2.1 Scheme of statistical research
Systems of statistical data analysis are a modern effective tool of statistical research. Extensive opportunities for processing statistical data have special statistical analysis systems, as well as universal funds - Excel, Matlab, Mathcad and more.
But even the most advanced tool cannot replace the researcher, which should formulate the purpose of the study, collect data, select methods, approaches, models and means of processing and data analysis, as well as interpret the results obtained.
Figure 2.1 presents the scheme of a statistical study.
Fig.2.1 - Concept of statistical research
The source point of statistical research is the wording of the problem. When it is determined, the purpose of the study is taken into account, it is determined which information is necessary and how it will be used when deciding.
Statistical research itself begins with the preparatory stage. During the preparatory stage, analysts are studying technical task - The document compiled by the customer of the study. In terms of technical specifications, research objectives should be clearly formulated:
the object of the study is determined;
the assumptions and hypotheses are listed, which during the study must be confirmed or refuted;
described how the results of the study will be used;
dates in which the study should be conducted and the study budget.
Based on the technical task being developed structure of an analytical report - then in any form The results of the study must be presented, as well as program of statistical observation. The program is a list of features subject to registration in the surveillance process (or questions that reliable answers must be obtained for each observation unit). The content of the program is defined as the features of the observed object and the objectives of the study and methods selected by analysts for further processing of the collected information.
The main stage of statistical research includes the collection of the necessary data and their analysis.
The final stage of the study is to prepare an analytical report and the provision of its customer.
In fig. 2.2 presents a diagram of statistical data analysis.

Fig.2.2 - The main stages of statistical analysis
2.2 Collection of statistical information
Collection of materials implies an analysis of the technical task of the study, the definition of sources of the necessary information and (if necessary) the development of a questionnaire. When studying sources of information, all required data is divided into primary(data that is not available and which should be collected directly for this study), and secondary (collected earlier for other purposes).
The collection of secondary data is often referred to as the "Cabinet" or "library" study.
Examples of primary data collection: observations of store visitors, questioning hospital patients, discussion problems at a meeting.
Secondary data is divided into internal and external.
Examples of sources of internal secondary data:
an information system of the organization (including an accounting subsystem, sales management subsystem, CRM (CRM system, reduction from English. Customer Relationship Management) - Application software for organizations intended to automate customer interaction strategies) and others);
previous studies;
written reports of employees.
Examples of sources of external secondary data:
reports of statistical and other government agencies;
reports of marketing agencies, professional associations, etc.;
electronic databases (address reference books, GIS, etc.);
libraries;
media.
The main output data at the data collection phase are:
planned sampling;
sampling structure (presence and size of quotas);
type of statistical observation (collecting data survey, questionnaire, measurement, experiment, examination, etc.);
information on the parameters of the survey (for example, the possibility of falsifying the questionnaire);
scheme of encoding variables in the program database selected for processing;
plan diagram of data conversion;
plan diagram of used statistical procedures.
The same stage includes directly the survey procedure. Of course, the questionnaires are developed only for obtaining primary information.
The data obtained must be appropriately edited and prepared. Each questionnaire or form of observation is checked and, if necessary, is adjusted. Each response is assigned numeric or alphabetic codes - information encoding is made. Data preparation includes editing, decoding and verification of data, encoding them and necessary transformations.
2.3 Definition of Sampling Characteristics
As a rule, the data collected as a result of statistical observation for statistical analysis are a selective set. The sequence of data conversion into the process of statistical research can be schematically represented as follows (Fig. 2.3)
Figure 2.3 Statistical Transformation Scheme
Analyzing the sample, you can draw conclusions about the general population represented by the sample.
Final definition of general sampling parameters Produce when all the questionnaires are collected. It includes:
determining the actual number of respondents
determination of the sampling structure
distribution at the survey location,
establishment of the confidence level of the statistical reliability of the sample,
calculation of the statistical error and determination of the representativeness of the sample.
Real number The respondents can be a large or smaller planned. The first option is better for analysis, but is unprofitable to customer research. The second may adversely affect the quality of the study, and, therefore, it is unprofitable to analysts or customers.
Sampling structure It may be random or non-random (respondents were selected on the basis of a predetermined criterion, for example, the quota method). Random samples of a priori are representative. The non-random samples can intend to be unrequentative relative to the general population, but to give important information for research. In this case, it should also be carefully taken to filter issues of the questionnaires that are intended specifically to screen unsuitable for the requirements of respondents.
For Definition of accuracy estimationFirst of all, it is necessary to set the level of trust probability (95% or 99%). Then the maximum statistical error samples calculated as
 or
or  ,
,
where  - sampling volume
- sampling volume  - the probability of the onset of the investigated event (the respondent's hit to the sample),
- the probability of the onset of the investigated event (the respondent's hit to the sample),  - the probability of a reverse event (non-payment of the respondent in the sample),
- the probability of a reverse event (non-payment of the respondent in the sample),  - trust probability ratio
- trust probability ratio  - dispersion of a sign.
- dispersion of a sign.
Table 2.4 shows the most consumed values \u200b\u200bof the trust probability and trust probability coefficients.
Table 2.4.
2.5 Data Processing on Computer
Analysis of data using a computer includes the execution of a number of necessary steps.
1. Determining the structure of the source data.
2. Entering data into the computer in accordance with their structure and requirements of the program. Editing and data conversion.
3. Setting data processing method according to research tasks.
4. Obtaining data processing. Its editing and saving in the desired format.
5. Interpretation of the processing result.
Steps 1 (preparatory) and 5 (final) is not capable of performing any computer program - their researcher does himself. Steps 2-4 are performed by a researcher using the program, but it is the researcher who determines the necessary procedures for editing and converting data, data processing methods, as well as the format for presenting the processing results. Computer help (steps 2-4) lies, ultimately, in the transition from the long sequence of numbers to more compact. At the "Login" of the computer, the researcher submits an array of source data that is not available to understanding, but is suitable for computer processing (step 2). The researcher then gives the program to the data processing command in accordance with the task and the data structure (step 3). At the "output", it receives the result of processing (step 4) - also an array of data, only smaller, accessible to understanding and meaningful interpretation. At the same time, an exhaustive data analysis usually requires multiple processing them using different methods.
2.6 Choosing Data Analysis Strategy
The choice of a strategy for analyzing the collected data is based on the knowledge of theoretical and practical aspects of the subject area under study, the specifics and known characteristics of information, the properties of specific statistical methods, as well as on the experience and views of the researcher.
It must be remembered that the analysis of the data is not the ultimate goal of the study. His goal is to get information that will help solve a certain problem and accept adequate management decisions. The choice of analysis strategy should begin with the study of the results of the previous steps of the process: determining the problem and developing a research plan. As a "draft" uses a preliminary analysis plan, developed as one of the elements of the research plan. Then, during the receipt at the subsequent stages of the process of studying additional information, it may be necessary to make certain changes.
Statistical methods are divided into single and multidimensional. One-dimensional methods (univariatetechniques) are used when all sample elements are estimated by one indicator, or if there are several of these indicators for each element, but each variable is analyzed at the same time separately from all others.
Multidimensional Methods (Multivariate Techniques) are well suited for data analysis, if two or more indicators are used to evaluate each element of the sample, and these variables are analyzed simultaneously. Such methods are used to determine dependencies between phenomena.
Multidimensional methods differ from one-dimensional primarily by the fact that when they use their use, the focus is shifted from levels (averages) and distributions (dispersions) of phenomena and focuses on the degree of relationship (correlation or covariance) between these phenomena.
One-dimensional methods can be classified based on what data is analyzed: metric or nonmetric (Fig. 3). Metric data (METRIC DATA) is measured by interval or relative scale. Nonmetric Data (Nonmetric Data) is estimated on a nominal or flat scale
In addition, these methods are divided into classes based on how many samples are one, two or more - analyzed during the studies.
The classification of one-dimensional statistical methods is presented in Fig.2.4.

Fig. 2.4 Classification of one-dimensional statistical methods depending on the analyzed data
The number of samples is determined by how work is underway with data for a specific analysis, and not how data was collected. For example, data on male and female people can be obtained within one sample, but if their analysis is aimed at identifying the difference in perception based on the difference in floors, the researcher will have to operate in two different samples. The samples are considered independent if they are experimentally connected with each other. Measurements conducted in one sample do not affect the values \u200b\u200bof the variables in another. For analysis, data relating to different groups of respondents, for example collected from female and male, are usually processed as independent samples.
On the other hand, if the data in two samples relate to the same group of respondents, the samples are considered combined into pairs - dependent.
If there is only one sample of metric data, Z- and T-criteria can be used. If there are two or more independent samples, in the first case, you can use the Z- and T-criterion for two samples, in the second - method of single-factor dispersion analysis. For two connected samples, a pair T-criterion is used. If we are talking about non-metric data in one sample, the researcher can use the criteria of the frequency distribution, chi-square, the criterion of Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K ~ S), the criterion of the series and the binomial criterion. For two independent samples with nonethender data, it is possible to resort to the following methods of analysis: chi-square, manna-white, medians, K-C, with single-factor dispersion analysis of Crooked Wallis (yes K-y). Unlike this, if there are two or more interrelated samples, the criteria of signs, Mak-Nemara and Wilcoxon should be used.
Multidimensional statistical methods are aimed at identifying existing patterns: the interdependence of variables, relationships or sequences of events, intersective resemblance.
It is enough to distinguish five standard types of patterns, the study of which is essential: association, sequence, classification, clustering and forecasting
The association takes place if several events are associated with each other. For example, a survey conducted in the supermarket may show that 65% of the Coca-Clause bought corn chips also take, and if there is a discount for such a kit, the Kola is acquired in 85% of cases. Having information about such an association, managers are easy to assess how effective the discount provided.
If there is a chain of events associated in time, then they talk about the sequence. For example, after buying a house in 45% of cases, a new kitchen stove is purchased within a month, and within two weeks, 60% of the newcomers are seized with a refrigerator.
With the help of the classification, features characterizing the group to which one or another object belongs to. This is done by analyzing already classified objects and the formulation of a certain set of rules.
Clustering is different from the classification by the fact that the groups themselves are not specified in advance. Using clustering, various homogeneous data groups are distinguished.
The basis for all sorts of prediction systems is the historical information stored in the form of temporary series. If you manage to build a regularity, adequately reflecting the dynamics of the behavior of targets, there is a chance that you can predict the behavior of the system in the future.
Multidimensional statistical methods can be divided into interconnection analysis methods and classification analysis (Fig. 2.5).

Fig.2.5 - Classification of multidimensional statistical methods
Statistical Study (SI) Allows you to get an idea of \u200b\u200bone or another phenomenon, study its size, level, identify patterns. The subject can be the health of the population, the organization of medical care, the factors of the external environment affecting health and so on.
When conducting C can be used 2 methodical approaches:
1) study of the intensity of the phenomenon in the medium, the prevalence of the phenomenon, the identification of the state of health of the population - are carried out on the general aggregates or quite large in the number of selective sets, allowing to obtain intensive indicators and reasonably transfer the data to the entire General Aggursement
2) carrying out strictly planned studies on the study of individual factors without identifying the intensity of the phenomenon in the medium - are carried out, as a rule, on small in numbers in numbers in order to identify new factors, studying unknown or little-known causal relationships
Stages of statistical research:
Stage 1. Drawing up a plan and research program - It is preparatory, it is determined by the purpose and objectives of the study, the plan and the research program is drawn up, the program of the statistical material report is developed and organizational issues are being developed.
A) the purpose and objectives of the study should be clearly formulated; The goal determines the main direction of the study and wears, as a rule, not only theoretical, but also practical, it is formulated clearly, clearly, unequivocally; For the disclosure of the goal, the objectives of the study are determined.
B) It is necessary to learn the literature on this topic.
C) need to develop Organizational plan - Provides definitions 1) Places (administrative-territorial observation boundaries), 2) time (specific timing of the monitoring, development and analysis of material) and 3) Student research (organizers, performers, methodological and organizational management, sources of research financing).
D) Development Research Plan - Includes definition:
- object of research (statistical aggregate);
- the scope of the study (solid, unpaid);
- species (current, one-time);
- methods for collecting statistical information.
D) need to be Research Program (Observations) - Includes:
- determination of a unit of observation;
- List of questions (accounting signs) subject to registration for each observation unit
- development of an individual accounting (registration) form with a list of issues and signs subject to accounting;
- Development of table layouts in which the results of the study are then entered.
A separate form is filled with each unit of observation, it contains a passport part, clearly formulated, supplied in a specific sequence of the program and the date of filling out the document. As accounting forms, medical institutions are used in the practice of medical and preventive institutions.
Sources of obtaining information can serve as other medical documents (medical history, and individual cards of outpatient patient, child development history, childbirth history), reporting forms of medical and preventive institutions, etc.
To ensure the possibility of a statistical data development of these documents, it makes a drawing of information on specially designed accounting forms, the content of which is determined in each individual case in accordance with the objectives of the study.
Currently, in connection with the machine processing of observation results using computer, the program questions may be formalized , When questions in the accounting document are put in the form of an alternative (yes, no) , Or are offered ready-made answers from which you should choose a specific answer.
E) It is necessary to make a program of a summary of the data obtained, which includes the establishment of the principles of grouping, the allocation of grouping signs , Determining the combinations of these features, drawing up statistical layouts.
Stage 2. Material Collection (statistical observation) - - It is to register individual cases of the studied phenomenon and characterizing their accounting signs into registration forms. Before and during the implementation of this work, instructions (oral or written) observation performers are carried out, providing them with registration forms.
Statistical observation can be:
BUT ) in time:
1) Current - The phenomenon is studied for some separate period of time (week, quarter , Year, etc.) by everyday registration of the phenomenon as each case occurs (taking into account the number of born , Died, sick crude , Discharged from the hospital). Thus are taken into account rapidly changing phenomena.
2) One-time - Statistical data are collected on a certain (critical) point in time (population census, study of the physical development of children, preventive inspections of the population). One-time registration reflects the state of the phenomenon at the time of study, is used to study slowly changing phenomena.
The choice of type of observation in time is determined by the purpose and objectives of the study (the characteristic of hospitalized patients can be obtained as a result of the current registration of retired from the hospital - the current observation or by a one-day census of patients in the hospital - one-time observation).
B) depending on the completeness of the coverage of the phenomenon:
1) Solid - all part of the observation unit included in the aggregate are studied, i.e., the general population. It is carried out in order to establish the absolute sizes of the phenomenon (total population, the total number of born or dead). It also applies in cases where information is necessary for operational work (accounting for infectious morbidity, the load of doctors, etc.)
2) Unbless - Only part of the general aggregate is studied, it is divided into several species:
1. Monographic method - gives a detailed description of individual units of aggregate characteristic of any respect and deep, comprehensive description of objects.
2. Method of the main massif - involves the study of those objects in which a significant majority of observation units are concentrated. The disadvantage of this method is that the part of the totality remains a non-engaged study, although a small size, but which can differ significantly from the main array.
3. Ankrug method - This is a collection of statistical data using a specially developed questionnaire addressed to a certain circle of persons. This study is based on the principle of voluntaryness, so the questionnaire is often incomplete. Often the answers to the questions are imprinting subjectivity and chance. This method is used to obtain an approximate characteristic of the phenomenon under study.
4. Selective method - The most common method is reduced to the study of some specially selected part of the observation units to characterize the entire general population. The advantage of this method is to obtain a high degree of reliability, as well as a significantly lower cost. The study employs less than performers , In addition, it requires smaller time spending. In medical statistics, the role and place of the sample method is especially great, since medical workers have a matter of usually only with part of the studied phenomenon (study a group of patients with one or another disease, analyze the work of individual units).
C) according to the method of obtaining information during the implementation and nature of its implementation
1. Direct observation (Clinical examination of patients , Conducting laboratory , Tool Research , Anthropometric measurements, etc.)
2. Sociological methods: Interview method (full-time survey), questionnaire (permanent survey - anonymous or non-anonymous), etc.;
3. Documentary research (Catching information from accounting and reporting medical documents, information of official statistics of institutions and organizations.)
3 stage. Material Development, Statistical Grouping and Summary- Begins with checking and clarifying the number of observations , Fullness and correct information , Identifying and eliminating errors, duplicate records, etc.
To properly develop material applied Encryption of primary accounting documents, That is, the designation of each character and its group is familiar with alphabet or digital. Encryption is a technical technique. , Facilitating and accelerating material development , Improving quality, development accuracy. CIFRES - CONDITIONAL SUBBOTS - are produced arbitrarily. When encrypted diagnoses, it is recommended to use the International Nomenclature and Classification of Diseases; With the encryption of professions - profession in the dictionary.
The advantage of encryption is that, if necessary, after the end of the main development, you can return to the material for development in order to clarify new links and dependencies. Encrypted accounting material allows you to make it easier and faster , The unencrypted. After checking, a grouping of signs is carried out.
Grouping - Dismemberment of the totality of data under study for homogeneous , Typical groups in the most essential features. The grouping can be carried out according to quality and quantitative features. The choice of a grouping feature depends on the nature of the common aggregate and objectives of the study.
BUT) Typology grouping produced by quality (descriptive, attribute) features (gender , Profession, group diseases)
B) Variational grouping (in quantitative features) is carried out on the basis of the numerical dimensions of the trait (age , Duration of the disease, the duration of treatment, etc.). Quantitative grouping requires a solution to the issue of the magnitude of the grouping interval: the interval may be equal, and in some cases - unequal, even to include the so-called open groups (open groups can be determined when grouping by age: up to 1 year, 50 years and older).
When determining the number of groups, research is based on the purpose and objectives. It is necessary that the groupings can open the patterns of the phenomenon under study. A large number of groups can lead to excessive crushing of material, unnecessary detail. A small number of groups leads to the simplicity of characteristic features.
Having finished grouping material, proceed to Summary - generalization of isolated cases , Received as a result of a statistical study, in certain groups, their calculation and the introduction of tables in layouts.
A summary of statistical material is carried out using statistical tables. Table , Not filled with numbers , Called Mockup.
Statistical tables are lugged , Chronological, territorial.
The table has to be both faithful. Statistical subjects are usually located along the horizontal lines on the left side of the table and reflects the main, the main feature. Statistical faithful placed from left to right along vertical graphs and reflects additional accounting.
Statistical tables are divided into:
BUT) Simple - presented numerical distribution of material on one basis , Components of it. A simple table contains usually a simple list or result over the entire totality of the phenomenon under study.
B) Group - presented a combination of two signs in connection with each other
IN) Combinational - the distribution of material in three and more interconnected features is given.
During tables, certain requirements must be complied with:
- each table must have a title reflecting its content;
- Inside the table, all graphs must also have clear brief names;
- When filling out the table, all table cells must contain the corresponding numeric data. The remaining blanks due to the lack of this combination of the table cells are firing ("-"), and in the absence of information in the cell is affixed with "n. S." or "…";
- After filling the table in the lower horizontal row and in the last right, the vertical column is summed up by the vertical graph and horizontal rows.
- Tables must have a single serial numbering.
In studies with a small volume of observations, the summary is carried out manually. All accounting documents are laid out into groups in accordance with the cipher of the feature. The following is calculated and recorded data into the appropriate table of the table. Currently, the computers and summary of the material are widely used. . Which allow not only to sort the material on the studied signs , But perform calculations of indicators.
4 stage. Statistical analysis of the studied phenomenon, formulation of conclusions - Responsible Stage of the study on which the calculation of statistical indicators is calculated (frequencies , Structures , The average sizes of the studied phenomenon), their graphic image is given. , The speaker is studied , Trends, set links between phenomena . Forecasts are given, etc. Analysis involves the interpretation of the data obtained, an assessment of the reliability of the research results. In conclusion, conclusions are made.
5 stage. Literary processing and registration of results - It is concluding, suggests the final registration of the results of a statistical study. Results can be decorated in the form of an article, report, report , Dissertations and others. For each type of registration there are certain requirements , Which must be respected in the literary processing of the results of a statistical study.
The results of medical and statistical research are being implemented in health care practice. Various options for using research results are possible: familiarization with the results of a wide audience of medical and scientists; preparation of guidance and methodological documents; Registration of rationalization offers and others
Upon completion of statistical research, recommendations and management decisions are developed, the implementation of the research results are being implemented, effectiveness is estimated.
In statistical research, the most important element is observing strict sequence in the implementation of these stages.
To obtain an idea of \u200b\u200bone or another phenomenon, draw conclusions, it is necessary to conduct a statistical study. The subject of statistical research in health care and medicine may be the health of the population, the organization of medical care, various sections of the activities of medical and preventive institutions, the factors of the external environment affecting the state of health.
The methodological sequence of the statistical study is made up of certain stages.
Stage 1. Drawing up a plan and research program.
Stage 2. Material collection (statistical observation).
3 stage. Material Development, Statistical Grouping and Summary
4 stage. Statistical analysis of the studied phenomenon, formulation of conclusions.
5 stage. Literary processing and registration of the results obtained.
Upon completion of statistical research, recommendations and management decisions are developed, the implementation of the research results are being implemented, effectiveness is estimated.
In statistical research, the most important element is observing strict sequence in the implementation of these stages.
First stage Statistical research - drawing up the plan and program - is the preparatory on which the purpose and objective objectives are determined, the plan and the research program is drawn up, the statistical report program is being developed and organizational issues are being developed.
Starting a statistical study should accurately and clearly formulate the purpose and objectives of the study, study on this topic the literature.
The goal determines the main direction of the study and is, as a rule, not only theoretical, but also practical. The goal is clearly formulated, clearly, unequivocally.
For the disclosure of the goal, the objectives of the study are determined.
An important point of the preparatory stage is the development of the organizational plan. The organizational plan of the study provides for the definition of a place (administrative and territorial borders of the observation), time (specific timing of monitoring, the development and analysis of material) and the subject of the study (organizers, performers, methodological and organizational management, sources of financing research).
PLbut h Islad. oVbut niaincludes:
Determination of the object of the study (statistical aggregate);
The volume of research (solid, unpaid);
Species (current, one-time);
Methods for collecting statistical information. Research programincludes:
Definition of observation unit;
List of questions (accounting) to be registered with respect to each observation unit *
Development of an individual accounting (registration) form with a list of issues and signs subject to accounting;
Development of table layouts in which the results of the study are then entered.
A separate form is filled with each unit of observation, it contains a passport part, clearly formulated, supplied in a specific sequence of the program and the date of filling out the document.
As accounting forms, medical institutions are used in the practice of medical and preventive institutions.
Sources of obtaining information can serve as other medical documents (medical history, and individual cards of outpatient patient, child development history, childbirth history), reporting forms of medical and preventive institutions, etc.
To ensure the possibility of a statistical data development of these documents, it makes a drawing of information on specially designed accounting forms, the content of which is determined in each individual case in accordance with the objectives of the study.
Currently, in connection with the machine processing of observation results using computer, the program questions may be formalized , when questions in the accounting document are put in the form of an alternative (yes, no) , or are offered ready-made answers from which you should choose a specific answer.
At the first stage of statistical research, along with the observation program, programs are drawn up * summary data reports, which includes the establishment of the principles of grouping, the allocation of grouping signs , determining the combinations of these features, drawing up statistical layouts.
Second phase - Collection of statistical material (statistical observation) - is to register individual cases of studied phenomenon and characterizing their accounting signs into registration forms. Before and during the implementation of this work, instructions (oral or written) observation performers are carried out, providing them with registration forms.
By time, statistical observation may be current and one-time.
For current Nabelyu deniathe phenomenon is studied for some separate period of time (week, quarter , year, etc.) through every day registration of the phenomenon as each case occurs. An example of current observation is the account of the number of born , died, sick crude , disposable from the hospital, etc. So the rapidly changing phenomena are taken into account.
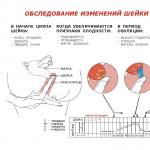
For one-time Nabelyu deniastatistics are collected on a certain (critical) moment of time. One-time observation is: a census of the population, the study of the physical development of children, accounting for hospital beds for the horses of the year, certification of medical and preventive institutions, etc. To this type of preventive examinations of the population. One-time registration reflects the state of the phenomenon at the time of study. This type of observation is used to explore slowly changing phenomena.
The choice of the type of observation in time is determined by the purpose and objectives of the study. For example, the characteristic of hospitalized patients can be obtained as a result of the current registration of retired from the hospital (current observation) or by a one-day census of patients in the hospital (one-time observation).
Depending on the completeness of the coverage of the studied phenomenon, they distinguish a solid and unpaid study.
For solidthe study studies all those part of the monitoring unit, i.e. General population. A continuous study is carried out in order to establish absolute sizes of phenomena, for example, the total population, the total number of born or dead, the total number of cases with one or another disease, etc. The solid method is also applied in cases where the information is necessary for operational work (accounting for infectious incidence. , load doctors, etc.)
For unblessthe study is studied only part of the general population. It is divided into several types: a questionnaire, monographic, main array, selective. The most common in medical studies is the selective method.
Monographic method - gives a detailed description of individual units of aggregate characteristic of any respect and deep, comprehensive description of objects.
Method of the main massif - involves the study of those objects in which a significant majority of observation units are concentrated. The disadvantage of this method is that the part of the totality remains a non-engaged study, although a small size, but which can differ significantly from the main array.
Ankrug method - This is a collection of statistical data using a specially developed questionnaire addressed to a certain circle of persons. This study is based on the principle of voluntaryness, so the questionnaire is often incomplete. Often the answers to the questions are imprinting subjectivity and chance. This method is used to obtain an approximate characteristic of the phenomenon under study.
Selective method - It comes down to the study of some specially selected part of the observation units for the characteristics of the entire general population. The advantage of this method is to obtain a high degree of reliability, as well as a significantly lower cost. The study employs less than performers , in addition, it requires smaller time spending.
In medical statistics, the role and place of the sample method is especially great, since medical workers deal usually only with part of the phenomenon under study: study a group of patients with one disease, analyzes the work of individual divisions and medical institutions. , assess the quality of certain events, etc.
By the method of obtaining information during the statistical observation and the nature of its implementation, several types are distinguished:
1) direct observation(Clinical examination of patients , conducting laboratory , tool Research , anthropometric measurements, etc.)
2) sociological methods: Interview method (full-time survey), questionnaire (permanent survey - anonymous or non-anonymous), etc.;
3) documentary researchbut nie(Catching information from accounting and reporting medical documents, information of official statistics of institutions and organizations.)
Third stage - grouping and a summary of the material - begins with checking and clarifying the number of observations , fullness and correct information , identifying and eliminating errors, duplicate records, etc.
Encryption of primary accounting documents , those. The designation of each character and its group is familiar with alphabet or digital. Encryption is a technical technique. , facilitating and accelerating material development , improving quality, development accuracy. CIFRES - CONDITIONAL SUBBOTS - are produced arbitrarily. When encrypted diagnoses, it is recommended to use the International Nomenclature and Classification of Diseases; With the encryption of professions - profession in the dictionary.
The advantage of encryption is that, if necessary, after the end of the main development, you can return to the material for development in order to clarify new links and dependencies. Encrypted accounting material allows you to make it easier and faster , the unencrypted. After checking, a grouping of signs is carried out.
Grouping- dismemberment of the totality of the data studied for homogeneous , typical groups in the most essential features. The grouping can be carried out according to quality and quantitative features. The choice of a grouping feature depends on the nature of the common aggregate and objectives of the study.
The typological group is made according to high-quality (descriptive, attribute) features, for example, on the floor , professions, disease groups, severity of the disease, postoperative complications, etc.
The grouping on quantitative (variational) features is carried out on the basis of the numerical dimensions of the feature , eg , by age , duration of the disease, duration of treatment, etc. Quantitative grouping requires a solution to the issue of the magnitude of the grouping interval: the interval may be equal, and in some cases unequal, even include the so-called open groups.
for example , under age grouping, open groups can be identified: up to 1 year . 50 years old and older.
When determining the number of groups, research is based on the purpose and objectives. It is necessary that the groupings can open the patterns of the phenomenon under study. A large number of groups can lead to excessive crushing of material, unnecessary detail. A small number of groups leads to the simplicity of characteristic features.
Having finished grouping material, proceed to the summary.
FROM vodka- generalization of isolated cases , received as a result of a statistical study, in certain groups, their calculation and the introduction of tables in layouts.
A summary of statistical material is carried out using statistical tables. Table , not filled with numbers , called layout.
Statistical tables are lugged , chronological, territorial.
The table has to be both faithful. Statistical subjects are usually located along the horizontal lines on the left side of the table and reflects the main, the main feature. Statistical faithful placed from left to right along vertical graphs and reflects additional accounting.
Statistical tables are divided into simple , group and combinational.
IN simple tablesthe numeric distribution of the material on one basis is presented. , compound parts of it (Table 1). A simple table contains usually a simple list or result over the entire totality of the phenomenon under study.
Table 1
Distribution of the dead in the hospital N. by age
IN group tablesa combination of two signs is presented in connection with each other (Table 2).
table 2
Distribution of dead in the hospital N. on the floor and age
IN combinbut q.about tablesthe distribution of material in three and more interconnected features (Table 3) is given.
Table 3.
Distribution of the dead in the hospital N. with different diseases by age and sex
| Diagnosis of the main disease | Age | ||||||||||||
| 0-14 | 15-19 | 20-39 | 40-59 | 60 and \u003e. | Total | ||||||||
| M. | J. | M. | J. | M. | J. | M. | J. | M. | J. | M. | J. | M + J. | |
| Diseases of the system of blood. | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Injuries and poisoning | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| Calm. new things. | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| Other bel. | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| All ill. | - | - |
When drawing up tables, certain requirements must be followed:
Each table must have a title reflecting its content;
Inside the table, all graphs must also have clear brief names;
When filling out the table, all table cells must contain appropriate numeric data. The remaining blanks due to the lack of this combination of the cell cells are firing ("-"), and in the absence of information in the cell, "N.S." is affixed or "...";
After filling the table in the bottom horizontal row and in the last right, the vertical column is summed up by the vertical graph and horizontal rows.
Tables must have a single sequential numbering.
In studies with a small volume of observations, the summary is carried out manually. All accounting documents are laid out into groups in accordance with the cipher of the feature. The following is calculated and recorded data into the appropriate table of the table.
Currently, the computers and summary of the material are widely used. . which allow not only to sort the material on the studied signs , but perform calculations of indicators.
Fourth stage - Statistical analysis - is the responsible stage of the study. At this stage, the calculation of statistical indicators (frequencies , structures , the average sizes of the studied phenomenon), their graphic image is given. , the speaker is studied , trends, set links between phenomena . prognoses are given, etc. An analysis involves the interpretation of the data obtained, assess the reliability of the results of the study. In conclusion, conclusions are made.
Fifth stage - Literary processing is the final. It implies the final design of the results of a statistical study. Results can be decorated in the form of an article, report, report , dissertations and others. For each type of registration there are certain requirements , which must be respected in the literary processing of the results of a statistical study.
The results of medical and statistical research are being implemented in health care practice. Various options for using research results are possible: familiarization with the results of a wide audience of medical and scientists; preparation of guidance and methodological documents; Registration of rationalization offers and others.
The quantitative characteristics of socio-economic processes in direct communication with their qualitative essence in the system of social production is impossible without a deep statistical research. The use of various methods and techniques of the statistical methodology involves the presence of exhaustive and reliable information about the object being studied. The study of mass social phenomena includes the stages of collecting statistical information and its primary processing, information and grouping of observation results into certain combustion, generalizations and analysis of the materials obtained.
At the first stage of statistical studies, primary statistical data is formed, or source statistical information, which is the foundation of the future statistical building. So that the building was durable, good and high-quality should be its basis. If an error or material was assumed to collect primary statistical data, it turned out poorly, it will affect the correctness and accuracy of both theoretical and practical conclusions. Therefore, statistical observation from the initial to the final stage is to obtain the final materials - should be carefully thought out and clearly organized.
Statistical observation gives the source material for generalization, the beginning of which is a summary. If, with statistical observation of each unit, they receive maintenance characterizing it from many sides, then these reports characterize the entire statistical set and separately part of it. At this stage, the aggregate is divided by the differences and combines the signs of similarities, the total indicators in groups and in general are calculated. Using the grouping method, the studied phenomena are divided into essential types, characteristic groups and subgroups for essential features. Using groups, limit qualitatively homogeneous substantially aggregate, which is a prerequisite for determining and applying summarizing indicators.
At the final stage of analysis, with the help of generalizing indicators, relative and average values \u200b\u200bare calculated, the consolidated assessment of the characterization of the signs is given, the dynamics of phenomena are characterized, indices, balance constructions are used. The indicators characterizing the tightness of the ties in the change of signs are calculated. In order to the most rational and visual presentation of the digital material, it is presented in the form of tables and graphs.
The concept of statistical observation
Stat. The study consists of 3 main stages:
1. Stat. Observation
2. Primary processing, summary and grouping of observation results
3. Analysis of the received summary results
The monitoring process includes a trace. Stages:
1. Preparation of observation
2. Conducting a mass collection of data
3. Preparation of data for automated processing and processing
4. Development of proposals for improving the stot observation
It should be noted that from completeness and quality collected in the process of observation of the material depends on the results of the analysis and quality.
15. Methodological issues of the organization stat. Observations.
Stat. Observation should be started with an accurate wording of its goals and specific tasks. Next are determined:
Object and Unit Observation
The program is being developed
Selects the view and method of observation
Under the object statch. Observations are understood by some. Stat-I aggregate in which the studied social system proceeds. Phenomena and processes
(N: Watch - p / p
Persons living on ODA. territory
Students, leisure. in universities)
Unit Navel. It is called an integral part of the objects of observation of the Yavl-Ca by the bearer of the signs to be registered (No. Department, P / P, Dep. Students, people)
The units of observation from reporting units under the cat should be distinguished. Understand the subjects, the presence of info on the unit of observation (often these concepts coincide)
The observation program is a list of questions on which information is collected or a list of features and indicators of subject to registration.
The observation program is drawn up in the form of a statistical form, form, questionnaire, questionnaire or census, etc., where primary research is entered.
A key issue in organizing the observation of the Yavl. The question of the place and time of it is, it depends mainly on the purpose of the study.
Choosing a Place of the NAMP. Tasks and objectives of the study (as Sovko-Ti want data to be obtained, according to and investigate)
The choice of time is closed in the ODR-II of the observation period and the critical moment of the NAM.
The observation period is the time during which registration must be carried out.
Critical date of observation is the date, as of which information is reported.
The critical moment is the moment of time, as of which the observed facts are registered.
Their differences are explained and often in the recruit period. It will continue to continue during this time. Those or other changes in the aggregate can occur. It must be reflected on others. Therefore, the results recruit. Fixir-Xia as of a critical moment. The following changes in the case in the future do not teach it.
The critical moment is like an instant photo of a picture of the population (or the study of Scoop)
As a rule, the critical moment is tested to the initial date of work.
Forms, types, methods Stat. Observations
Forms.
1. Stat. Reporting is such an organizing form at which the units of Navel-I predictive information about its deet-ti in the form of the formulations, the regulant of the device.
The peculiarity of the reporting of the COST is that it is obliged - but justified, the obligations-on performed and JUR-KI is confirmed by the signature of the head or responsible person.
2. Specially organized observation is the brightest and simple example of this form of the Navel-I. census. The census is usually carried out at equal intervals, simultaneously on the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe territory at the same time.
The Russian statistical censuses are held by the population of individual species of P / P and Org-Qii, Mother resources, perennial plantings, construction NZ objects, etc.
4. Register form of observation is based on the conduct of the state register. In the register of each Unit Nabe Har-Sm is a number of indicators. In domestic statistical practice, the registers of us and the registers of P / P received the laborer.
Registration of the population - is conducted by the registry offices
Registration of P / P - EGRPO Ved.Org. statistics.
Views.
you can smash the following groups. Signs:
a) by registration time
b) on the coverage of units of owl
By time reg. they are:
Current (continued)
Interrupted (periodic and one-time)
With tech. Nat. Changing phenomena and processes is fixed as they arrive (registration of birth, death, marriage, divorce, etc.)
Periodic. Nat. Conducted through ODA. Time intervals (N Population Census every 10 years)
One-line. Nat. It is carried out either not regularly or only once (referendum)
By coverage. Sovie Stat-e navel. There are:
Solid
Unbless
Solid recruit. It is a survey of all units of owl
Disabled. It suggests that only a part of the studies of the owl is subject to.
It is a few kinds of unbless name:
Method OSN. Massiva
Selective (independently)
Monographic
This method is X-Xia by the fact that the most creatures are usually selected, usually the largest units. owl in the cat. Social ones. Part of all recruitations.
When monographic recruit-and-acting en. We are deposited. units. The studies of the owl or m. or typical for this owl unit. Or a preferred new species of phenomena.
MNGROM-E NAP. It is carried out in order to identify either the emerging trends in the development of this phenomenon.
Methods
Direct recruit
Documentary NAM.
Immediately called. Such a call. with a cat. The registrars themselves by the restraint, counting, deterrenced, the fact that is subject to register and on this basis make entry in the form.
Documentary method. Based on the OK-AI as sources of infection of the Split-x docks as a rule of accounting X-RA (i.e. stat. reporting)
Survey is a way of conviction with a cat. The necessary information is obtained by the respondent (i.e. responded) (oral, correspondent, questionnaire, uncertain, etc.)
The result of the first stage of statistical research - statistical observation is the information characterizing each unit of a statistical aggregate. However, the ability to reflect the patterns and trends in the dynamics of studied phenomena with the help of even the most complete characteristics of single facts are limited. Such data is obtained only as a result of a statistical report. Summary is an ordering, systematization and generalization of statistical data obtained during statistical observation. Only the proper processing of statistical material makes it possible to identify the essence of socio-economic phenomena, characteristic features and essential features of individual types, detect patterns and trends in their development. There are a summary of a simple and group, or a summary in a narrow and wide understanding. A simple summary is counting common results in groups and subgroups and the design of this material in the table. As a result, a simple report of statistical data can be determined by the number of enterprises, the total number of personnel, the volume of manufactured products in monetary terms. These general results are mainly informative. They give a generalized characteristic of a totality in the form of absolute values.
A group summary, or a summary of a wide understanding, is a complex process for multilateral processing of primary statistical data, i.e. Data obtained as a result of observation. It includes a grouping of statistical data, the development of a system of indicators for the characteristics of groups, counting group and general outcome, the calculation of generalizing indicators. The task of a statistical summary as the second stage of statistical research is to obtain generalizing indicators for information and reference and analytical purposes. A summary of mass statistical data is carried out according to a previously developed program and plan. In the process of developing the program, the subject and leaky reports are determined. This is the object of the study, dissected on groups and subgroups. Taken - indicators that characterize the subject to reports. The report program is determined by the tasks of statistical research.
The statistical summary is performed according to a predetermined plan. In terms of summary, questions are resolved about how to carry out information on the generalization of information - manually or by a mechanized manner, about the sequence of individual reports. The timing of the execution of each stage and the summary as a whole, as well as the methods of presenting the results of the summary are set. These can be distribution rows, statistical tables and statistical graphs.