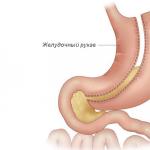
The navel (umbilicus) is located in the middle of the linea alba of the abdomen. This is a retracted scar at the site of the umbilical ring, which passed the embryonic urinary duct, two arteries (aa. umbilicales) and one vein (v. umbilicalis) of the embryo. The umbilical ring with a diameter of 0.7-1 cm is limited by the edge of the linea alba. In the area of the ring there is only skin, transverse fascia and peritoneum, fused with each other due to the absence of connective tissue layers. The umbilical ring can be the site of an umbilical hernia.
Internal fascia of the abdomen (f. endoabdominalis). Lining the inside of the transverse abdominal muscle, it is described as the transverse fascia (f. transversa abdominis). The fascia is thickened at the navel and becomes more pronounced at the inguinal ligaments. Preperitoneal tissue is more pronounced in the lower section and closer to the lower back. Through the fiber they pass through their main trunks a. epigastrica inferior and a. circumflexa ilium profunda. They are accompanied by veins of the same name.
The parietal peritoneum is the last layer of the abdominal wall. At the top it continues onto the diaphragm and at the bottom it descends into the pelvic cavity. On the inner surface of the anterior abdominal wall, the peritoneum forms folds and depressions. Three folds are defined between the navel and the bladder. One is located along the midline of the body and is directed to the top of the bladder - the median umbilical (plica umbilicalis mediana), the rest follow to the lateral surfaces of the bladder - the middle umbilicals (plicae umbilicales mediales). The first fold contains an overgrown urinary duct, the other two contain obliterated umbilical arteries (Fig. 130). Outward from the last folds, focusing on the middle of the inguinal ligaments, there is one more fold of the peritoneum - the lateral umbilical (plica umbilicalis lateralis), (containing the lower epigastric vessels (a. et v. epigastricae inferior). At the lower border of the anterior abdominal wall there are five mentioned folds the peritoneum forms paired depressions, or pits. The supravesical fossae (fossae supravesicales) are limited by the median and middle umbilical folds. The middle inguinal fossae (fossae inguinales media) are located between the middle and lateral umbilical fold of the peritoneum. The external inguinal fossae (fossa inguinales lateralis) lie outward from the lateral umbilical fold, correspond to the internal opening of the inguinal canal.
Rice. 130. Anterior wall of the abdomen. View from the abdominal cavity. On the right, the peritoneum and transverse fascia have been removed. 1 - m. transversus abdominis; 2 - m. rectus abdominis; 5 - a. epigastrica Inferior and plica umbilicale lateralis; 4 - lig. inguinalis; 5 - bone; 6 - a. femoralis; 7 - v. femoralis; 8 - ductus deferens; 9 - lig. umbilicalis lateralis and plica umbilicale media; 10 - bladder; 11 - peritoneal incision line; 12 - plica umbilicale mediana; 13 - fossa supravesicalis; 14 - fossa inguinalis medialis; 15 - fossa inguinalis lateralis; 16 - navel.
The umbilical ring is the weakest point on the anterior abdominal wall. Therefore, it is one of those places where hernial protrusions most often form. Loops of intestine, omentum and other organs can exit through the umbilical ring in adults.
Facts about umbilical hernias:
- constitute 5% of all abdominal hernias in adults;
- most often found in women over 40 years of age;
- the disease was first described by the ancient Roman physician Celsus, who lived in the 1st century AD;
- The first successful operation for an umbilical hernia was performed in France in 1885.
Features of the anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall and navel area
The side and front walls of the abdomen, which protect the internal organs, consist mainly of the abdominal muscles. They are arranged in three layers, their bundles extend in different directions and provide different types of movements.The only place where the abdomen is not protected by muscles is the narrow white line, which runs in the front center from the sternum to the pubis.
White line – this is the junction of the abdominal muscles located on the right and left. It is formed by their aponeuroses - bundles of connective tissue. In the upper part, the white line of the abdomen is narrower and thicker, in the lower part it is wider and thinner, and therefore weaker.
While the fetus is in the womb of a pregnant woman, it has a rounded hole in the linea alba of the abdomen - the umbilical ring. The umbilical cord passes through it, connecting the mother and child.  The umbilical cord includes:
The umbilical cord includes:
- umbilical arteries;
- umbilical veins;
- urinary duct.
The organs that prolapse into the hernial protrusion are located in the hernial sac. It is represented by the peritoneum - a thin film of connective tissue that lines the inside of the abdominal cavity and covers the internal organs.
Causes of umbilical hernia in adults:
- Congenital expansion of the umbilical ring, when it is not completely scarred and a small hole remains. This may not manifest itself in any way in childhood, but over time, under certain conditions, an umbilical hernia forms.
- Pregnancy and childbirth. During pregnancy, a woman's belly increases and the navel stretches because of this. Constipation occurs, which leads to increased pressure inside the abdomen. The risk is especially high in women who have given birth more than once and who did not follow doctor's recommendations during pregnancy. Also, the occurrence of an umbilical hernia can be caused by difficult childbirth, a large fetus, polyhydramnios, and pregnancy with twins and triplets.
- Sedentary lifestyle. If a person neglects physical activity, his abdominal muscles weaken.
- Excessive exercise. When lifting heavy weights, the pressure inside the abdomen increases greatly.
- Diseases accompanied by a constant increase in intra-abdominal pressure. These may be diseases of the digestive system, during which there is constant constipation, chronic cough, etc.
- Obesity. Subcutaneous fat is extra weight. It leads to stretching of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Postponed surgeries. Hernias in the navel area can also occur at the site of postoperative sutures. The risk increases greatly if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations and begins to exercise too early.
- Abdominal injury.
- Losing weight too quickly. This can happen when a person is on a strict diet or is seriously ill, resulting in exhaustion. The umbilical ring is weakened, creating conditions for the formation of a hernial protrusion.
Signs of an umbilical hernia in adults
 Protrusion in the navel area. The most characteristic and clearly visible symptom of an umbilical hernia. It can be of various sizes. Sometimes the protrusion is barely noticeable; in a lying position it is not visible at all. And sometimes it’s very big.
Protrusion in the navel area. The most characteristic and clearly visible symptom of an umbilical hernia. It can be of various sizes. Sometimes the protrusion is barely noticeable; in a lying position it is not visible at all. And sometimes it’s very big. If you put your fingers on the protrusion and cough slightly and strain, you can feel a characteristic jolt.
If you press on the protrusion, it usually disappears - the hernia is reduced inside the abdomen. A large hernia, complicated by adhesions in the navel area, can become irreducible - it never disappears. Usually this causes pain, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, and constipation. If part of the bladder gets into the hernial protrusion, problems with urination arise.
Pain in patients with an umbilical hernia usually occurs only during intense physical activity, during coughing, sneezing, and constipation.  Symptoms of an umbilical hernia in a pregnant woman:
Symptoms of an umbilical hernia in a pregnant woman:
- the navel protrudes strongly;
- when feeling the navel, it feels like an empty cavity;
- There are clicks in the stomach: the sound resembles the bursting of bubbles.
Complications of umbilical hernia

- Infringement. If part of the intestine or other organ is pinched in the umbilical ring, acute pain occurs (they can be of varying strength) associated with compression of nerves and blood vessels. Constipation, nausea, and vomiting occur. After 2-8 hours, the strangulated part of the organ begins to die due to the fact that blood does not flow to it. Symptoms intensify, the patient's condition becomes more severe. After 8 hours, the wall of the organ usually dies, and peritonitis develops - inflammation of the abdominal cavity. The patient's life is in danger.
- Intestinal obstruction- a condition in which the part of the intestine located in the hernia becomes clogged with feces. This complication is very similar to strangulation and manifests itself with similar symptoms.
- Inflammation of an organ located in the hernial sac. Pain, swelling, redness in the area of the hernial protrusion occurs, body temperature rises, and the general condition of the patient is disturbed.
Diagnosis of umbilical hernia in adults
Which doctor should I contact for an umbilical hernia?
 If you have symptoms similar to those of an umbilical hernia, you need to contact a surgeon. An umbilical hernia is dangerous not only because of its complications. If a protrusion and thickening occurs in the navel area, this may be a metastasis of a malignant tumor of the stomach. This rarely happens, but in every case it must be excluded. The doctor will examine you and prescribe an examination.
If you have symptoms similar to those of an umbilical hernia, you need to contact a surgeon. An umbilical hernia is dangerous not only because of its complications. If a protrusion and thickening occurs in the navel area, this may be a metastasis of a malignant tumor of the stomach. This rarely happens, but in every case it must be excluded. The doctor will examine you and prescribe an examination. How does the surgeon's examination proceed?
- The doctor asks the patient to undress to the waist.
- He examines the abdomen in a standing or lying position.
- The surgeon feels the protrusion, asks the patient to cough a little and strain to feel the push characteristic of an umbilical hernia.
- The doctor can also examine the groin area, thigh, and scrotum in men in order to rule out an inguinal and femoral hernia.
What questions might the doctor ask?
- When did the protrusion in the navel appear?
- Are you bothered by pain?
- Are you worried about digestive disorders: bloating, constipation, heaviness, belching, heartburn, nausea, vomiting?
- Have you had any previous surgical interventions?
- Did the patient's immediate family suffer from an umbilical hernia?
Examination for umbilical hernia
| Study title | Description | How is it carried out? |
| Ultrasound for umbilical hernia | Information that ultrasound can provide for an umbilical hernia:
| Ultrasound examination for umbilical hernia is carried out in the usual way. The doctor asks the patient to lie on his back, applies a special gel to the skin in the navel area and conducts an examination using an ultrasound probe.  |
| Herniography | An X-ray contrast agent is injected into the patient's abdomen, which penetrates the hernial sac and stains it. It becomes clearly visible on x-rays. The doctor prescribes herniography when there is doubt about the diagnosis. |
|
| CT scan | The study is carried out when the symptoms are unclear and doubts arise about the diagnosis. Computed tomography is a study that allows you to obtain layer-by-layer sections of a certain area of the body, a clear three-dimensional image. |  |
| X-ray of the stomach and duodenum with contrast | The study allows us to suspect tumor processes in the stomach and duodenum, diseases that accompany an umbilical hernia and lead to abdominal pain. | The patient is given a contrast drink - usually a barium sulfate solution. Then x-rays are taken.  |
Gastroduodenoscopy – endoscopic examination of the stomach and duodenum.  |
|
Treatment of umbilical hernia in adults
Treatment of umbilical hernia in adults is only surgical. Different types of operations are used, depending on the size of the hernia and the condition of the anterior abdominal wall.Usually, surgery for an umbilical hernia, if there is no strangulation, is carried out as planned. During the first appointment, the doctor examines the patient, prescribes a preoperative examination and a date for hospitalization.
Preoperative examination in a patient with an umbilical hernia
- tests for hepatitis, HIV, syphilis;
- coagulogram - blood test for clotting;
- chest x-ray.
Types of operations for umbilical hernia
An operation aimed at eliminating a hernial protrusion is called hernioplasty. Types of hernioplasty that are performed for umbilical hernia:- Tension. The patient's umbilical ring is strengthened with his own tissue. In order to close the defect, they are pulled, which is why the operation got its name.
- Non-tensioned. To strengthen the umbilical ring, special synthetic mesh is used.
- Laparoscopic. The operation is performed without an incision, through punctures in the abdominal wall.
 Tension hernioplasty
Tension hernioplasty
- The surgeon makes an incision and provides access to the hernial sac.
- Depending on the size of the hernial sac, it is either simply immersed in the stomach, or stitched and cut off.
- The umbilical ring is stitched and reinforced with adjacent tissues.
 Tension-free hernioplasty
Tension-free hernioplastyThe operation is performed in a similar way, but the surgeon uses a special synthetic mesh to strengthen the navel. Subsequently, it grows into surrounding tissues.
The advantage of tension-free hernioplasty is the relatively low likelihood of relapse. The hernia occurs again on average in only 2 patients out of 100. The rehabilitation period lasts only 30 days, even for those people who play sports professionally.  Laparoscopic hernioplasty
Laparoscopic hernioplasty
During laparoscopic surgery, a mesh implant is also used; it is installed through a puncture in the abdominal wall. The surgeon does not make a large incision, which significantly reduces postoperative rehabilitation time.
But there are also certain difficulties. Laparoscopic hernioplasty requires special equipment and trained surgeons. Not every hospital has this opportunity. Surgeries through a puncture are contraindicated in patients with pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, with a large expansion of the umbilical ring.
Surgery for strangulated umbilical hernia
If an umbilical hernia is strangulated, surgery must be performed as an emergency.
The risk of strangulation does not depend on the size of the hernia - it increases the more the longer the patient does not see a doctor.
During surgery, the doctor opens the hernial sac and examines the organ that is inside. If it is not changed, then it is simply immersed in the stomach. If part of the organ is dead, it is excised. And if the doctor has doubts, he covers the organ with napkins soaked in warm saline and injects a solution of novocaine.
Rehabilitation after surgery for umbilical hernia in adults

- Usually, if the operation goes without complications, the patient is allowed to get up on the first day.
- In the postoperative period, wearing a special bandage is recommended (about a month when using mesh implants).
- On days 10-14, you can start doing therapeutic exercises, but you are prohibited from performing abdominal exercises.
- After the operation, daily dressings are performed, the sutures are removed on the 7th day (if they do not dissolve on their own).
- For pain, painkillers are prescribed.
- The doctor may also prescribe antibiotics, vitamins, and immunomodulators.
Wearing a bandage for an umbilical hernia
 The bandage is not a treatment for an umbilical hernia. It only helps, while wearing it, to correct the hernia and prevent it from being strangulated.
The bandage is not a treatment for an umbilical hernia. It only helps, while wearing it, to correct the hernia and prevent it from being strangulated. Indications for wearing a bandage:
- After surgery for an umbilical hernia and in general during any surgical intervention when the incision passed through the navel.
- If there are temporary contraindications to surgery: acute diseases, exacerbations of chronic ones. After normalization of the patient's condition, surgical treatment is performed.
- Severe diseases: significant dysfunction of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, exhaustion, old age, malignant neoplasms, etc.
- Late-stage pregnancy is also a contraindication for surgery.
 The bandage is a wide belt made of elastic fabric, on the inner surface of which a special anatomically shaped pad is attached. She presses the navel and does not allow the hernia to protrude outward. The pelot can be connected to the bandage or attached to it with Velcro.
The bandage is a wide belt made of elastic fabric, on the inner surface of which a special anatomically shaped pad is attached. She presses the navel and does not allow the hernia to protrude outward. The pelot can be connected to the bandage or attached to it with Velcro. Traditional methods of treating umbilical hernia
An umbilical hernia in an adult is a disease that can only be eliminated with surgery.“Spells” and gluing coins to the navel, methods that traditional medicine often recommends, “help” only small children, since their umbilical hernia can close on its own before the age of 5. This doesn't happen in adults.
Decoctions, infusions, and lotions with medicinal plants are ineffective. With their help, an umbilical hernia in an adult cannot be eliminated.
Prevention of umbilical hernia
| What do we have to do? | What should you avoid? |
 |
 |
An umbilical hernia is a pathology in which the intestines and greater omentum extend beyond the peritoneum through the umbilical ring. In infants, its appearance is associated with:
- with intrauterine malformations,
- with gas accumulation,
- with poor umbilical cord ligation,
- constipation,
- coughing,
- with frequent strong and prolonged crying.
An umbilical hernia in children can also occur due to early standing on their feet.
Every fifth child has this surgical pathology. Among premature babies, it occurs in every third.
Symptoms
A hernia in the navel area usually appears at the age of one month. A protruding navel is not yet a pathology. This may well be an anatomical feature. It is located under the navel. It is caused precisely by the weakness of the umbilical ring.
Favor the development of pathological diseases that reduce muscle tone (hypotrophy, rickets).
A hernia looks like a rounded protrusion in the area of the umbilical ring. It can be easily reduced into the abdominal cavity. Often a hernia is accompanied by divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles, since the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall are very weak.
Important: If the umbilical ring is too large, then self-healing becomes impossible.
The size of the umbilical ring determines how large the hernial protrusion will be. The doctor determines the size of the ring by palpating the abdomen in the navel area. If the child's ring is large, the hernia will be constantly visible. If a finger falls into the abdominal cavity, then using this technique you can determine the size of the hernial orifice.
Consequences for the child
Many pediatricians note that children with an umbilical hernia are more anxious. They also respond to weather changes.
The child does not experience pain with this pathology. But it can cause bloating, which causes significant discomfort. By and large, pathology can be attributed to cosmetic defects.
Treatment
 Mostly doctors advise to wait. If the baby develops correctly, he has enough physical activity, and has normal intestinal activity, then by the age of 5-7 years, self-healing will most likely occur. However, it would not be amiss to perform exercises that strengthen the abdominal muscles, as well as do a special massage.
Mostly doctors advise to wait. If the baby develops correctly, he has enough physical activity, and has normal intestinal activity, then by the age of 5-7 years, self-healing will most likely occur. However, it would not be amiss to perform exercises that strengthen the abdominal muscles, as well as do a special massage.
If spontaneous healing does not occur, then surgical treatment methods are used. For boys, surgical intervention is performed only if the patient complains of pain. Girls aged 5-7 years are operated on, as a hernia can affect fertility in the future. This is only possible if there are no contraindications.
If the umbilical ring is too large, then self-healing becomes impossible. Such children, as prescribed by a doctor, undergo surgery earlier (at the age of 3-4 years).
Conservative treatment methods
Parents can massage the anterior abdominal wall themselves. It's not difficult at all. It is enough to simply stroke the baby's tummy clockwise, and then put it on the stomach for about 5-10 minutes. The procedure must be done before feeding. Children older than two months are prescribed massage in a medical facility.
2. Applying an adhesive bandage
Methods for applying the patch:
- use patches from various companies (Hartmann, Chicco);
- the bandage is applied by the attending physician.
3. Special bandage
The disadvantage of this method is the constant slipping of the bandage.
Surgery
The operation lasts for 15-20 minutes. General anesthesia is used. Rehabilitation takes no more than two weeks. After the operation, there is a ban on physical activity for a month. If the patient's age is less than 4 years, then he stays in the hospital with his mother.
The umbilical ring (anulus umbilicalis) is located not quite strictly in the middle of the white line, indicated on the side of the skin by its peculiar fold - the skin navel. Usually the sword-umbilical distance is 2-4 cm longer than the umbilical-pubic distance.
Anatomically, the umbilical ring is a round or slit-like gap of larger dimensions than the usual gaps between the fibers of the aponeuroses along the white line. Often, through the skin fold of the navel, it is not possible to palpate the aponeurotic fissure and in this place simply a fossa is determined. Only in very young children can we talk about a through aponeurotic ring of the navel in the full sense of the word. After 2-3 years of life it is no longer end-to-end due to closure. This closure is facilitated by 3 factors: wrinkling of the aponeurotic umbilical ring itself, the development of strong connective tissue formations in place of the obliterating umbilical vessels, as well as the progressive development and compaction of a special section of the transverse fascia, called Richet's umbilical fascia.
More durable closure of the umbilical ring in the aponeurosis of the white line is facilitated by the absence of a layer of preperitoneal fatty tissue. The aponeurotic edges of the ring are intimately connected to the parietal layer of the peritoneum, which is usually more compacted. The fact of the almost constant closure of the umbilical ring by scars and umbilical fascia means that in practice, umbilical hernias in the true sense of the word almost never occur in adults; As a rule, a hernial protrusion always has a peri-umbilical location, and the hernia canal often runs close, somewhat higher and laterally.
The skin navel is formed by differently located skin folds. The bays between them sometimes turn out to be the site of localization of various pathological processes.
In the composition of the scar-aponeurotic formations involved in the apparatus for closing the umbilical ring, in addition to the umbilical fascia, connective tissue strands also play a role, intertwined in a ring and fused with each other. From below they are formed by the obliterated remnants of the urinary duct (urachus) and both umbilical arteries, and from above by the obliterated remnant of the umbilical vein, surrounded by elements of the round ligament of the liver. This circumstance contributes to the fact that pathological processes (except for hernias) develop more often in the navel area than in its other parts. The participation of the remnants of the urachus often contributes to the occurrence of a number of congenital diseases in the navel area.
The participation of the remnants of the umbilical vein in combination with the round ligament of the liver determines that a number of diseases in the area of the umbilicus and mesogastric part of the white line are accompanied by painful irradiations and functional disorders (and sometimes organic) of the organs of the upper floor of the abdominal cavity, since through the system of the round ligament of the liver various irritations can be transmitted to the solar plexus through the remnants of the duct of Arantius.
The article was prepared and edited by: surgeonVideo:
Healthy:
Related articles:
- An umbilical hernia is a pathological protrusion of abdominal organs through the umbilical ring. This disease can...
- The white line (linea alba) is an aponeurotic plexus of individually different widths, like a septum between the medial...
Difference between umbilical hernia and umbilical ring enlargement
It is necessary to distinguish between frequently confused concepts: “ umbilical hernia" and "hypotonicity of the umbilical ring", or expansion of the umbilical ring.
Photo 1 shows a classic hernia in an adult. This is a muscle protrusion that can form for several reasons, including:
- severe diseases that disrupt tissue turgor and muscle tone;
- weakness and insufficient density of the abdominal fascia;
- covering the umbilical ring with the abdominal fascia, and so on.
A hernia creates discomfort and poses risks to human health; it can only be cured surgically.
In everyday practice, enlargement of the umbilical ring in infants is also called a hernia for simplicity (photo 2). Although in fact it occurs for other reasons - usually due to prematurity or due to the fact that, when the umbilical cord has already fallen off, the umbilical ring closes more slowly than necessary. Unlike a true hernia, such a bulge can be treated without surgery - bandages, exercise therapy massages, and special exercises are used for this. The baby should also be placed on a flat, hard surface in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
How dangerous is an “umbilical hernia” in newborns?

The most important thing for parents is not to remain ignorant and not to exaggerate the scale of the problem. So-called hernia in newborns appears not so rarely, and it is found in girls more often than in boys. At risk are babies born prematurely, as well as those whose birth weight was less than three kilograms.
If a child is found umbilical ring expansion, this is not a reason to panic! And even more so, this does not mean that surgery will necessarily be required. In the vast majority of cases, it is enough to use reliable and effective Rupfix umbilical plates from the Arilis company, which have already helped many children get rid of the so-called hernia, as well as follow other doctor’s recommendations.
Myths about umbilical hernia in newborns
Despite the development of medicine and the educational work of doctors, many parents are still at the mercy of myths and prejudices. Thus, some are confident that an increase in intra-abdominal pressure can supposedly provoke a hernia in a child, and therefore call coughing, screaming, crying, vomiting and bloating as dangerous phenomena.
All this has nothing to do with reality. In fact, expansion of the umbilical ring can only appear if there is an anatomical predisposition or with developmental disorders of the abdominal fascia, which is usually diagnosed already in the first weeks after the birth of the child. These reasons, in turn, are not associated with factors that provoke a true umbilical hernia (severe illnesses, etc.).
As for screaming and crying, they are precisely the consequence, not the cause. With the development of hypotonicity of the umbilical ring, the baby experiences severe discomfort, which prompts him to cry. To eliminate this problem, it is necessary to deal with it under the guidance and supervision of a pediatrician or perinatologist.
How and when is umbilical ring enlargement detected in children?
The umbilical ring is the anatomically weak point of any child. In some children, the muscles close quickly enough, in others this does not happen, resulting in a small protrusion in the navel area. It is clearly visible to the naked eye, and in this case the child will rarely feel well. Fortunately, getting rid of this problem is quite easy.
Discover umbilical ring expansion The child can be visually examined by the parents or the doctor. Usually any abnormalities are detected in the first weeks or months after the birth of the child. Quite rare, but cases are still possible when the problem is detected in a child already at the age of one or even one and a half years. The resulting protrusion is difficult to miss, especially when the child is sitting or standing, when he cries or strains his stomach for other reasons.
It should be remembered that at an early age, a protrusion in the navel area is not a hernia: it is temporarily reduced if you just press lightly with your fingers. But if suddenly a child aged three or more years develops a muscle bulge that was not there before, this is most likely the beginning of the development of a true umbilical hernia. The reasons for it can be different, and they differ from those that provoke a convex navel in newborns. An older child should definitely be shown to a doctor - most likely, he will confirm a true umbilical hernia, and surgical intervention will be required.
Do I need to see a doctor?
Yes, you should definitely contact a specialist! The baby's parents are not professional doctors, and they cannot make an accurate diagnosis. Only a pediatric surgeon can do this. It will be enough for parents to report that they have discovered a hernia-like protrusion in their child. Possible additional symptoms are fever, change in skin color, and abnormal bowel movements.
In any case, you should not delay seeing a doctor! The sooner you report a problem, the easier it will be to fix it, avoiding risks and complications. According to statistics, about two thirds of cases are eliminated exclusively by conservative methods, that is, without surgery. It is strictly necessary to excise the hernia and perform plastic surgery only in severe cases, and also at the age of five years. But regardless of age, diagnosis is needed.
Can the situation return to normal without treatment?
In some children, the deviation in the development of the umbilical ring from the norm is less than seven millimeters, while the protrusion is very small or completely invisible. In this case, the doctor diagnoses “enlarged umbilical ring.” Sometimes it goes away on its own - this is what the children's parents hoped for when medicine was not yet developed.
But today there are ways to solve the problem with guarantee, and you should not neglect them:

- The child should be seen regularly by a doctor.
- will allow you to fix problem muscles and painlessly, gradually return them to their normal position. Due to the lack of allergenic properties, the plates can be worn for a very long time.
- Therapeutic massage is prescribed, which can be performed both in clinical and at home conditions.
- Special gymnastic exercises for newborns, regular placing baby on stomach on a hard surface - additional measures to get rid of hypotonicity of the umbilical ring.
- With an integrated approach, you can count on quickly getting rid of the problem. Wearing them will be key as they will have a positive effect all the time.
The Arilis company has proven itself well among parents. According to many reviews, you can see significant improvements in just ten to twenty days. Rupfix plates do not cause discomfort, do not cause allergies, yet they adhere very well and significantly surpass any medical bandages in their characteristics. Thanks to the use of such plates, it is possible to significantly speed up the process of getting rid of the so-called umbilical hernia in a newborn.