot rise to the overlying parts of the intestine, where this compound is absorbed into the bloodstream. The main sources of vitamin B 12 are animal products, fish and seafood, such as:
- Beef liver (60 mcg of vitamin B 12 per 100 g of product);
- Pork liver (30 mcg per 100 g);
- Beef kidneys (25 mcg);
- Octopus (20 mcg);
- Chicken liver (16 mcg);
- Mackerel (12 mcg);
- Mussels (12 mcg);
- Sardine (11 mcg);
- Atlantic herring (10 mcg);
- Chum salmon (4.1 mcg);
- Beef (3 mcg);
- Notothenia (2.8 mcg);
- Sea bass (2.4 mcg);
- Lamb (2 – 3 mcg);
- Egg (1.95 mcg);
- Turkey fillet (1.6 mcg);
- Cod (1.6 mcg);
- Carp (1.5 mcg);
- Cottage cheese (1.32 mcg);
- Shrimp (1.1 mcg);
- Cheeses (1.05 - 2.2 mcg);
- Broiler chickens (0.2 – 0.7 mcg);
- Milk and sour cream (0.4 mcg);
- Yogurt (0.4 – 0.7 mcg).
Foods rich in vitamin B 12 - video
Vitamin B 12 – norm of consumption for people of different ages
At different age periods, the need for vitamin B 12 varies, which is associated with metabolic characteristics and the rhythm of life. Moreover, the need for cobalamin does not depend on the gender of the person. Therefore, for different age categories, regardless of gender, different daily intakes of vitamin B12 are recommended, ensuring the normal functioning of vital processes in all cells of the body. The consumption standards for vitamin B 12 for people of different ages are shown in the table.The given norms are called adequate consumption levels, which ensure full coverage of the body's needs for vitamin B 12 compounds. However, these adequate intake levels are only valid for healthy person living a measured and calm life. At physical activity, emotional stress, smoking or drinking alcohol, the need for vitamin B 12 increases by 10–25%, which should be taken into account when planning your own diet.
Minimum permissible safe intake level of vitamin B 12 at dietary nutrition is 1 mcg per day. Maximum amount vitamin B 12, which can be consumed without any harm to health, is 9 mcg per day.
Vitamin B 12 in the blood is normal
 The content of vitamin B 12 in the blood is determined by colorimetric methods. In this case, blood is donated in the same way as for usual biochemical analysis. Normal levels of vitamin B 12 in the blood vary among individuals. of different ages, but does not depend on gender. Currently, the CIS countries have adopted the following standards for the content of vitamin B 12 in the blood at different age periods:
The content of vitamin B 12 in the blood is determined by colorimetric methods. In this case, blood is donated in the same way as for usual biochemical analysis. Normal levels of vitamin B 12 in the blood vary among individuals. of different ages, but does not depend on gender. Currently, the CIS countries have adopted the following standards for the content of vitamin B 12 in the blood at different age periods: - Newborns from 0 to one year – 118 – 959 pmol/l;
- Children over one year old and adults under 60 years old – 148 – 616 pmol/l;
- Adults over 60 years of age – 81 – 568 pmol/l.
- Alcohol;
- Aminoglycoside antibiotics (for example, chloramphenicol, etc.);
- Aminosalicylic acid;
- Colchicine;
- Oral contraceptives;
- Pentamidine;
- Pyrimethamine;
- Anticonvulsants (for example, phenobarbital, phenytoin, etc.);
- Triamterene;
- Phenformin;
- Cholestyramine;
- Cimetidine;
- Irradiation small intestine cobalt.
What vitamins B 12 exist for medical use?
Currently in preparations for medical use The following chemical modifications of vitamin B 12 are used as active substances:- Cyanocobalamin;
- Hydroxocobalamin;
- Cobamamide.
Cyanocobalamin preparations have the weakest and slowest therapeutic effect. Hydroxocobalamin begins to have a therapeutic effect faster than cyanocobalamin, remains in the blood longer and is excreted from the body by the kidneys more slowly. Thus, the duration of action of hydroxocobalamin also exceeds that of cyanocobalamin, so it can be administered less frequently, reducing the number of injections required per full course treatment.
Cobamamide has an almost instantaneous therapeutic effect, beginning to exert its physiological effects immediately after administration. In terms of the speed of development of the effect, cobamamide is the best option vitamin B 12. Therefore, if necessary, get a quick effect, for example, in severe and emergency conditions, it is necessary to use preparations containing vitamin B 12 in the form of cobamamide. In terms of other properties, cobamide is comparable to hydroxocobalamin.
Vitamin B 12 with cobamide and cyanocobalamin is available in the form of lyophilized powder, ready-to-use solution and tablets. And vitamin B 12 in the form of hydroxocobalamin is available only in the form of a ready-to-use sterile solution.
Vitamin B 12 in ampoules - characteristics and names of drugs
 Vitamin B 12 is produced in ampoules in two pharmaceutical forms:
Vitamin B 12 is produced in ampoules in two pharmaceutical forms:
1. Lyophilized powder for the preparation of solution for injection;
2. Ready-to-use sterile solution for injection.
Lyophilisate is preferable to a ready-made solution, since in this form when long-term storage The properties of vitamin B 12 are better preserved.
In addition to dosage forms, vitamin B 12 in ampoules is available in three chemical varieties (cyanocobalamin, hydroxocobalamin and cobamide) under the following commercial names:
- Cobamamide lyophilisate (cobamamide) – ampoules containing 0.1 mg, 0.5 mg and 1 mg active substance;
- Oxycobalamin solution (hydroxocobalamin) – ampoules containing the active substance in dosages of 50 mcg/ml, 0.1 mg/ml and 1 mg/ml;
- Cyanocobalamin solution and lyophilisate (cyanocobalamin) – ampoules containing 30 µg/ml, 50 µg/ml, 100 µg/ml, 200 µg/ml and 500 µg/ml of the active substance;
- Cyanocobalamin bufus (cyanocobalamin) solution – ampoules containing 500 mcg/ml of active substance;
- Cyanocobalamin-Vial (cyanocobalamin) solution – ampoules containing 200 µg/ml and 500 µg/ml of the active substance.
Vitamin B 12 in tablets - characteristics and names of drugs
In the dosage form of tablets, vitamin B 12 is available only under two commercial names - Cobamamide and Cyanocobalamin. Moreover, both drugs contain as an active substance the same forms of vitamin B12, which are reflected in their names.Cobamamide tablets are available in three dosages - 0.1 mg, 0.5 mg and 1 mg. And Cyanocobalamin tablets contain 30 mcg, 50 mcg and 100 mcg of the active substance. Vitamin B 12 in tablet form is well absorbed and tolerated by humans, so it can be used in long courses instead of injections to reduce the traumatic effects of injections.
Many people of the older generation remember that vitamin B 12 was produced only in ampoules and was administered exclusively by injection, and therefore they greet with distrust the news about the availability of cyanocobalamin tablets, which can be safely taken orally, like many other vitamins. However, vitamin B 12 tablets are now a reality and are as effective and efficient as injections, which some people find are quite painful and unpleasant. Therefore, if possible, painful injections of vitamin B 12 can be replaced by taking tablets.
In addition to tablets, vitamin B 12 is currently also available in the form of rectal suppositories, which are inserted into the rectum. Data rectal suppositories are called Cycomin and are an excellent alternative to the injection of vitamin B 12, since the vitamin is very quickly absorbed from the rectum into the blood through the plexus of hemorrhoidal veins.
Complex preparations with vitamin B 12
IN last years Thanks to the achievements of organic synthesis, chemistry and pharmacology, it was possible to create complex preparations that included several vitamins that were previously considered incompatible and could not be in the same solution or tablet. Vitamin B 12 is included in such complex preparations along with B 1, B 6 and folic acid, which often need to be used together. Complex drugs very convenient to use because they allow you to reduce the number of injections and pills taken.Today in the domestic pharmaceutical market there are the following complex therapeutic drugs containing vitamin B 12:
- Angiovit (B 6, B 12 + folic acid);
- Binavit (B 6, B 1 and B 12 + lidocaine);
- Vitagamma (B 6, B 1 and B 12 + lidocaine);
- Vitaxon (B 6, B 1 and B 12 + lidocaine);
- Combilipen (B 6, B 1 and B 12 + lidocaine);
- Compligam B (B 6, B 1 and B 12 + lidocaine);
- Medivitan (B 6, B 12 and folic acid);
- Milgamma (B 6, B 1 and B 12);
- Multi-Tabs B-complex (B 1, B 2, B 3, B 5, B 6, B 12 + folic acid);
- Neurobion (B 6, B 1 and B 12);
- Neuromultivitis (B 6, B 1 and B 12);
- Pentovit (B 1, B 3, B 6, B 12 + folic acid);
- Pician (B 6 and B 12);
- Trigamma (B 6, B 1 and B 12 + lidocaine);
- Ferro-Folgamma (B 12, folic acid and ferrous sulfate);
- Foliber (B 12 and folic acid.).
In addition to the indicated therapeutic vitamins, the pharmaceutical market has wide range various complexes for the prevention of hypovitaminosis, such as, for example, Vitrum, Centrum, Supradin, Alphabet, etc. These complexes usually contain almost all vitamins and several minerals in dosages recommended for the prevention of hypovitaminosis, which are relatively low, and therefore the products cannot be used to treat various diseases. Typically, such complexes are called preventive and their main difference from therapeutic vitamins is the low dosage of components, insufficient for medicinal use. Vitamin B 12 is included in almost any vitamin and mineral preventive complex in the dosage recommended for daily consumption. We do not give the names of these complexes, since the list will be too long.
Vitamin B 12 – indications for use
 Various forms of vitamin B 12 (cyanocobalamin, hydroxocobalamin, cobamamide), in principle, are indicated for use in the treatment of the same diseases. However, there are minor differences in the indications for the use of different forms of vitamin B12, due to the characteristics of their metabolism, the rate of development of the therapeutic effect and the duration of action. Therefore, first we will consider the indications for use common to all forms of vitamin B 12, and then we will indicate specific ones for cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin.
Various forms of vitamin B 12 (cyanocobalamin, hydroxocobalamin, cobamamide), in principle, are indicated for use in the treatment of the same diseases. However, there are minor differences in the indications for the use of different forms of vitamin B12, due to the characteristics of their metabolism, the rate of development of the therapeutic effect and the duration of action. Therefore, first we will consider the indications for use common to all forms of vitamin B 12, and then we will indicate specific ones for cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin. Indications for use of all forms of vitamin B 12
Indications for the use of all forms of vitamin B 12 are as follows:- Chronic anemia (Addison-Beermer, iron deficiency, posthemorrhagic, aplastic, toxic, nutritional);
- Acute and chronic;
- Myelosis;
- Lateral amniotrophic sclerosis;
- Diabetic neuropathy;
- Skin diseases (photodermatosis, herpetic, neurodermatitis);
- Bone injuries;
- Polyneuritis;
- Radiculitis;
- Neuralgia;
- Causalgia.
Indications for the use of cyanocobalamin and kabamamid
Indications for the use of cyanocobalamin and kabamamid are as follows:- Injuries and inflammatory processes in peripheral nerves (wound, radiculoneuritis, phantom pain);
- Encephalomyelitis;
- Slow bone healing;
- To speed up the body's recovery after surgical interventions on the musculoskeletal system;
- Diseases digestive tract in which the absorption of vitamin B 12 is impaired (resection of part of the stomach or small intestine, celiac disease, sprue);
- Prevention of vitamin B12 deficiency when taking biguanides, para-aminosalicylic acid, large amounts of vitamin C (more than 100 mg per day);
- Malignant tumors of the pancreas and intestines;
- Prolonged stress;
- Long-term infectious diseases;
- Kidney diseases;
- Strict or vegetarianism.
Indications for use of hydroxocobalamin
Indications for the use of hydroxocobalamin are as follows:- Cyanide poisoning (intentional or accidental);
- Dystrophy or lack of body weight in newborns, including premature babies;
- Recovery after infectious diseases;
- Sprue;
- Trigeminal neuralgia;
- Leber's disease (hereditary optic atrophy);
- Alcoholic psychosis ("delirium tremens").
Vitamin B 12 – instructions for use
How to inject vitamin B 12
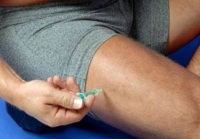 First of all, you need to read the instructions attached to the drug and find out what active substance is contained in the purchased drug, since this determines what types of injections can be given.
First of all, you need to read the instructions attached to the drug and find out what active substance is contained in the purchased drug, since this determines what types of injections can be given. Hydroxocobalamin can be administered by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, cobamamide by intravenous and intramuscular injection, and cyanocobalamin by intramuscular, subcutaneous, intravenous, or intralumbar (lower back) injection. Best methods injections of vitamin B 12 are subcutaneous and intravenous. Intramuscular administration is the most dangerous and least preferred option for using vitamin B 12, so it is recommended to avoid this type of injection. Intralumbar administration of the vitamin is used only for treatment or.
You can independently make subcutaneous or intramuscular injections, and intralumbar and intravenous administration medications must be administered by a doctor or nurse in a medical facility or at home.
Intramuscular injection is best done in the upper lateral surface thighs, not the buttocks. The subcutaneous injection is optimally made in the area of the inner surface of the forearm, where the Mantoux test is usually placed. Immediately before an intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, the area of skin must be wiped with cotton wool moistened antiseptic solution(alcohol, chlorhexidine, Belasept, etc.). For intramuscular injection It is necessary to insert the needle perpendicular to the skin and slowly release the medicine into the tissue. The needle should also be removed while holding it perpendicular to the skin. For a subcutaneous injection, you need to gather 1 cm of skin into a fold with your fingers and insert a needle under it parallel to the bone of the forearm, then slowly inject the solution into the tissue. Remove the needle without straightening the skin fold.
Before injection, a solution is prepared and drawn into a syringe. To do this, either simply open the ampoule with a ready-made solution of the required concentration, or pour the required amount of sterile distilled water into the bottle with the lyophilisate so that the contents dissolve. The resulting or ready-made solution of vitamin B 12 is drawn into a syringe with a needle. Then the syringe is turned over with the needle up and the surface of the tube is lightly tapped with the tip of a finger in the direction from the piston to the needle. This is necessary so that air bubbles break away from the walls of the syringe and rise to the surface of the solution. Then, by lightly pressing the plunger, you need to release a few drops of the solution from the syringe so that all the air comes out with them. After this, the syringe is considered ready for injection. It can be set aside on a clean surface and prepare the area of skin where the injection will be placed.
The dosage and duration of use of vitamin B 12 depend on the type of disease, the speed of recovery and the age of the person. The course of therapy can range from 7 to 30 days, and the dosage from 10 mcg to 500 mcg per day. The specific dosage should be checked with your doctor or in the instructions for use of a particular drug.
How to take vitamin B 12 orally
 Cobamamide and cyanocobalamin can also be taken orally in tablet form. Adults need to take the tablets half an hour before meals with plenty of water. The tablets can be chewed. For children, tablets are dissolved in a 5% dextrose solution or boiled water and also give 30 minutes before meals. In this case, to dissolve tablets containing 500 mcg of active substance, you need 5 ml of a 5% dextrose solution or 50 ml of boiled water.
Cobamamide and cyanocobalamin can also be taken orally in tablet form. Adults need to take the tablets half an hour before meals with plenty of water. The tablets can be chewed. For children, tablets are dissolved in a 5% dextrose solution or boiled water and also give 30 minutes before meals. In this case, to dissolve tablets containing 500 mcg of active substance, you need 5 ml of a 5% dextrose solution or 50 ml of boiled water. Vitamin B 12 in tablet form is recommended to be taken several times a day - from 2 to 6, depending on the frequency of meals. That is, if a person eats 3 times a day, then the daily dosage of vitamin B 12 is recommended to be divided into three doses, etc. The dosage and duration of the course of taking vitamin B 12 is determined by the rate at which clinical improvements appear, as well as the condition for which the decision was made to use vitamin preparations. On average, the course of treatment can last from 7 to 30 days, and the dosage can range from 250 mcg to 1000 mcg per day.
Vitamin B 12 Compatibility
The concept of compatibility applies only to intravenous, intramuscular or subcutaneous administration of vitamins, since undesirable effects may occur between them chemical reaction. When taken orally, all B vitamins are compatible with each other and can be taken simultaneously.So, when administered by injection, vitamin B 12 is well compatible with vitamins B 6, C, U (U), H and folic acid. This means that cyanocobalamin can be administered simultaneously with compatible vitamins on the same day, but from different syringes. Despite the compatibility, you should not mix vitamin solutions in the same syringe, as this may lead to a weakening or complete loss of their therapeutic activity. Therefore, compatible vitamins can be administered at the same time, but from different syringes. If vitamins are administered intravenously, then this is done one at a time, without removing the needle from the vein, with intervals between them of 5 - 10 minutes. If vitamins are administered intramuscularly, then each drug is drawn into a separate syringe and injected into different places.
Vitamin B 12 is poorly compatible with vitamin B 1, so it is not recommended to administer them together. However, there are currently combination drugs, containing both vitamins B 1 and B 12, which are administered simultaneously. In the form of such preparations, these vitamins can be administered simultaneously, since during the production process they are given special properties that make them compatible.
Vitamin B 12 is completely incompatible with copper, iron and manganese.
Vitamin B 12 for hair
 Vitamin B 12 accelerates the rate of hair growth and makes it strong, elastic and shiny. With a lack of cobalamin, hair begins to break off, grow slowly and fall out. The best way Vitamin B 12 affects hair when taken orally as part of food or in the form of vitamin preparations. External use of vitamin B 12 can only help maintain the good condition of already healthy hair. However, to treat and improve hair structure, vitamin B 12 must be taken orally in tablet form or injected.
Vitamin B 12 accelerates the rate of hair growth and makes it strong, elastic and shiny. With a lack of cobalamin, hair begins to break off, grow slowly and fall out. The best way Vitamin B 12 affects hair when taken orally as part of food or in the form of vitamin preparations. External use of vitamin B 12 can only help maintain the good condition of already healthy hair. However, to treat and improve hair structure, vitamin B 12 must be taken orally in tablet form or injected. Folic acid with vitamins B12 and B6 pills
For women's health and beauty
What does a woman want? You can answer without hesitation. Captivate with charm and beauty, be healthy and, of course, experience the happiness of motherhood - give birth to a strong healthy baby. Look beautiful and be healthy woman can only under one condition: if her body has enough vitamins and microelements necessary for the full functioning of the whole organism. This is especially true "female" vitamins, which include folic acid.
Scottish scientists believe folic acid the most useful vitamin for women's health and beauty. It is one of the main participants in the process of formation of new cells in the body: white blood cells - leukocytes, red blood cells - erythrocytes, new skin and hair cells. Thanks to this, folic acid ensures healthy skin color, which is very important for every woman. It is thanks to folic acid that hair is renewed, its structure improves and fragility is reduced, and nails grow better.
Folic acid can be called the “motherhood vitamin”. For a woman planning a pregnancy, folic acid is the most important vitamin, since it is responsible for the formation of the fetus and its proper development. If there is insufficient amount of folic acid in the female body, there is a high probability that the subsequent pregnancy will be accompanied by various deviations in the development of the baby.
Taking folic acid is important for young women, as it regulates the menstrual cycle and prevents the development of osteoporosis. In addition, folic acid has an estrogen-like effect and can slow down the onset of menopause and even reduce unpleasant symptoms after it occurs.
Also folic acid necessary for the circulatory system to function normally, the vessels and capillaries were healthy and strong.
The body does not produce folic acid on its own and it is impossible to fill the body with it once and forever, so it is necessary to regularly replenish its supply.
It is very important to receive vitamins B6 and B12 along with folic acid.
Vitamin B12 and folic acid are related vitamins. A lack of vitamin B12 leads to the development of folic acid deficiency.
Vitamin B6 participates in the transformation of amino acids, promotes the normal formation of red blood cells. Insufficient intake of vitamin B6 is accompanied by poor circulation, increased fatigue, depression, and hair loss.The optimal dosage, high quality and affordable price will please every woman and help maintain women's health, which can be more valuable than anything in the world!
Compound
Folic acid, vitamin B6, vitamin B12.Release form
tablets of 0.22 g in a blister. Directions for use: Adults take 1 tablet daily with meals. Duration of treatment is 4-6 weeks. If necessary, the reception can be continued. Pregnant and lactating women should take under medical supervision. Not recommended for persons with individual intolerance to the components of the product. It is recommended to consult a doctor before use.Latin name: DOPPELHERZ ACTIVE FOLIC ACID
+ VITAMINS B6 + B12 + C + E
ATX code: B03BB01
Active substance: Folic acid, vitamins
Manufacturer: Queisser Pharma, Germany
Conditions for dispensing from a pharmacy: Over the counter
Folic acid is an indispensable participant in metabolic processes in the body. As part of the drug Doppelgerz, its effect is enhanced by B vitamins and important components of the vitamin order. A set of vitamins promotes the slow release of individual components for improved absorption and greater effectiveness.
Indications for use
“Doppelhertz active folic acid” is used as a prophylactic for vitamin deficiency and as an additional drug in the complex treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
- Stroke Prevention
- Atherosclerosis
- Pregnancy
- Brain dysfunction
- Improved memory
- With high mental or physical overload (exams)
- Lack of vitamins.
Compound

The price in pharmacies is from 400 to 480 rubles.
Yellowish oblong tablets with a slight pleasant odor and taste contain:
- Folic acid 600 mcg
- Pyridoxine (B6) 6 mcg
- Cyanocobalamin (B12) 5 mcg
- Tocopherol (E) 36 mg
- Ascorbic acid (C) 300 mg
The vitamins are sold in packs of 30, which is enough for use for a month.
Pharmacology
The action of folic acid is aimed at maintaining normal cell function and renewal. Its participation is necessary for the process of metabolism of proteins and some amino acids. In combination with vitamin B12, folic acid is transformed into methionine, which the body needs for fat metabolism. Lack of acid leads to severe anemia. The human body is unable to store or synthesize folic acid. It can be obtained from food or medicine.
During pregnancy, folic acid reduces the risk of deformities in the fetus. Pregnant women require up to 600 mcg of acid daily.
B6 as part of the complex is aimed at improving the formation of hemoglobin and strengthening the protective functions of the body. It is involved in the construction of skin cells and is necessary for constant renewal. Pyridoxine is indispensable in the metabolism of lipids and amino acids. An important stimulant of muscle activity.
B12 is important for the normal functioning and health of nerve cells. With its deficiency, carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted. Participates in the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
Vitamin C is most important for maintaining the body's protective functions. It is an essential component of drugs in the complex treatment of various infectious and viral diseases. Ascorbic acid takes part in the metabolic processes of carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. When it is deficient, the quality of connective tissue is impaired, which leads to a host of diseases.
Vitamin E is best known as a powerful antioxidant that can protect the body from the effects of free radicals and the negative effects of toxic substances at the cellular level. Participates in the functioning of the immune system. Reduces the risk of high vascular permeability and helps make the walls more elastic. Tocopherol is one of the most important components for slowing down the aging process, and is considered a “beauty vitamin”.
Drug standards
If there is a deficiency of vitamins included in the Doppelhertz Active Folic Acid complex, you should take 1 capsule per month.
The tablets are not chewable. Drink plenty of water or non-acidic juice.
Pregnancy and lactation
Folic acid is recommended as an essential vitamin during pregnancy to prevent the formation of deformities in the unborn baby. Before using a vitamin complex, you must undergo an examination and consult a doctor. An excess of vitamins included in the complex can negatively affect the child.
During breastfeeding, the drug is contraindicated in most cases.
Precautionary measures
The content of folic acid and vitamin B6 in the composition of the drug is contained in maximum daily doses. The amount of ascorbic acid exceeds the body's daily requirement. With a balanced diet, it is better to refrain from consuming Doppelhertz Active Folic Acid. Take dietary supplements after consultation with a therapist, who will assess the need to use the product.
Interactions with drugs
Reduces the effectiveness of painkillers, anticonvulsants and sulfonamides.
Side effects
Increased intake of dietary supplements can lead to negative consequences. It is necessary to avoid exceeding the norm once and using the drug for a long time.
Doppelhertz Active Folic Acid may cause allergic reactions to one or more of its components.
Cannot be used to fortify the body for children.
Storage conditions
Store for no more than three years in a cool, dark place away from children.
Analogs
 Folic acid preparation produced by the Croatian company JADRAN
Folic acid preparation produced by the Croatian company JADRAN
Price packs of 30 tablets in pharmacies from 150 rubles.
Available in the form of tablets weighing 0.5 mg, yellowish in color, without any side odor. Take no more than one tablet per day for symptoms of folic acid deficiency and as recommended by a doctor.
The instructions contain a reference to the prohibition of use in the detection of malignant tumors and neoplasms.
Pros:
- Low price
- No additional components.
According to reviews from those who have taken Folacin, the drug is not inferior to more expensive analogues and is a fairly effective remedy for replenishing folic acid deficiency. There were no negative reviews when using the drug from the Croatian company.
Minuses:
- The company does not provide information about the studies conducted.
Folic acid
The drug under this name is produced by Russian companies (Altaivitamins, Ecopharm and others)
Lower price limit from 30 rubles for 30 tablets.
 In pharmacies there are packages containing from 30 to 100 tablets of folic acid containing 0.5 mcg of the active substance. Tablets from Russian manufacturers are made according to the standard: light-colored tablets without taste or odor.
In pharmacies there are packages containing from 30 to 100 tablets of folic acid containing 0.5 mcg of the active substance. Tablets from Russian manufacturers are made according to the standard: light-colored tablets without taste or odor.
Pros:
- Low cost
- Quality of the drug.
Minuses:
- Rarely found in pharmacies.


