Anemia due to vitamin B 12 deficiency
And folic acid
V.V. Dolgov, S.A. Lugovskaya,
V.T.Morozova, M.E.Pochtar
Russian Medical Academy
postgraduate education
Anemia associated with impaired DNA synthesis can be either hereditary or acquired. A common feature These anemias are caused by the presence of megaloblastic hematopoiesis in the bone marrow. These are megaloblastic anemias. More often there is an isolated deficiency of vitamin B12, less often - folic acid.
Anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency
Pernicious anemia was described in 1849 by Addison. Somewhat later, in 1872, Birmer defined it as “progressive pernicious anemia". Ehrlich discovered in the bone marrow large cells with a peculiar chromatin structure and called them “megaloblasts”. In 1926, Minot and Murphy showed the possibility of curing pernicious anemia by administering raw liver containing an external factor - vitamin B 12. Almost simultaneously, Castle (1929) discovered the intrinsic gastric factor, and Smith and Rickes (1948) discovered vitamin B12, which contributed to the establishment of the pathogenesis of pernicious anemia.
Frequency of occurrence B 12 -deficiency anemia increases with age and is 0.1% in young people, 1% in elderly people, after 75 years it is registered in 4% of people.
- Metabolism of vitamin B 12 [show]
The chemical structure of vitamin B 12 is presented in the form of two parts - one resembles a nucleotide, the second, the most characteristic part, is a corrin structure containing 4 pyrrole rings, in the center of which is a cobalt atom (Co +3). Vitamin B 12 is also known as cobalamin. Vitamin B 12 is found in foods rich in protein: meat, eggs, cheese, milk, especially in the liver and kidneys. In food it is associated with protein.

In order for vitamin B 12 to be absorbed, it is first released from food proteins by acid hydrolysis in the stomach or trypsin proteolysis in the intestine and binds to the R protein produced salivary glands. Under the influence of proteases of pancreatic secretion, the RB 12 complex is destroyed and vitamin B 12 is released.
Then vitamin B 12 combines with Castle's internal factor (IF - intrinsic factor) - a protein secreted by the parietal cells of the mucous membrane of the fundus and body of the stomach. The VF-B 12 complex is formed, which dimerizes and binds to specific receptors in the ileum. The number of receptors in the ileum is a factor that limits the speed of the process of vitamin B 12 entering the body. In the presence of Ca 2+ and pH 7.0, this complex is broken down, and vitamin B 12 penetrates the cells of the intestinal mucosa. From here, vitamin B 12 enters the blood, where it combines with transport proteins transcobalamin I, II and III, which deliver the vitamin to liver cells, bone marrow and other cells (Fig. 36).
The release of vitamin B 12 from the complex with transcobalamin II in the cell occurs in three stages:
- binding of the complex to cell receptors;
- its endocytosis;
- lysosomal hydrolysis with vitamin release
Transcobalamins I and III release vitamin B 12 only in the liver. The main depot of the vitamin is the liver, 1 g of which contains 1 mcg of vitamin B12. The daily requirement for the vitamin for an adult is 5-7 mcg. Vitamin B 12 is mainly excreted in bile, but is also lost in feces. 0.1% of the total amount of deposited vitamin is lost per day. The existence of an intestinal-hepatic circulation of vitamin B 12 has been proven - about % of the vitamin excreted in bile is reabsorbed. This explains the development of megaloblastic anemia 1-3 years after the complete cessation of vitamin intake into the body.
- The role of vitamin B 12 [show]
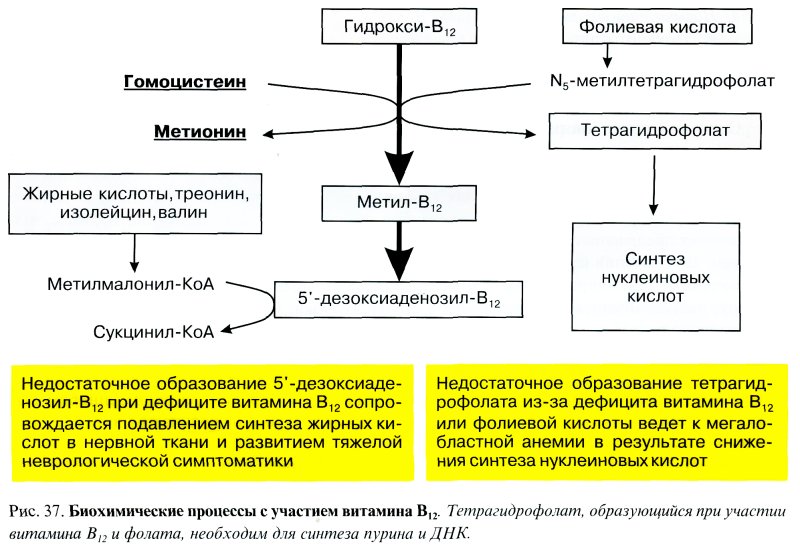
In humans, two biochemical reactions are known in which the participation of vitamin B 12 is necessary: 1) the formation of tetrahydrofolate from N5-methyltetrahydrofolate, in the same process homocysteine is converted into methionine, 2) a derivative of vitamin B 12 - 5 "-deoxyadenosylcobalamin acts as a Co-factor in the transition of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA (Fig. 37).
The first reaction is the key one in the development of megaloblastic anemia with a lack of vitamin B 12 or folate. What is important is the inability of N5-methyltetrafolate to transform into tetrafolate (the so-called tetrafolate block develops); the formation of folates necessary for the synthesis of purine and pyrimidine is reduced. Violation of thymidine formation leads to a slowdown in DNA synthesis, cell division, and the appearance of a megaloblastic type of hematopoiesis. Impaired DNA synthesis with B 12 deficiency can be expected in almost all nucleated cells, however, vitamin B 12 deficiency primarily affects hematopoiesis, since hematopoietic cells have the highest proliferative activity compared to other systems.
The second reaction, in which vitamin B12 participates, is necessary for normal fatty acid metabolism. During the breakdown of fatty acids, propionic acid is formed, during the metabolism of which a number of intermediate products are synthesized, in particular methylmalonic acid, the latter, under the influence of 5"-deoxyadenosylcobalamin, is converted into succinic acid. In the absence or deficiency of this enzyme, methylmalonic acidemia is noted, the synthesis of fatty acids is disrupted, resulting in which are neurological disorders.
The main cause of vitamin B12 deficiency is atrophic gastritis, in which the synthesis of internal factor stops or decreases. Between production disruption internal factor and a decrease in the acid- and enzyme-forming functions of the stomach there is no parallelism. It is possible that a combination of several factors is necessary for the disease to occur.
Hereditary predisposition is essential in the development of vitamin B12 deficiency; 20-30% of patients have relatives with a similar disease. The role of immune mechanisms is important in the appearance of atrophic gastritis. Autoantibodies directed to gastric parietal cell antigens, intrinsic factor, and immunocomplex deposits in the stomach wall were detected. Immune mechanisms may play a leading role in the development of B 12 deficiency anemia in young people. It is often combined with other autoimmune diseases (Hashimoto's goiter, hemolytic anemia).
Megaloblastic anemia may occur while taking anticonvulsants and cytostatics.
Clinical picture consists of symptoms of damage to the hematopoietic system, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract. Patients complain of fatigue, weakness, palpitations, shortness of breath. In severe anemia, mild yellowing of the sclera is noted. Some patients complain of pain and burning in the tongue, however, the symptom of glossitis is not an absolutely pathognomonic sign of vitamin B12 deficiency, as it can also occur with IDA. Hepato- or splenomegaly is observed. Gastric secretion is sharply reduced. Ahilia is manifested by unstable appetite, aversion to food, and dyspepsia.
Neurological disorders are based on funicular myelosis of the lateral and/or posterior columns of the spinal cord, which is a consequence of demyelination, and then degenerative changes nerve fibers V spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Disturbances from the nervous system are detected in the form of peripheral polyneuropathy: weakness in the legs, a crawling sensation, numbness in the fingers, impaired sensitivity in the extremities, a feeling of constant coldness in the legs. Muscle weakness is often observed, and muscle atrophy is possible. First of all, the lower extremities are affected symmetrically, then the abdomen, the upper extremities are affected less frequently. In the most severe cases, areflexia and persistent paralysis develop lower limbs, dysfunction of the pelvic organs. With B 12 deficiency anemia, convulsive seizures, hallucinations, weakening of memory, spatial orientation, mental disorders, psychoses with depressive or manic states are possible. Severe complication is the development of pernicious coma, which occurs as a result of rapid anemia and cerebral ischemia.
Bone marrow . Characterized by a megaloblastic type of hematopoiesis with high level ineffective erythropoiesis. The bone marrow is hypercellular due to an increase in the number of nucleated red cells. The leuko/erythro ratio is 1:2-1:3 (normal 3:1-4:1). As a result of disruption of cell division, erythroid cells become very large (megaloblasts) and their structure changes qualitatively. The nuclei of megaloblasts always have a characteristic delicate reticular distribution, asynchronous maturation of the nucleus and cytoplasm. As the polychromatophilic and oxyphilic megaloblast matures, the nucleus is often located eccentrically.
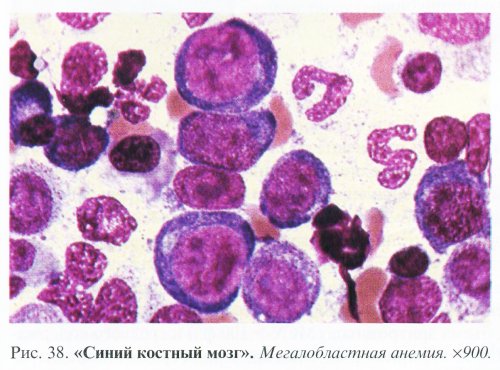

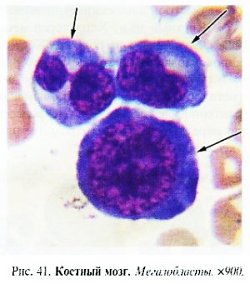
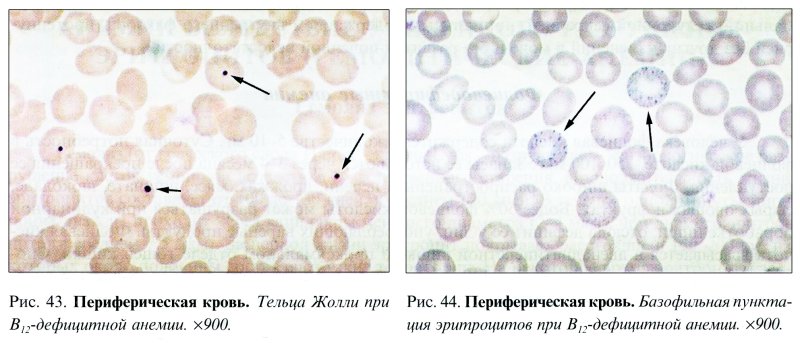
The quantitative relationships between megaloblasts of different degrees of maturity are very variable and depend on the activity of bone marrow hematopoiesis. The predominance of promegaloblasts and basophilic megaloblasts creates a picture of “blue” bone marrow (Fig. 38). Characteristic feature megaloblasts is the early hemoglobinization of their cytoplasm while maintaining the delicate structure of the nucleus (Fig. 39, 41). There are significant degenerative changes in the cell nuclei, ugliness, karyorrhexis, and mitoses. The lifespan of megaloblasts is 2-4 times less than normal, so most cells die in the bone marrow without maturing.
Violation of cell division during normal hemoglobin synthesis creates a condition for enhancing ineffective erythropoiesis. The results of autoradiographic and cytophotometric studies showed elongation phases S-G 2 cell cycle and cell death during this period. Megaloblasts form megalocytes and macrocytes. Intrabone marrow hemolysis of erythrokaryocytes (ineffective hematopoiesis) and the short life span of megalocytes leads to increased levels of indirect bilirubin.
A lack of vitamin B 12 entails changes in leukopoiesis, since DNA synthesis is disrupted in all cells. Slowing down the proliferation processes leads to an increase in the size of myelocytes, metamyelocytes, band and segmented neutrophils (Fig. 40). The number of megakaryocytes is usually normal, but decreases in severe cases. In megakaryocytes, platelet release may be impaired.
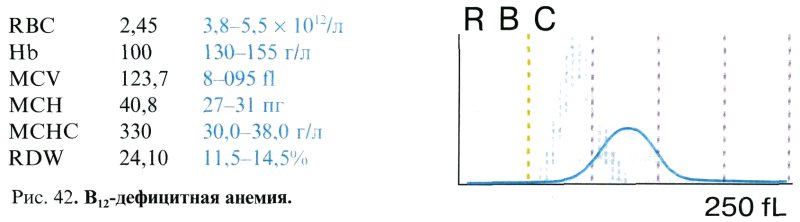
Peripheral blood . The result of megaloblastic hematopoiesis is the development of macrocytic hyperchromic anemia (Hb concentration can decrease to 25-40 g/l). The number of red blood cells is sharply reduced (1.0-1.5 x 10 12 / l). There is a high color index (1.1-1.4), an increase in the average volume of erythrocytes (MSV> 100 fL) and the average hemoglobin content in the erythrocyte (MSI> 32 pg) with normal values average hemoglobin concentration in one red blood cell (MCHC). The erythrocyte histogram shifts significantly to the right, flattens, stretching along the X axis (Fig. 42).
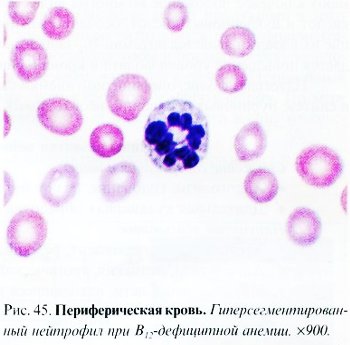
Red blood cells are characterized by their saturation with hemoglobin - hyperchromic, without central clearing, with a diameter of more than 10 microns (macrocytes and megalocytes). They are characterized by anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, schizocytosis, there are erythrocytes with remnants of the nuclear substance (Cabot rings, Jolly bodies) (Fig. 43), basophilic punctation (RNA remains) (Fig. 44), polychromatophilic erythrocytes. Megaloblasts are often present. The number of reticulocytes may be normal, but as differentiation is impaired, it decreases sharply.
B12-deficiency anemia is characterized by leukopenia, neutropenia with relative lymphocytosis, monocytopenia, aneosinophilia or abasophilia may be observed. The appearance of giant hypersegmented neutrophils (the number of segments more than 5) in the blood is noted (Fig. 45), sometimes a shift to the left to myelocytes and metamyelocytes.
Thrombocytopenia is moderate in nature, platelets are rarely less than 100 x 109/l, giant forms are found, but their function is not impaired and hemorrhagic syndrome rarely observed. Depending on the severity of anemia, ESR accelerates to 50-70 mm/h. There is a decrease in the content of vitamin B 12 in the blood serum (the norm for adults is 148-616 pmol/l, over 60 years old - 81-568 pmol/l).
The diagnosis of B 12 deficiency anemia can only be established with morphological study bone marrow, which is advisable to produce before the administration of vitamin B 12. An injection of vitamin B 12 for 1-2 days changes the type of hematopoiesis in the bone marrow. Megaloblasts decrease in size, the structure of the nucleus changes, and the cells become macronormoblasts. Only the presence of giant forms of neutrophils can suggest that megaloblastic hematopoiesis took place.
Reticulocyte crisis occurs 5-7 days after the start of treatment, ahead of the rise in hemoglobin concentration and the number of erythrocytes and indicates a switch from megaloblastic to normoblastic hematopoiesis. Hematological remission is determined by the normalization of bone marrow hematopoiesis and peripheral blood parameters. In patients who undergo vitamin therapy for a long time, iron deficiency anemia may develop over time due to the activation of hemoglobin synthesis. In these cases, normo- or moderately hypochromic red blood cells are observed (color index 0.8-0.9). Normalization of red blood counts usually occurs after one to two months of treatment with vitamin B12.
Imerslund-Griesbeck syndrome. Rare hereditary pathology(there are about 100 observations). The absorption of vitamin B 12 is impaired due to the lack of receptors in the jejunum that bind the B 12 complex - intrinsic factor. Manifested by megaloblastic anemia, normal gastric secretion, normal internal factor content, proteinuria without other changes in urine and without development renal failure.
Causes of folic acid deficiency
|
Folate deficiency anemia
In humans, folic acid is contained in an amount of 5-10 mg. The daily requirement for folic acid is 50-100 mcg. Its reserves are depleted 3-4 months after its supply ceases.
Folates are widely distributed in liver, yeast, meat, spinach, chocolate, raw vegetables and fruits. More than 50% of folic acid can be destroyed by culinary processing food, hence its deficiency among people who consume cooked foods.
Folic acid is absorbed into duodenum and proximal jejunum. The intestines' ability to absorb folic acid exceeds the daily requirement for the vitamin.
In blood plasma it binds to various proteins (β 2 -macroglobulin, albumin). Most of folate is transported to the liver, where it is deposited in the form of polyglutamates, a small amount is excreted in the urine. Folates, like vitamin B12, occupy a key position in many types of cellular metabolism, including the synthesis of amino acids and nucleic acids, especially important for proliferating cells. Their penetration into cells is a vitamin B 12-dependent process, therefore, with B 12 deficiency, an increase in the level of folate in the blood and a decrease in it in red blood cells is observed.
The pathogenesis of folate deficiency anemia is associated with its participation, together with vitamin B12, in the synthesis of purine bases necessary for the formation of DNA.
Clinic . People get sick more often young, pregnant women. Signs of anemia predominate: pale skin with mild subicterus, tachycardia, weakness. Neurological symptoms are not typical for these patients; gastrointestinal disorders are minor.
In people suffering from epilepsy and schizophrenia, folic acid deficiency leads to an increase in seizures.
Changes in the blood and bone marrow are similar to B 12 deficiency anemia. There is a decrease in folate levels in the blood serum (normal 6-20 ng/ml), its concentration is also reduced in erythrocytes (normal 160-640 ng/ml).
BIBLIOGRAPHY [show]
- Berkow R. The Merck manual. - M.: Mir, 1997.
- Guide to Hematology / Ed. A.I. Vorobyova. - M.: Medicine, 1985.
- Dolgov V.V., Lugovskaya S.A., Pochtar M.E., Shevchenko N.G. Laboratory diagnostics iron metabolism disorders: Tutorial. - M., 1996.
- Kozinets G.I., Makarov V.A. Study of the blood system in clinical practice. - M.: Triada-X, 1997.
- Kozinets G.I. Physiological systems human body, basic indicators. - M., Triada-X, 2000.
- Kozinets G.I., Khakimova Y.H., Bykova I.A. and others. Cytological features of erythron in anemia. - Tashkent: Medicine, 1988.
- Marshall W.J. Clinical biochemistry. - M.-SPb., 1999.
- Mosyagina E.N., Vladimirskaya E.B., Torubarova N.A., Myzina N.V. Kinetics of blood cells. - M.: Medicine, 1976.
- Ryaboe S.I., Shostka G.D. Molecular genetic aspects of erythropoiesis. - M.: Medicine, 1973.
- Hereditary anemia and hemoglobinopathies / Ed. Yu.N. Tokareva, S.R. Hollan, F. Corral-Almonte. - M.: Medicine, 1983.
- Troitskaya O.V., Yushkova N.M., Volkova N.V. Hemoglobinopathies. - M.: Publishing house Russian University Friendship of Peoples, 1996.
- Shiffman F.J. Pathophysiology of blood. - M.-SPb., 2000.
- Baynes J., Dominiczak M.H. Medical Biochemistry. - L.: Mosby, 1999.
Source: V.V. Dolgov, S.A. Lugovskaya, V.T. Morozova, M.E. Pochtar. Laboratory diagnosis of anemia: A manual for doctors. - Tver: "Provincial Medicine", 2001
Folic acid is a B vitamin, also called B9 in medicine. Women who have had a child know that it is necessary to take it during pregnancy. But they can’t always clearly explain why.
To answer this question, you must first understand what kind of vitamin it is and what its importance is for human health. It's also helpful to know how much folic acid costs and what forms it comes in.
Why are medications with vitamin B9 prescribed?
 This water soluble vitamin, an indispensable companion to numerous processes in the human body. A person gets the vitamin from food; it is found in liver and meat, soybeans, oranges, egg yolks, brewer's yeast, and seeds.
This water soluble vitamin, an indispensable companion to numerous processes in the human body. A person gets the vitamin from food; it is found in liver and meat, soybeans, oranges, egg yolks, brewer's yeast, and seeds.
But during pregnancy, when a woman needs twice as much nutrients To build a new body and maintain the normal functioning of your own, the need for folic acid increases significantly.
B9 deficiency also occurs with long-term diets, antibiotic treatment, nervous overload, and alcohol abuse. In these cases, it is necessary to take additional folic acid supplements.
Benefits and harms
What are the benefits of folic acid? It is needed to perform several essential functions:
- Hematopoiesis. It is involved in the formation of red blood cells, supports required level hemoglobin in the blood.
- Normalization of liver and intestinal function, that is, the vitamin increases appetite and stimulates digestion.
- Improving performance and memory.
- Fight depression and chronic fatigue.
- Preparing the body for conception child, normal pregnancy and childbirth without complications.
- Prevention of hereditary and genetic diseases and abnormalities in the child not only in the womb, but also after birth.
It is especially important to get enough folic acid when the neural tube and essential vital functions are forming. important organs future child.
Vitamin B9 also enhances the activity of male sperm and delays the onset of menopause in women. In general, folic acid is human and also prevents the accumulation of bad cholesterol in the body, preventing heart attack and stroke.
This is the vitamin of vitality and Have a good mood , apathy, irritability, fatigue are one of the main signs of folic acid deficiency. The following symptoms will also help identify a deficiency of this vitamin:

An excess of folic acid occurs only if you take a dose of the vitamin exceeding the daily dose for several months in a row. This is fraught increased excitability in children, attacks of nausea, suppression of vitamin B12 in the body.
Approximately 90% of vitamin B9 contained in food is destroyed during heat treatment. Therefore, it is recommended to periodically take a course of vitamin complex to prevent deficiency, and before conceiving a child and immediately after it, this is an immutable rule.
Review of products: release forms and prices in pharmacies
Pharmacies offer folic acid as in pure form– in the form of pills or drops, and in combination with other vitamins and microelements.
Monopreparation
The drug has direct relation to the group of vitamins B. Interacting with vitamin C, it turns into folinic acid. It takes part in the process of formation of red blood cells and leukocytes.
Acid is necessary for the synthesis of protein cells in the skin and hair. The vitamin is prescribed to pregnant women (about folic acid during pregnancy), as well as for the treatment of gastritis, with a decrease in hemoglobin, to reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
A deficiency of this vitamin is indicated by fatigue, weight loss, anemia, depression, weakness, diarrhea, and memory impairment.
Adults need 200 mcg of this vitamin per day(for prevention). During the period of bearing a child, you should drink 400 mcg of folic acid per day, during lactation - 300 mcg.
For treatment, adults are prescribed 500 mcg of vitamin per day. For children, the vitamin is prescribed in the smallest doses. This vitamin should be taken for a month.
The drug is available in dosages of 100 mg, 400 mg.
Price at the pharmacy: from 29 rubles to 689 rubles(depending on the country of origin).
Folibert
Includes folic acid and vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin). These components, when interacting, prevent the formation of homocysteine - harmful product interaction of amino acids, protects against the appearance of atherosclerosis.
 Used to prevent heart disease. Can be used by women at the time of pregnancy planning and in the first three months of pregnancy to prevent fetal development defects.
Used to prevent heart disease. Can be used by women at the time of pregnancy planning and in the first three months of pregnancy to prevent fetal development defects.
The drug is contraindicated in persons with intolerance to the components. Should be taken with caution by persons with impaired absorption of glucose and lactose.
Take 1 tablet. a day an hour before meals. Prevention course - 20-25 days
Foliber cost: from 120 to 257 rubles.
Doppelhertz active Folic acid
The composition of the drug includes: vitamin B9 - 600 mg, vitamin C - 300 mg, B6 - 6 mg, B12 - 5 mg, E - 36 mg.
This combination of vitamins in the complex promotes cell growth and serves as a prevention of heart and vascular diseases.
 Prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding, for heart disease, to reduce the risk of complications in heart and vascular diseases, and for gynecological diseases.
Prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding, for heart disease, to reduce the risk of complications in heart and vascular diseases, and for gynecological diseases.
Contraindications include intolerance to the components.
Doppelhertz active Folic acid is prescribed one tablet per day. Should be taken with meals. The duration of taking the vitamin complex is 1 month.
Price at the pharmacy: from 185 to 525 rubles.
Maltofer
This mineral and vitamin complex contains: folic acid - 0.35 mg and iron polymaltosate hydroxide - 357 mg.
 Maltofer is prescribed for a lack of iron and folic acid, iron deficiency anemia, during lactation and childbearing.
Maltofer is prescribed for a lack of iron and folic acid, iron deficiency anemia, during lactation and childbearing.
Contraindications include: non-iron deficiency anemia, deterioration of iron processing, iron overload in the body, intolerance to the components of the complex.
The dosage and duration of treatment depends on the condition of the body. For iron deficiency anemia, 1-3 tablets per day are prescribed for four to five months. During pregnancy, you need to take one tablet twice a day until the desired hemoglobin level is reached.
For mild iron deficiency, take one tablet per day.
Price at the pharmacy for Maltofer - folic acid with iron: from 504 rubles to 615 rubles.
Fenyuls Zinc
IN vitamin complex includes: folic acid, pyridoxine hydrochloride, zinc sulfate monohydrate, ferrous sulfate.
 Prescribed for the treatment and prevention of iron, folic acid, and zinc deficiency, even in children. Also used for complex therapy for the treatment of skin diseases (juvenile acne, atopic dermatitis).
Prescribed for the treatment and prevention of iron, folic acid, and zinc deficiency, even in children. Also used for complex therapy for the treatment of skin diseases (juvenile acne, atopic dermatitis).
: obstructive gastrointestinal changes, childhood up to 13 years of age, immunity to components in the composition, non-iron deficiency anemia, excess iron in the body. The drug should be used with caution when peptic ulcer, intestinal diseases.
The duration of administration and daily dosage depend on the level of iron deficiency. For the treatment of moderate and small iron deficiency, it is necessary to take the drug for three months, twice a day, one tablet. During pregnancy, you need to take 1 capsule per day until the end of pregnancy. For skin diseases - 1 capsule per day.
Price: from 62 rubles to 157 rubles.
Folic acid with B6 and B12 from Evalar
 The composition of the drug includes: folic acid - 600 mcg, B12 - 5 mcg, B6 - 6 mg. Is a dietary supplement.
The composition of the drug includes: folic acid - 600 mcg, B12 - 5 mcg, B6 - 6 mg. Is a dietary supplement.
It should be used to prevent the occurrence of atherosclerosis and thrombosis due to the fact that the substances included in the drug lower homocysteine levels.
The drug is indicated for pregnant women. Prevents the occurrence of heart diseases and their complications.
Contraindications include intolerance to the components of the drug.
For the purpose of prevention, adults should take one tablet every morning during meals. The duration of taking the drug Folic acid with B6 and B12 from Evalar is 60 days.
Price at the pharmacy: from 80 to 180 rubles.
Hemoferon
 Solution for oral administration. Includes: ammonium ferric citrate - 40 mg, folic acid - 0.3 mg, Excipients.
Solution for oral administration. Includes: ammonium ferric citrate - 40 mg, folic acid - 0.3 mg, Excipients.
It is used for folate deficiency and iron deficiency anemia, after surgery on the stomach, during pregnancy and lactation, renal failure, and helminthic infestation.
Contraindications: excess iron, peptic ulcer, acute enterocolitis, individual intolerance to the components of the solution.
Must be taken 30 minutes before meals. The dosage is determined using a measuring cup. Children and adults should take 15-20 ml per day (one dose). Children under one year old: 3-6 mg per day per 1 kilogram of weight.
Price at the pharmacy: from 67 to 152 rubles.
Elevit Pronatal
The drug includes: iron, vitamins B, A, D3, C, E, folic acid, copper, magnesium, calcium pantothenate, phosphorus, zinc, manganese, nicotinamide.
 The complex is intended for iron deficiency, folic acid deficiency during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Helps reduce the risk of birth defects in the fetus.
The complex is intended for iron deficiency, folic acid deficiency during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Helps reduce the risk of birth defects in the fetus.
Contraindications: intolerance to the components of the complex. At the time of taking the drug, problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract may occur, but you should not stop taking the drug. Do not do it long time take the complex to persons with excess calcium in the blood.
The drug is taken one tablet once a day after meals.
Price for these vitamins with B9 in the pharmacy: from 430 rubles to 1669 rubles.
Folic acid "9 months"
 The drug consists of folic acid - 400 mcg.
The drug consists of folic acid - 400 mcg.
Designed to replenish the lack of folic acid during pregnancy, to reduce the risk of developing pathologies. It is important to start taking the drug 1-3 months before the expected conception.
Contraindications include: childhood, malignant tumor, cobalamin deficiency, pernicious anemia.
You should take 1 tablet per day in the first trimester.
Price at the pharmacy: from 110 rubles to 230 rubles.
Why is vitamin B9 important before pregnancy and how should men and women take it correctly during this time? Everything about .
Folic acid is far from the only vitamin needed during pregnancy. Why and in what quantity is vitamin E needed? .
Find out about products containing vitamin E - the leaders in concentration:
Instructions for use
 Average, daily dose for a healthy adult or child is 200 to 300 mcg per day, for those who experience constant physical exercise– up to 400 mcg, for pregnant and lactating women – from 600 to 800 mcg per day.
Average, daily dose for a healthy adult or child is 200 to 300 mcg per day, for those who experience constant physical exercise– up to 400 mcg, for pregnant and lactating women – from 600 to 800 mcg per day.
Nutrients are better absorbed if taken with meals. A balanced diet should also be introduced, rich in products and vitamins containing folic acid. Find out more about healthy products with this vitamin.
Reception of any medicinal product, even vitamins and microelements, must be carried out only after consulting a specialist, he also determines the dosage and duration of treatment.
More detailed instructions on the use of folic acid.
This vitamin is one of the essential substances necessary for the normal functioning of the body. What are the benefits of folic acid? Folic acid plays an important role in the human body. It is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and the synthesis of nucleic acids. This component is indispensable in the formation of new cells and hematopoiesis.
Folic acid plays an important role in the human body. It is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and the synthesis of nucleic acids. This component is indispensable in the formation of new cells and hematopoiesis. Folic acid helps normalize emotional background. The substance is also necessary for the immune and cardiac systems.
Here's what scientists say:
- During adolescence, folic acid corrects puberty girls, helps with acne.
- Consumption of folic acid helps to avoid problems with the child’s spine and promotes the proper formation of the fetal nervous system. In addition, this vitamin is indispensable in the treatment postpartum depression, therefore it is rightfully considered the most important vitamin for women.
- Folic acid ensures healthy skin color. And together with pantothenic and para-aminobenzoic acids it can for a long time prevent hair graying.
- Vitamin B9 affects cell division, growth and development of all tissues, improves the functioning of immune system, supports the cardiovascular system.
- Folic acid in combination with vitamins B6 and B12 reduces the risk of developing eye diseases by 30%.
- Long-term intake of vitamin B9 (folic acid) not only allows you to get rid of many complications during pregnancy and childbirth, but is also good for health female body until the onset of menopause.
- Lack of folic acid in women can lead to lack of normal reaction reproductive organs to estrogen.
- IN male body Folic acid works in tandem with testosterone, promoting sperm maturation. In order for a young man to develop normal sexual characteristics such as a voice, a beard and an enlarged prostate to produce semen, he needs folic acid daily.
The benefits and harms of folic acid have been compared by scientists. The professors came to the conclusion that vitamin B9 can almost never cause harm. However, his excess anyway It entails unpleasant consequences. Among them are problems such as the formation of kidney stones, tumors in the mammary glands and others.
Indications for use
In what cases should it be taken? The instructions indicate that vitamin B9 is prescribed in case of its deficiency in the body.
Signs of folic acid deficiency in the body:
- Early gray hair.
- Anemia.
- Growth retardation.
- Memory impairment.
- Feeling of fear.
- Depression.
- Unreasonable anxiety.
- Absent-mindedness.
- Digestive disorders.
- Inflammation of the oral mucosa.
- The tongue takes on an unnatural bright red color.
- Spontaneous abortions and various fetal development defects.
Basic natural springs folic acid: legumes, lettuce, spinach, cabbage, green onions, green pea, beans, soybeans, beets, carrots, tomatoes, wholemeal flour and bakery products from this flour, buckwheat and oatmeal, millet, yeast. Among animal products, liver, kidneys, cottage cheese, cheese, caviar, and egg yolk are rich in folic acid.
The intestinal microflora normally synthesizes a certain amount of folic acid on its own. However, to make up for daily norm folic acid, you need to eat a huge amount every day necessary products . Therefore, sometimes it is considered advisable to take it in tablets. Moreover, the cost of the drug is quite low. The cost of the medication depends on the production and number of tablets. The dosage also matters, because one tablet may contain 400, 800 or 1000 mcg of active substance.
Doctors say that the substance is not accumulated by the body, so there is always a need to replenish useful reserves. Poor absorption of folic acid is caused by long-term treatment antibiotics that interfere with absorption.
Contraindications:
- glucose-galactose malabsorption;
- isomaltase deficiency;
- B12 deficiency anemia;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- sucrase deficiency;
- fructose intolerance;
- children's age (up to 3 years).
Carefully: folate deficiency anemia with cyanocobalamin deficiency.
What do doctors say?
Gynecologists say that taking the drug “Folic acid” cannot cause harm. Doctors explain their words as follows. During pregnancy, a woman's diet changes. Often, expectant mothers feel disgusted by foods that contain vitamin B9. These are meat, mushrooms, root vegetables, greens. There is a lack of folic acid in the body. This is aggravated by the fact that the fetus needs this vitamin every day. Therefore, pregnant women are often prescribed the drug without additional examinations.
How is folic acid beneficial for women over 40, 45 and 50 years old?
Experts say folate increases the body's resistance to hormonal changes and relieves the associated discomfort during menopause.
In older patients age group Hormonal fluctuations affect the condition of the skin and hair. Vitamin B9 controls processes new to the body, preventing them from deteriorating structures important for female beauty.
Taking folic acid is a harmless prevention of heart disease and cancer processes developing in the mammary glands, cervix and large intestine.
Tablets are prescribed in courses with breaks.
For children, the medication is prescribed much less frequently. There must be good reasons for this. Most children get the required amount of folic acid from food.
Poor absorption of folic acid is facilitated by long-term treatment with antibiotics, which impair absorption.
Daily requirement of vitamin B9 (folic acid)
The human liver typically contains some reserves of folacin, which can protect against folate deficiency for 3-6 months.
An adult's need for vitamin B9 is 400 mcg/day, pregnant and lactating women - 400-600 mcg; children of the first year of life - 40-60 mcg.
Beauty vitamin
It is not for nothing that folic acid is also called the beauty vitamin. Many people do not realize that skin problems are explained by insufficient dietary intake of this substance. The main symptom of deficiency is whitish spots on the surface of the skin. When there is a lack of vitamin B9, cells cannot renew and multiply as they should.
To maximize the positive effect, experts recommend combining the intake of folic acid with the intake of copper minerals and ascorbic acid. You can find ready-made complex preparations on sale.
Vitamin B9 will also help get rid of age spots and prevent their appearance. It will help improve the skin's resistance to harmful sun rays. This will protect against unnecessary pigmentation and the formation of melanoma.
Taking folic acid will improve the condition of hair and nails and accelerate their growth. They will become stronger and healthier. Cosmetologists often advise their clients to take a course of taking the drug.
Since the vitamin fights the development of anemia, you will forget about the paleness of your face and its unhealthy color.
When thinking about your appearance, you need to remember not only cosmetics and procedures, but also about vitamins. Don't forget to eat enough greens, cabbage, tomatoes, and various fruits.
Ready-made folic acid preparations, which can be found in pharmacies, will help compensate for the deficiency of the substance. This is an excellent solution during the spring-winter season, when there are not many fresh fruits on the shelves.
How to take folic acid (instructions)
Folic acid tablets are a convenient form of dosing of the substance (one pill contains at least 1 mg of the vitamin).
They are released under the following names:
- “Folio” - in addition to vitamin B9, the drug contains iodine. The drug is taken to prevent vitamin deficiency. It does not meet the increased needs for folic acid.
- "Folacin" and "Apo-Folik" - each tablet contains 5 mg of vitamin B9. Excess substances are removed from the body. These drugs are not prescribed for the prevention of vitamin deficiency. Indication for fortification is acute and severe deficiency of FA.
- Multivitamins for pregnant women “Elevit”, “Pregnavit”, “Multi-Tabs Perinatal”, “Vitrum Prenatal Forte”, “Materna” contain a preventive dose of vitamin B9. Of these, the body of the expectant mother assimilates much better useful substance than from food products.
The instructions for use of folic acid state daily dose of vitamin:
- for teenage girls and children – no more than 20 mcg per day,
- for adult women it is 400 mcg,
- A dosage of 400 mcg of folate is prescribed to pregnant women and those who are just planning to conceive.
At the same time, doctors take into account the amount of FA that enters the body with food and calculate it so that total dose vitamin per day did not exceed 1 mg. Take the tablets with water.
Despite all the benefits of folic acid, it is not recommended to take it for a long time and uncontrollably. The substance can reduce the concentration of its own cyanocobalamin in the body (vitamin B12).
Side effects
- From the gastrointestinal tract: anorexia, nausea, bloating, bitterness in the mouth.
- Allergic reactions: skin rash, itchy skin, bronchospasm, erythema, hyperthermia.
- With prolonged use, hypovitaminosis may develop.
Questions and answers
- Please tell me why people get better from folic acid? What is the best way to take it to avoid weight gain?
Kristina Lobanovskaya (nutritionist):
“It is impossible to predict your body’s reaction to taking folic acid, since each body is individual and reacts differently. I can tell you unequivocally that not everyone gets better, the main thing is to choose correct dosage and monitor your caloric intake.
You need to consult a gynecologist; a specialist will help you determine the amount of folic acid you need.”
All information is provided for informational purposes. Before taking the drug, be sure to consult your doctor.


