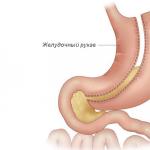
An umbilical hernia in a baby is a congenital defect in the area of the umbilical ring, through which the contents of the abdominal cavity can escape, but do not be alarmed: in most cases, an umbilical hernia is a loop of intestine, and doctors successfully cope with this phenomenon.
SYMPTOMS OF UMBILIAL HERNIA IN NEWBORNS Normally, at the birth of a baby, the umbilical ring is a narrow hole that allows only the vessels through which the little person was connected to the placenta in the mother’s tummy, that is, the umbilical cord. After the baby is born, his umbilical cord is tied and the remainder falls off, the umbilical ring closes and is scarred. Of course, this does not happen immediately; it usually takes several weeks.
If at the time of birth the umbilical ring is larger than expected, then with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure (crying, screaming, gases), some intestinal loops may come out through it, which will prevent the umbilical ring from healing. This is an umbilical hernia. A baby diagnosed with an umbilical hernia is born with an already dilated umbilical ring. It is not possible to predict who will have it of normal size and who will have it enlarged, so there are no specific measures to prevent umbilical hernia. As already mentioned, it takes time for the umbilical ring to tighten. However, if the healing process does not go as it should, even an inexperienced mother will notice a protrusion in the navel area by the end of the first year of life. In addition, the visiting nurse or local pediatrician who is observing the child is unlikely to miss the presence of a hernia in the baby. This means that the little patient will be registered with a surgeon in his clinic.
TREATMENT OF UMBILICAL HERNIA
Not so long ago, one could hear the recommendation to apply circles of hard material to the hernia and bandage them tightly. Today, this method is no longer used, since it is not effective: even the protruding part of the internal organ, pressed down from above by a circle, does not allow the umbilical ring to heal. A competent doctor will reduce the hernia inward, connect the skin near the navel into a longitudinal or transverse fold and secure it with a plaster. This type of compression bandage will prevent the internal organs from “peeping out” and will help the umbilical ring to tighten. The patch is applied for ten days.
On the first day with the patch, the baby is usually not bathed, and on the remaining days you can carry out all hygiene procedures as usual, bathing the baby. After the indicated ten days, the baby should be examined by a surgeon, remove the patch and check the condition of the navel. In accordance with the result, further treatment is determined. It is quite possible that after several “sessions” with the patch, the umbilical ring will heal.
If by the age of two months wearing the patch does not produce tangible results, it is advisable to abandon it. The baby's abdominal muscles have already become stronger, the skin has become quite elastic, and the patch may tighten it too much, causing irritation.
UMBILICAL HERNIA MASSAGE
At this stage, doctors and parents have massage and gymnastics in their arsenal. Yes, yes, exactly that one!.. When changing the baby’s diapers, mommy can massage the umbilical ring, first clockwise, then counterclockwise. It is the umbilical ring that should be massaged, and not the entire tummy, otherwise the baby’s digestion may be disrupted.
And when the baby begins to hold his head, he can and should be placed on his tummy. All babies are placed on their tummy, but if your baby has an umbilical hernia, make sure that the surface on which he will lie is hard. Such simple exercises strengthen the muscles of the small tummy and can help tighten the umbilical ring on its own.
Taping, massage and placing on the tummy are conservative methods of treatment. Surgeons try not to resort to anesthesia and a scalpel until the child is 3–5 years old, because any operation is stressful for the child’s body. And yet, the main indication for surgical intervention is not the age of the baby, but the condition of the umbilical hernia.
If a hernia causes concern, causes discomfort to the child, or there is a risk of complications, surgery can be performed at the tender age of 3–6 months. If the hernia is small and does not interfere with the child’s growth and development, there is a chance that it will disappear on its own. You can watch the hernia for quite a long time. But if by the age of 5 there is no progress towards “self-liquidation”, the child will have to undergo surgery, and here’s why: strangulated hernias are rare in children, but much more common in adults. If you do not treat and operate on a hernia, and forget about it, for example, until adulthood, then this can result in serious plastic surgery in adulthood. For children, it is somewhat easier to operate on a hernia.
It remains to add that there are no general schemes for the treatment of any disease, including umbilical hernia. Only an observing specialist can tell you how often a mother should bring her baby for examination to a surgeon. He, based on his observations, makes a decision about when to operate on an umbilical hernia and whether surgery is needed at all.
Umbilical ring divergence is a condition caused by changes in the position of muscle fibers. Pathology may be the first sign of the formation of an umbilical hernia, but does not always lead to it. In this case, expansion with protrusion already indicates the formation of this disease. According to ICD 10, the code for umbilical hernia is K42, but for the expansion of the umbilical ring as an independent disease, such a code is not provided.
Causes of umbilical hernia in children and adults
The reasons for the expansion of the ring and the formation of a hernia in infants and adults differ. In children, the main factors causing pathology are:
- Incorrect development of the anterior abdominal wall or underdevelopment of fibers. This condition is caused by various reasons, including infections in the woman, constant exposure of the mother's body to toxic substances, or overexertion during pregnancy.
- High pressure inside the peritoneum. In this case, the hernia is not considered a congenital pathology; it is formed in the first year of life (most often a few weeks after birth) due to intense, frequent crying and screaming.
- Weakness of the umbilical ring and connective tissue dysplasia. These are congenital pathologies that can appear later than a year after birth.
In adults, divergence of the umbilical ring and the formation of a hernia are due to a wide range of reasons:
- difficult childbirth and pregnancy;
- carrying a child multiple times;
- multiple pregnancy;
- operations localized in the peritoneal area;
- injuries of the abdomen and anterior abdominal wall;
- adhesions and tissue scarring;
- prolonged cough;
- constipation and straining during bowel movements;
- excessive physical activity;
- ascites (often occurs with cirrhosis);
- obesity or sudden weight loss of 10 kilograms or more;
- decreased muscle tone due to lack of physical activity.
There are factors that contribute to excessive divergence of the umbilical ring, followed by the formation of a hernia. Similar disorders are observed in women who become pregnant after 35-40 years of age. Some professions can provoke the disease, for example, playing wind instruments.
Most of the reasons for the formation of discrepancy and umbilical hernia are associated with impaired muscle tone in the peritoneal area. In adults and children, they can be either congenital or acquired. And the disease can develop at any age.
Symptoms of the onset of a hernia
 Only a doctor can determine ring discrepancy in a newborn or adult. The pathology is not always immediately accompanied by a symptom such as navel prolapse.
Only a doctor can determine ring discrepancy in a newborn or adult. The pathology is not always immediately accompanied by a symptom such as navel prolapse.
A normal umbilical ring has a fairly high density. It is narrow, and if you insert a finger there, it will immediately hit the wall without penetrating into the abdominal cavity. With the development of pathological processes, the ring becomes much wider, and the tone of the navel decreases. The tip of the index finger passes through it easily. An umbilical hernia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain – does not occur in all cases, but if it does, it can radiate to the navel, lower back and along the spinal column;
- protrusion always occurs with a hernia, but may be absent if the ring has just begun to expand;
- in the first stages, the prolapsed sac is easily repositioned and has a soft consistency;
- the size of the hernia depends on the duration of the disease.
If the pouch is pinched, acute symptoms occur: problems with bowel movements, severe pain in the navel area, high fever, nausea and weakness, loss of appetite. After infringement, complications may begin.
Diagnosis of the disease
The surgeon can recognize an umbilical hernia at the first examination, as well as determine the presence of an enlarged umbilical ring. The patient cannot independently diagnose these pathologies.
Ultrasound, x-rays and laboratory tests are necessary to exclude hidden complications, inflammatory and infectious processes. They are most often prescribed when complications are suspected.
Complications of umbilical hernia
 Complications of umbilical protrusion begin only with a long course of the pathology. The primary consequence is a pinched hernia, due to which adverse symptoms develop and the patient’s well-being worsens. In adults, strangulation is quite rare; inguinal and femoral hernias are significantly ahead of it in terms of indicators. Due to the compression of the sac by the hernial orifice, necrosis of the tissues trapped in this formation is formed.
Complications of umbilical protrusion begin only with a long course of the pathology. The primary consequence is a pinched hernia, due to which adverse symptoms develop and the patient’s well-being worsens. In adults, strangulation is quite rare; inguinal and femoral hernias are significantly ahead of it in terms of indicators. Due to the compression of the sac by the hernial orifice, necrosis of the tissues trapped in this formation is formed.
The next complication that occurs regardless of the infringement is secondary infection. It covers the part of the organ that is trapped in the hernial sac. Patients whose hernia covers intestinal loops are faced with a consequence such as coprostasis.
The long course of the disease causes painful shock, and sometimes intestinal obstruction and peritonitis develop. The most advanced stages can lead to coma, but this consequence is extremely rare.
The lack of timely diagnosis and adequate treatment is the main factor in the occurrence of hernia complications. If the patient feels painful tingling in the navel area, or there is a suspicion that the umbilical ring is expanding, he needs to consult a surgeon or therapist.
Treatment methods
 In children from birth to 1 year, active expectant treatment is used, which includes:
In children from birth to 1 year, active expectant treatment is used, which includes:
- constant monitoring of the condition of the navel;
- use of support bandages;
- operation if containment measures are ineffective.
In adults and older children, the only method of effective treatment for umbilical hernia is surgery. With its help, the surgeon isolates the hernial sac and returns its contents back into the abdominal cavity. Then a special mesh is installed to restrain the hernial orifice. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the patient’s condition.
The rehabilitation period is 6 months, the first weeks must be kept in bed.
If a hernia occurs in parallel with multiple malformations in a newborn child, the prognosis will be unfavorable. Early surgery or restraining therapy helps eliminate the hernia without recurrence. Adults tolerate surgery well; in the absence of associated complications, the risk of relapse is unlikely.
Prevention of ring expansion and hernia
 To prevent the child from stretching the umbilical ring, the mother must take the course of pregnancy responsibly, follow the doctor’s recommendations and refuse to use hazardous substances or live in an area with a high risk of chemical poisoning. Immediately after birth, the child is prescribed gymnastics and massage to protect against expansion of the umbilical ring.
To prevent the child from stretching the umbilical ring, the mother must take the course of pregnancy responsibly, follow the doctor’s recommendations and refuse to use hazardous substances or live in an area with a high risk of chemical poisoning. Immediately after birth, the child is prescribed gymnastics and massage to protect against expansion of the umbilical ring.
In adults, prevention methods include the following:
- it is necessary to engage in moderate exercise and eat properly to ensure normal digestion;
- during pregnancy, wear a support bandage and perform preventive exercises so that there is no discrepancy after the birth of the child;
- monitor weight, obesity is not allowed;
- If there are diseases that cause coughing or any infections, they immediately begin to treat them.
To avoid relapse after surgery, the patient must follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
An umbilical hernia, which often occurs after the ring has expanded, can be treated. However, advanced disease can lead to complications. If you visit a doctor and follow his recommendations, unpleasant consequences can be avoided.
An umbilical hernia is a pathology in which the intestines and greater omentum extend beyond the peritoneum through the umbilical ring. In infants, its appearance is associated with:
- with intrauterine malformations,
- with gas accumulation,
- with poor umbilical cord ligation,
- constipation,
- coughing,
- with frequent strong and prolonged crying.
An umbilical hernia in children can also occur due to early standing on their feet.
Every fifth child has this surgical pathology. Among premature babies, it occurs in every third.
Symptoms
A hernia in the navel area usually appears at the age of one month. A protruding navel is not yet a pathology. This may well be an anatomical feature. It is located under the navel. It is caused precisely by the weakness of the umbilical ring.
Favor the development of disease pathologies that reduce muscle tone (hypotrophy, rickets).
A hernia looks like a rounded protrusion in the area of the umbilical ring. It can be easily reduced into the abdominal cavity. Often a hernia is accompanied by divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles, since the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall are very weak.
Important: If the umbilical ring is too large, then self-healing becomes impossible.
The size of the umbilical ring determines how large the hernial protrusion will be. The doctor determines the size of the ring by palpating the abdomen in the navel area. If the child's ring is large, the hernia will be constantly visible. If a finger falls into the abdominal cavity, then using this technique you can determine the size of the hernial orifice.
Consequences for the child
Many pediatricians note that children with an umbilical hernia are more anxious. They also respond to weather changes.
The child does not experience pain with this pathology. But it can cause bloating, which causes significant discomfort. By and large, pathology can be attributed to cosmetic defects.
Treatment
 Mostly doctors advise to wait. If the baby develops correctly, he has enough physical activity, and has normal intestinal activity, then by the age of 5-7 years, self-healing will most likely occur. However, it would not be amiss to perform exercises that strengthen the abdominal muscles, as well as do a special massage.
Mostly doctors advise to wait. If the baby develops correctly, he has enough physical activity, and has normal intestinal activity, then by the age of 5-7 years, self-healing will most likely occur. However, it would not be amiss to perform exercises that strengthen the abdominal muscles, as well as do a special massage.
If spontaneous healing does not occur, then surgical treatment methods are used. For boys, surgical intervention is performed only if the patient complains of pain. Girls aged 5-7 years are operated on, as a hernia can affect fertility in the future. This is only possible if there are no contraindications.
If the umbilical ring is too large, then self-healing becomes impossible. Such children, as prescribed by a doctor, undergo surgery earlier (at the age of 3-4 years).
Conservative treatment methods
Parents can massage the anterior abdominal wall themselves. It's not difficult at all. It is enough to simply stroke the baby's tummy clockwise, and then put it on the stomach for about 5-10 minutes. The procedure must be done before feeding. Children older than two months are prescribed massage in a medical facility.
2. Applying an adhesive bandage
Methods for applying the patch:
- use patches from various companies (Hartmann, Chicco);
- the bandage is applied by the attending physician.
3. Special bandage
The disadvantage of this method is the constant slipping of the bandage.
Surgery
The operation lasts for 15-20 minutes. General anesthesia is used. Rehabilitation takes no more than two weeks. After the operation, there is a ban on physical activity for a month. If the patient's age is less than 4 years, then he stays in the hospital with his mother.
Pathological protrusion of abdominal organs through the umbilical ring is classified in medicine as an umbilical hernia. Such a protrusion can significantly decrease in size or disappear altogether if the person is in a horizontal position. More often, umbilical hernia is diagnosed in women.
Causes of umbilical hernia
The disease in question is acquired, provoked by the divergence of muscle fibers along the white line of the abdomen - this condition can appear for various reasons.
According to statistics, the following factors can provoke an umbilical hernia:
- chronic;
- pregnancy;
- tumors of a malignant and/or benign nature in the abdominal cavity, characterized by rapid growth;
- excessive physical activity;
- ascites.
These conditions lead to weakening of the muscular and ligamentous apparatus - holding the abdominal organs in a normal position becomes almost impossible and they protrude through the umbilical ring. It is noteworthy that the size of the hernia can be completely different - from 1 to 20 cm or even more.
Note:in most cases, the umbilical ring for the disease in question expands by no more than 10 cm, everything else is considered an exception. If the hernia is small, then the omentum protrudes through the umbilical ring, but if the hernia is large enough, then both the omentum and the intestinal loops protrude through the ring.
Some experts suggest that umbilical hernia in adults has a genetic predisposition. However, such a theory has not been proven, so whether to take it seriously or not is a “purely voluntary” matter.

Symptoms of an umbilical hernia
An umbilical hernia can have intense and somewhat blurred symptoms - this depends on several factors:
- are there any adhesions in the abdominal cavity;
- general health of the patient;
- size of the umbilical hernia;
- whether there is strangulation of the hernial sac.
At the very beginning of the development of the disease in question, the patient does not experience any inconvenience, constraint or pain at all. The only thing that immediately attracts attention is a small protrusion in the navel area, but they do not attach any importance to this - the protrusion does not bother and disappears as soon as the patient takes a horizontal position, and pregnant ladies even take it as a feature of their condition.
In some cases, the omentum protrudes so strongly that it blocks the umbilical ring. Such a hernia never changes in size, and the disease itself occurs without pronounced symptoms.
Note:if the omentum begins to pass through the expanded muscles, then the hernia greatly increases in size and is characterized by severe manifestations.
If the disease in question progresses, then adhesions begin to form in the abdominal cavity - this prevents the reduction of the hernial sac. In this case, any movement, tension, or straining leads to intestinal dysfunction. The patient begins to complain of chronic constipation and constantly present nausea, regardless of the time of eating. This condition is especially severe in women during pregnancy and with existing obesity - a growing belly puts pressure on the muscles of the abdominal wall, which provokes a deterioration in the patient’s condition.
Possible complications
No matter how long the disease in question develops, it can lead to the development of the following complications:
- hernia inflammation;
- stagnation of feces in the large intestine;
 Of course, such complications are not necessary - many patients live with an umbilical hernia for years and do not worry about it, but you need to be prepared for any development of events. Most often, strangulation of the hernial sac is recorded - a rather serious complication. Firstly, this condition provokes a cessation of blood circulation in the strangulated organ (omentum or intestinal loop), its tissues simply die. Secondly, strangulation of the hernial sac is always accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process in the omentum, peritoneum or intestines. Thirdly, if the peritoneal tissue is infringed, the patient develops acute pain.
Of course, such complications are not necessary - many patients live with an umbilical hernia for years and do not worry about it, but you need to be prepared for any development of events. Most often, strangulation of the hernial sac is recorded - a rather serious complication. Firstly, this condition provokes a cessation of blood circulation in the strangulated organ (omentum or intestinal loop), its tissues simply die. Secondly, strangulation of the hernial sac is always accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process in the omentum, peritoneum or intestines. Thirdly, if the peritoneal tissue is infringed, the patient develops acute pain.
Incarceration of an umbilical hernia occurs even with minor physical exertion - for example, when coughing, after sneezing, laughing, or against the background of chronic constipation. It is noteworthy that the type of complication in question always begins acutely, suddenly and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the patient experiences acute, powerful pain in the navel area;
- the hernial sac becomes hot and tense to the touch, it is impossible to reduce it;
- Nausea, vomiting, headache, increased body temperature rapidly develop - all signs of general intoxication of the body.
Note:the appearance of signs of strangulation of the hernial sac is a reason to immediately seek professional medical help. Usually, surgical treatment is performed in this condition, but only a specialist can determine the specific methods and scope of procedures.
Treatment of umbilical hernia
First of all, you need to understand which doctor to contact if you suspect an umbilical hernia. Such a specialist is a surgeon - he will conduct the necessary examinations and make an accurate diagnosis. But you will also need a consultation with a gastroenterologist and nutritionist - these specialists will help you get rid of chronic constipation and excess weight.
 The only method of effective treatment of umbilical hernia in medicine is surgical intervention. Yes, there is a lot of information on the therapeutic treatment of the disease in question - the hernia is reduced. But you need to understand that such measures in almost 100% of cases lead to the development of complications.
The only method of effective treatment of umbilical hernia in medicine is surgical intervention. Yes, there is a lot of information on the therapeutic treatment of the disease in question - the hernia is reduced. But you need to understand that such measures in almost 100% of cases lead to the development of complications.
Before the doctor prescribes surgical treatment for an umbilical hernia, the patient will have to undergo a full examination - treatment may be postponed if heart failure is diagnosed, during pregnancy, or against the background of exacerbated chronic diseases. If there are no interfering factors, then the specialist will offer the patient several methods of surgical treatment of the disease in question:
- Tension hernioplasty. In this case, plastic surgery is performed using the Mayo and Sapezhko method, using only local tissue. The surgeon sutures the umbilical ring in two layers in two directions (transverse and vertical). If a patient is diagnosed with obesity, then during surgery the specialist removes excess fatty tissue.
Disadvantages of tension hernioplasty - the rehabilitation period is long, there is no guarantee that a recurrence of the umbilical hernia will not occur.
- Plastic surgery with mesh implants. The surgeon uses “patches” in his work - special materials that are inert to the internal tissues of the human body. This mesh is placed above or below the umbilical ring and can even be used in the treatment of large hernias. According to statistics, it is plastic surgery with mesh implants that is characterized by a short recovery period and a low percentage of the likelihood of relapses (within 1%).
Note:These two methods of surgical treatment of umbilical hernia can be performed either with classical penetration into the abdominal cavity or using laparoscopy. Local anesthesia is used for pain relief, but if surgery is performed in the classical way, the patient is given general anesthesia.
Recovery after surgery
Of course, a lot depends on the general condition of the patient, on how professionally the operation was performed. But as a rule, doctors’ recommendations during the recovery period boil down to the following:
- on the same day, almost immediately after surgery, the patient is allowed to get out of bed;
- you need to wear a special bandage - it will reduce the pressure on the seam;
- on the second and subsequent days, physical activity should gradually increase;
- The duration of use of a special bandage will be determined only by a doctor - this device cannot be removed without his permission;
- after 10-15 days the patient is allowed to go for short runs and do simple exercises as part of exercise;
- The patient is allowed to lift heavy objects or any kind of forceful exercise only 30 days after surgery, even if the laparoscopic method of surgical treatment was used.
How to treat an umbilical hernia in pregnant women
According to statistics, the pathology in question is most often diagnosed in women during pregnancy. But this does not mean that doctors will prescribe surgical treatment - stress and drugs used for anesthesia are unlikely to have a beneficial effect on the intrauterine development of the fetus. What to do for pregnant women diagnosed with an umbilical hernia:

It is believed that the optimal time for surgical treatment of an umbilical hernia will be 6-8 months after birth. By the way, during his work, the surgeon can eliminate defects in the abdominal wall that formed during pregnancy (for example, stretch marks), and excess fatty tissue.
To prevent the development of the condition in question, clear preventive measures must be followed. These include:
- abdominal muscle training – you can do abdominal exercises every day, which will lead to building and strengthening muscle mass;
- – obesity is one of the causes of umbilical hernia, so you need to promptly adjust your diet and lifestyle when you discover extra pounds;
- refusal to lift weights and excessive physical activity - naturally, this does not apply to professional athletes;
- During the period of bearing a child, wearing a special bandage should be mandatory.

In this article:
The displacement of some internal organs in the abdominal cavity beyond the navel ring leads to the diagnosis of an umbilical hernia in a newborn. This pathology occurs in every fifth baby born as a result of a normal pregnancy and childbirth, and in every third baby who was born prematurely.
Umbilical hernia, diagnosed in infants, is the most common surgical disease in the 1st year of a child’s life. It is worth noting that minor defects of the umbilical ring are observed in almost all newborns.
The structure of the umbilical hernia
It is important for parents to understand what an umbilical hernia is if it is found in an infant. In the central part of the abdomen is the umbilical ring, consisting of ligaments. It was thanks to him that during pregnancy the child received nutrition and oxygen through the mother’s umbilical cord. After childbirth, the umbilical cord is ligated, its vessels should normally tighten, and the ring itself should close and heal with connective tissue.
If this does not happen, the internal organs (usually the omentum and intestinal loops) begin to protrude through it from the inside. A similar situation can occur in a mother: if the umbilical ring stretches and weakens during pregnancy, a hernia after or usual is guaranteed.
After birth, all children have a weak and not completely overgrown umbilical ring, so minor visual signs of an umbilical hernia in a newborn will be noticeable. But in most children, this condition quickly and independently goes away within 1 month, while others are diagnosed and prescribed the necessary treatment to prevent strangulation of the umbilical hernia in newborns.
Causes
The main reasons that result in an umbilical hernia in a baby are associated with anatomically weak tissues in the navel area. But if there are predisposing factors, the disease develops more often.
These include:
- infant deficiency at birth;
- genetic predisposition;
- frequent conditions during which intra-abdominal pressure increases (crying, etc.);
- weak muscle tone, characteristic of rickets;
- gender: umbilical hernia in newborn boys is diagnosed less often than among girls .
Many parents believe that the disease is preceded by improper ligation of the child's umbilical cord immediately after birth. This is just a myth, since this action cannot in any way affect the weakness of the muscles and the expansion of the umbilical ring.

Anatomical features
There are two types of hernia in infants - congenital and acquired.
Congenital pathology develops as a result of the anatomical features of the child’s body. Some children are born with connective tissue dysplasia. The muscles and tissues of the umbilical ring and abdominal wall in such children are also weak. Therefore, newborns develop an umbilical hernia, which requires treatment.
An acquired hernia is formed against the background of frequent tension in the abdominal wall, when the internal organs are affected by increased intra-abdominal pressure. In this case, compliance with preventive measures will help get rid of the expected development of an umbilical hernia in newborns.
Reasons for prolonged non-closure of the umbilical ring
If a child cries for a long time and often, suffers from constipation and bloating, his tummy is in constant tension. The same condition often occurs in infants when it is summer outside and the baby reacts to the heat with severe anxiety. Increased intra-abdominal pressure prevents the normal contraction of the umbilical ring, which means that loops of intestine or omentum may end up in it. In this case, young parents can see what an umbilical hernia looks like in newborns with the naked eye.
To prevent this, it is necessary to pay more attention to the child and prevent prolonged crying. At the first signs of protrusion, treatment should not be carried out at home, especially using a spell that does not have a healing effect. If you have signs of the disease, you should inform your doctor, who will give appropriate recommendations.
Symptoms
An umbilical hernia in infants is detected as early as 1 month of life. A navel that sticks out forward is visible to the naked eye, however, in some babies it is just an anatomical feature called a “cutaneous navel.” In order not to confuse this condition with a true disease, parents should be aware of umbilical hernia in infants.
So, the symptoms of a navel hernia in a child will be as follows:
- a rounded protrusion in the area of the umbilical ring, easily retractable, its diameter varies between 1-10 cm;
- when the baby is relaxed, the pathology is most often invisible, but as soon as the abdominal wall is strained, the disease returns again;
- the child is restless, weather sensitive;
- The hernia itself does not cause pain in a child, but is often accompanied by flatulence, which leads to unnecessary anxiety in the baby.
If, against the background of this disease, severe bloating, pain, general weakness, nausea and vomiting occur, most likely we are talking about a complication of an umbilical hernia in infants - coprostasis. In this case, there is an accumulation of feces in the intestines, which causes serious discomfort to the child. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.

How to determine the presence of an umbilical hernia?
Externally, the navel looks enlarged, and when the baby cries, it becomes even larger. When pressed, it goes inside the abdominal cavity, and a specific gurgling sound appears. Based on these signs, the mother herself can determine the presence of a hernia in the baby.
The final diagnosis is made by a pediatrician or surgeon during an examination of the child. If the situation is advanced, additional diagnostic methods are prescribed - radiography, ultrasound, herniography, which are necessary before surgical treatment.
Treatment
An umbilical hernia in a newborn requires mandatory treatment under the supervision of a physician. When choosing a tactic, the specialist takes the size and symptoms of an umbilical hernia in infants as a basis. If the protrusion is more than 2 cm, surgery is necessary. The doctor may also suggest massage, wearing a bandage and an umbilical hernia patch for newborns. How to treat an umbilical hernia?
Massage
If the pathology is mild, the specialist will offer observation and will not rush into surgical treatment. A simple procedure for umbilical hernia in newborns, performed by a professional, gives good results.
Movements during the procedure should be light, without physical effort or pressure in the following directions:
- clockwise;
- counter;
- along the oblique muscles.
These movements must be supplemented by rubbing the abdomen and gentle pinching around the umbilical ring. Also during the massage you should perform light soothing strokes.
Laying on the tummy
Prevention and treatment of umbilical hernia in newborns can be practiced in this simple way. Pediatricians recommend placing the baby on a hard surface on his stomach a quarter of an hour before feeding. Once in this position, the baby will be active, moving all parts of the body. At the same time, intra-abdominal pressure is noticeably reduced due to the removal of gases. Systematic placement on the tummy strengthens the muscles of the abdominal wall.

Surgery
Surgery for umbilical hernia in newborns is performed for the following indications:
- increase in size of protrusion (in children from 1 year);
- strangulated hernia;
- Diagnosis persistence for up to 5 years.
The main goal of the operation is to remove the defect of the umbilical ring. The method is called hernioplasty. The doctor excises the hernial sac, sutures and strengthens the hernial orifice, returning the internal organs to the abdominal cavity. The operation lasts no more than half an hour. On the same day, if there are no complications, the child can return home.
Traditional methods
Among the popular folk methods for treating umbilical hernia in infants, a conspiracy stands out. Our ancestors believed that this pathology appears in children due to the influence of evil forces. The technique is as follows: after the child wakes up, the mother needs to lightly bite the protrusion on her stomach and say the following spell: “Hernia, I’m gnawing on you, you have one tooth, and I have all seven, I’ll eat you.” Read the plot three times, each time spitting over your left shoulder.
Whether or not to believe that treatment of an umbilical hernia in newborns using this method will work is up to everyone. But it is better to entrust the child’s health to professionals.
An umbilical hernia bandage for newborns is also used. This is a belt made of natural elastic fabric. The product strengthens the abdominal muscles, promoting the healing of the umbilical ring. It is put on in the morning, after first setting the hernial sac into the abdominal cavity, and worn throughout the day.
You can also purchase an umbilical hernia patch for newborns, which is sold at the pharmacy. A wide band of plaster fixes the abdominal wall, allowing the protrusion to be reduced. The patch is changed every 10 days. It is better to entrust the procedure of gluing the patch to a doctor.

Pinching
If the umbilical hernia of a newborn is pinched, it is necessary to urgently go to the hospital. This condition is a complication of this disease - the internal organs trapped in the umbilical ring are blocked in it as a result of spasm. The blood vessels of the intestine are under pressure, no blood flows into them, and the child’s condition deteriorates sharply.
Apart from surgery, nothing can help with a pinched hernia. Fortunately, this complication is very rare.
Prevention
Proper care of the baby and implementation of preventive measures can prevent the development of an umbilical hernia in a child under 1 year of age, even if there is a predisposition to this disease.
So, what should be the prevention:
- keeping it with the mother allows children to avoid digestive problems in the 1st year of life, namely constipation, flatulence,;
- a nursing mother must observe, avoiding foods that cause flatulence in the child (grapes, beans, cabbage, etc.);
- You should not allow your child to cry for a long time and often; you need to protect him from colds, since crying and coughing increase intra-abdominal pressure, and therefore can aggravate the symptoms of an umbilical hernia in newborns.
Despite the fact that this disease is in fact easily curable, the lack of preventive measures and the basic ignorance of parents about what an umbilical hernia looks like in newborns, what to do and how to treat this condition can cause serious consequences. The most dangerous of them is pinching of the hernial sac and the organs that were in it at that time. Without the necessary treatment, this condition can result in necrosis and peritonitis, which is life-threatening to the child.
Useful video about umbilical hernia