In the recipe, one gram is taken per unit of mass. (1,0), per unit volume - one milliliter (1 ml).
If the medicinal product contains a medicinal substance in drops, then the number of drops is indicated by a Roman numeral, preceded by gtts(short for guttas - accusative case plural).
If the composition of the medicinal product includes a medicinal substance dosed in units of action, then the number of units of action is indicated in the prescription instead of weight quantities - UNITS
When dosing medicinal substances you have to use quantities less than one gram:
· Dose is the amount of drug introduced into the body. There are different doses prescribed per dose - one-time, during the day - daily allowance, for a course of treatment - coursework. Each of these doses can be average therapeutic, highest therapeutic or minimal (threshold). Medium therapeutic is called an effective dose that causes a certain therapeutic effect. Higher therapeutic is a dose of a drug that does not reach its minimum toxic dose and is conventionally accepted as the highest permissible for administration into the body. Minimum or threshold, dose - This is the smallest dose that causes changes at the body level that go beyond physiological reactions.
The therapeutic dose may vary depending on age, weight, route of administration of the drug, and the desired therapeutic effect. Regular therapeutic doses, offered in various reference publications, are designed for a 24-year-old person weighing 70 kg. When recalculating doses for people over 60 years of age, age-related sensitivity to various groups of drugs is taken into account. Doses of drugs that depress the central nervous system (hypnotics, neuroleptics, narcotic analgesics), cardiac glycosides, diuretics are reduced by 50 %. Doses of other drugs included in lists A and B are reduced by 1/3. Doses antibacterial drugs and vitamins are usually not reduced. Upon appointment medicines for children it is possible to recalculate per 1 kg of body weight, per 1 m 2 of body surface or per 1 year of the child’s life. There are empirical formulas for calculating doses of drugs for children, where the dose of an adult is taken as a basis.
Conversion by weight:

In children who are overweight or underweight, an overdose or a low dosage based on body weight may be observed. In this case, it is better to use the calculation based on body surface area. There are special normograms that allow you to switch from the patient’s weight to the body surface area when calculating (they are offered in the corresponding reference books).
Recalculation by age (for children over one year):

However, this recalculation does not take into account the pharmacodynamics of the substance, age characteristics of resistance and sensitivity to this medicine, as well as the individual characteristics of a particular child. Therefore, drug doses for children are determined in clinical trials, and they are available in relevant reference publications.
Calculation of doses of medicinal substances in grams
Determination of drug mass and daily dose in a prescription
Checking and calculating doses in recipes.
Designation of drug doses in prescriptions
Drug doses are indicated in the decimal measurement system. The unit of mass is 1 g.
In the recipe this is indicated as 1.0. When dosing medications, values less than 1.0 are also used: 0.1 - one decigram; 0.01 - one centigram; 0.001 - one milligram; 0.0001 - one decimilligram; 0.00001 - one centigram; 0.000001 is one microgram.
The amount of liquid substances is indicated in milliliters (ml). If included dosage form include the drug in drops, the number of drops is indicated by a Roman numeral, preceded by gtt (an abbreviation for the word guttas - drops - in accusative case plural), for example gtt V (five drops).
When prescribing antibiotics, doses are indicated in action units (AU), vaccines and serums - in international units (IU), stimulants of immunological processes - in immunizing units (IU).
Solutions for oral use are measured in graduated cups or tea, dessert and tablespoons, as well as drops, which are diluted with water or milk before use.
You should know that 1 teaspoon contains 5 ml aqueous solution, 1 dessert spoon - 10 ml, 1 tablespoon - 15 ml. There are 20 drops in 1 ml of aqueous solution.
Example 1. Determine the daily dose of prednisolone.
Rp.: Prednisoloni 0.005
D.t.d. N. 100 in tab.
S. One tablet 4 times a day.
The solution of the problem. A single dose of prednisolone is 0.005 (5 mg). In order to determine the daily dose, it is necessary to multiply the single dose by the number of drug doses per day: 0.005 x 4 = 0.02 g.
Prednisolone belongs to list B. Its IRR = 0.015 g, IRR = 0.1 g, therefore, neither one-time nor daily dose not overpriced.
Answer: The daily dose of prednisolone is 2 centigrams (20 mg).
Example 2. Write out a prescription, calculate the amount of substance contained in 1 ml of the specified solution: Take: Atropine sulfate solution 0.1% - 1 ml, Give such doses N. 6 in ampoules, Label. 1 ml under the skin.
The solution of the problem. 0,1 % solution means that 0.1 g of atropine sulfate is contained in 100 ml of solution, and in 1 ml of solution - X g of substance. X == 0.1 g x 1 ml: 100 ml = 0.001 g.
Answer: 1 ml of 0.1% solution contains 0.001 g (1 mg) of atropine sulfate. This prescription is written as follows:
Rp.: Sol. Atropini sulfatis 0.1% - 1 ml
D.t.d. N. 6 in amp.
S. 1 ml under the skin.
The solution of the problem. The correct proportion is as follows: 1 ml of solution contains 0.01 g of drug, and 100 ml -X. X will be equal to 1%.
Answer: solution concentration 1%
High concentrations of glucose in the blood have a detrimental effect on all systems of the body. It is characteristic of type 1-2 diabetes mellitus. Sugar increases due to insufficient production of the hormone by the pancreas or its poor absorption. If diabetes is not compensated for, then the person will face serious consequences (hyperglycemic coma, death). The basis of therapy is the introduction of short- and long-acting artificial insulin. Injections are required mainly for people with type 1 disease (insulin-dependent) and severe forms of the second type (non-insulin-dependent). The attending physician should tell you how to calculate the insulin dose after receiving the examination results.
Features of correct calculation
Without studying special calculation algorithms, selecting the amount of insulin for injection is life-threatening, as a person can expect lethal dose. An incorrectly calculated dosage of the hormone will reduce blood glucose so much that the patient may lose consciousness and fall into a hypoglycemic coma. To prevent consequences, the patient is recommended to purchase a glucometer to constantly monitor sugar levels.
Correctly calculate the amount of hormone by following the following tips:
- Buy special scales for measuring portions. They must capture mass down to fractions of a gram.
- Write down the amount of protein, fat, and carbohydrates you consume and try to take them in the same amount every day.
- Carry out a weekly series of tests using a glucometer. In total, you need to take 10-15 measurements per day before and after meals. The results obtained will allow you to more carefully calculate the dosage and ensure that the selected injection regimen is correct.
The amount of insulin for diabetes is selected depending on the carbohydrate ratio. It is a combination of two important nuances:
- How much does 1 IU (unit) of insulin cover consumed carbohydrates?
- What is the degree of sugar reduction after injection of 1 unit of insulin.
It is customary to calculate the stated criteria experimentally. This is due to individual characteristics body. The experiment is carried out in stages:
- It is advisable to take insulin half an hour before meals;
- measure glucose concentration before eating;
- after the injection and finishing the meal, take measurements every hour;
- Based on the results obtained, add or reduce the dose by 1-2 units for full compensation;
- Correctly calculating the dose of insulin will stabilize sugar levels. It is advisable to write down the selected dosage and use it in a further course of insulin therapy.
High dosages of insulin are used for diabetes mellitus Type 1, as well as after suffering stress or trauma. For people with the second type of disease, insulin therapy is not always prescribed and when compensation is achieved, it is canceled, and treatment continues only with the help of tablets.
The dosage is calculated, regardless of the type of diabetes, based on the following factors:
- Duration of the disease. If the patient has been suffering from diabetes for many years, then only a large dosage reduces sugar.
- Development of renal or liver failure. Having problems with internal organs requires a downward adjustment of the insulin dose.
- Excess weight. The calculation begins by multiplying the number of units of medication by body weight, so obese patients will need more medication than thin people.
- The use of third-party or hypoglycemic medications. Medicines can enhance or slow down the absorption of insulin, so when combining medication and insulin therapy, you will need to consult an endocrinologist.
Select formulas and dosage better to a specialist. He will assess the patient’s carbohydrate ratio and, depending on his age, weight, as well as the presence of other diseases and medications, will draw up a treatment regimen.
Dosage calculation
The dosage of insulin is different in each case. It is influenced by various factors throughout the day, so a glucometer should always be at hand to measure your sugar level and give an injection. To calculate the required amount of the hormone, you do not need to know the molar mass of the insulin protein, but simply multiply it by the patient’s weight (IU * kg).
According to statistics, 1 unit is the maximum limit for 1 kg of body weight. Exceeding the permissible threshold does not improve compensation, but only increases the chances of developing complications associated with the development of hypoglycemia (low sugar). You can understand how to choose the dose of insulin by looking at the approximate indicators:
- after diabetes is diagnosed, the basic dosage does not exceed 0.5 units;
- in a year successful treatment the dose is left at 0.6 units;
- if diabetes is severe, then the amount of insulin increases to 0.7 units;
- in the absence of compensation, the dose is set to 0.8 units;
- after identifying complications, the doctor increases the dosage to 0.9 units;
- if a pregnant girl suffers from type 1 diabetes, then the dosage is increased to 1 unit (mainly after the 6th month of pregnancy).
Indicators may vary depending on the course of the disease and secondary factors affecting the patient. The algorithm below will tell you how to correctly calculate the insulin dosage by choosing the number of units from the list above:
- No more than 40 units are allowed to be used at a time, and the daily limit varies from 70 to 80 units.
- How much to multiply the selected number of units depends on the patient’s weight. For example, a person weighing 85 kg and successfully compensating for diabetes for a year (0.6 units) should inject no more than 51 units per day (85*0.6=51).
- Long-acting (long-term) insulin is administered 2 times a day, so the final result is divided by 2 (51/2=25.5). In the morning the injection should contain 2 times more units (34) than in the evening (17).
- Short-acting insulin should be used before meals. It accounts for half of the maximum permissible dosage (25.5). It is distributed over 3 times (40% breakfast, 30% lunch and 30% dinner).
If before the administration of the hormone short acting Since glucose is already elevated, the calculation changes slightly:
- 11-12 +2 units;
- 13-15 +4 units;
- 16-18 +6 units;
- 18> + 12 UNITS
The amount of carbohydrates consumed is displayed in bread units (25 g of bread or 12 g of sugar per 1 XE). Depending on the grain indicator, the amount of short-acting insulin is selected. The calculation is carried out as follows:
- in the morning, 1 XE covers 2 units of the hormone;
- at lunchtime, 1 XE covers 1.5 units of the hormone;
- V evening time the ratio of insulin and bread units is equal.
Calculation and technique of insulin administration
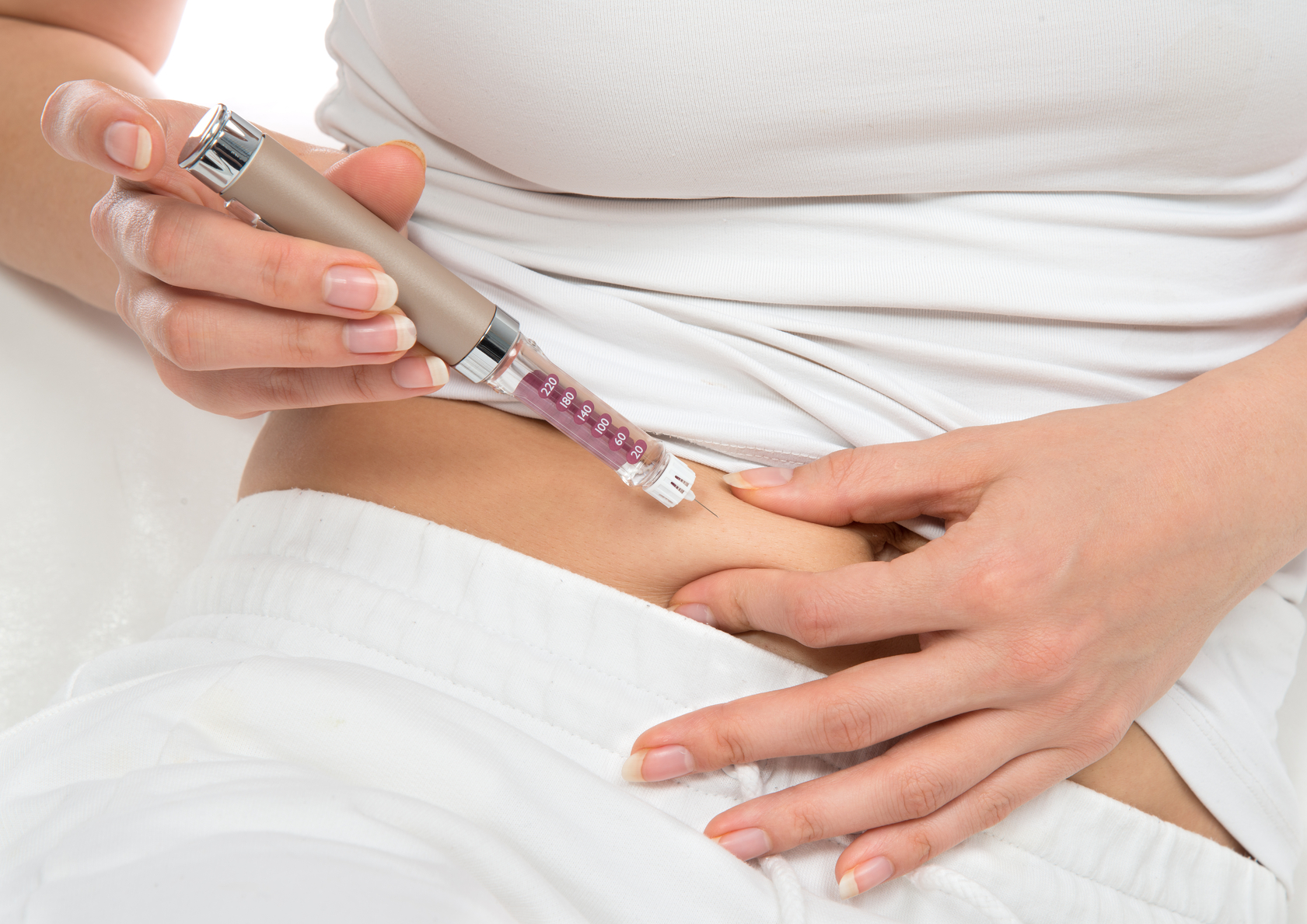
Dosage is important knowledge for any diabetic. Depending on the type of disease, possible minor changes in calculations:
- In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas completely stops producing insulin. The patient has to take short-acting and long-acting hormone injections. To do this, take the total number of permissible units of insulin per day and divide by 2. The long-acting type of hormone is injected 2 times a day, and the short-term type at least 3 times before meals.
- In type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulin therapy is required if the disease is severe or if drug treatment does not give results. Long-acting insulin is used for treatment 2 times a day. The dosage for type 2 diabetes usually does not exceed 12 units at a time. A short-acting hormone is used for complete depletion of the pancreas.
After completing all the calculations, you need to find out what technique for administering insulin exists:
- wash your hands thoroughly;
- disinfect the stopper of the medicine bottle;
- draw air into the syringe equivalent to the amount of insulin injected;
- Place the bottle on a flat surface and insert a needle through the stopper;
- release the air from the syringe, turn the bottle upside down and draw in the medicine;
- the syringe should contain 2-3 units more than the required amount of insulin;
- stick out the syringe and squeeze out the remaining air from it, while adjusting the dosage;
- disinfect the injection site;
- inject the medicine subcutaneously. If the dosage is large, then intramuscularly.
- Disinfect the syringe and injection site again.
Alcohol is used as an antiseptic. Wipe everything with a piece of cotton wool or a cotton swab. For better absorption, it is advisable to inject in the stomach. Periodically, the injection site can be changed on the shoulder and thigh.
How much does 1 unit of insulin reduce blood sugar?
On average, 1 unit of insulin lowers glucose concentration by 2 mmol/l. The value is checked experimentally. In some patients, sugar drops by 2 units once, and then by 3-4, so it is recommended to constantly monitor glycemic levels and inform your doctor about all changes.
How to use
The use of long-acting insulin creates the appearance of the pancreas working. Administration occurs half an hour before the first and last meals. Short-acting and ultra-short-acting hormones are used before meals. The number of units varies from 14 to 28. Various factors influence the dosage (age, other diseases and medications, weight, sugar level).


