Content:
The main types of vitamin D. Where is it found. The daily norm, the danger of deficiency and excess. Instructions for use.
Even in the Middle Ages, doctors were convinced that problems with rickets were solved by taking fish oil. At the same time, medieval healers did not know which element plays the main role in restoring the body. Only hundreds of years later, vitamin D was discovered, which will be discussed in the article.
What are the characteristics of this substance? What effect does it have on the body? We will also consider the consequences of vitamin D deficiency, instructions for use and a number of other issues.
Varieties
Studies have shown that vitamin D is synthesized under the action of UV rays in plant tissues and living organisms. In this case, the substance is represented by a group that includes:
- ergocalciferol (D2);
- cholecalciferol (D3);
- 22,23-dihydro-erogalciferol (D4);
- 24-ethylcholecalciferol (D5);
- 22-dihydroethylcalciferol (D6).
Of the above elements, only two vitamins are most widely used: D2 and D3. Today, it is these substances that have found application in medicine and are actively prescribed in the treatment (prevention) of diseases.
Cholecalciferol is different in that it is synthesized under the influence of sunlight and comes with food. With ergocalciferol, the story is different - the body receives it only with food. 
Indications for use
Additional intake of vitamin D is required for a disease such as rickets, when signs of a deficiency of the substance appear, or in case of slow development of the joints. It is also prescribed for the following problems:
- joint diseases;
- bone fractures;
- osteoporosis;
- problems with the absorption of phosphorus and calcium;
- lupus erythematosus;
- inflammation of the bone marrow;
- tetany;
- spasmophilia;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- chronic gastritis and enteritis;
- tuberculosis and so on.
In medical practice, vitamin D3 capsules are often prescribed for a number of related diseases - hypoparathyroidism, enterocolitis and others.
It is worth knowing that the appointment of the drug in all the cases described above is possible only after the examination. Only a doctor should determine the dosage and make recommendations regarding the use of the supplement..
Contraindications
Despite the versatility of the action, the intake of the considered elements can carry risks for the body. Doctors prohibit taking ergocalciferol or cholecalciferol in the following cases:
- hypervitaminosis;
- hypercalcemia;
- calcium nephrourolithiasis;
- excessive sensitivity and others.
In some cases, doctors prescribe the supplement with caution, namely:
- with heart failure;
- with atherosclerosis;
- with renal failure;
- with pulmonary tuberculosis;
- in the presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys.
Vitamin D3 is not always useful for adult women during pregnancy and while breastfeeding. 
Dosage
To avoid deficiency, it is worth considering the dosage requirements. So, the daily norm of D2 or D3 is 10 mcg. If a person during the day is in the sun with a bare torso for at least 3-5 hours, then the body receives the full amount of the beneficial substance. Otherwise, it is recommended to saturate the diet with D-containing foods or take additional drugs.
In international terms, the IU parameter is accepted, which corresponds to 0.025 mg of a substance. Accordingly, 1 μg is equal to 40 IU, and daily dosage - 400 IU. At the same time, the needs of the body differ depending on a number of factors - the country of residence, age, purpose of destination, and so on.
Most often, the substance is prescribed in the following dosages:
- prevention of rickets - 620 IU per day;
- premature babies - 1250 IU;
- newborn baby - 300 IU;
- during pregnancy - 600 IU.
It is worth considering that when prescribing a vitamin for the treatment of various diseases, the dosage increases:
- with osteoporosis - 1300-3000 IU;
- in the treatment of rickets - 1200-5000 IU;
- with hypoparathyroidism - 10-20 thousand IU;
- with osteomalacia - 1200-3200 IU.

The body's needs for the substance in question also increase in the presence of the following factors:
- insufficient exposure to the sun;
- living in regions with polluted air;
- vegetarianism, diet abuse;
- poor sleep, work at night;
- living in the northern regions;
- dark skin;
- intestinal upset (associated with poor digestibility).
Only a doctor can tell adults and children how to take vitamin D correctly. When making a verdict, he focuses on the factors mentioned above and determines the method of administration - tablets, capsules or oil solution.
Where is it contained?
Vitamin D enters the body with many foods. Main sources:
- fish fat;
- sprats in oil;
- kidneys and liver (pork, beef);
- mushrooms;
- some vegetables and fruits.
It is worth remembering that the main supplier - skin that synthesizes the vitamin under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.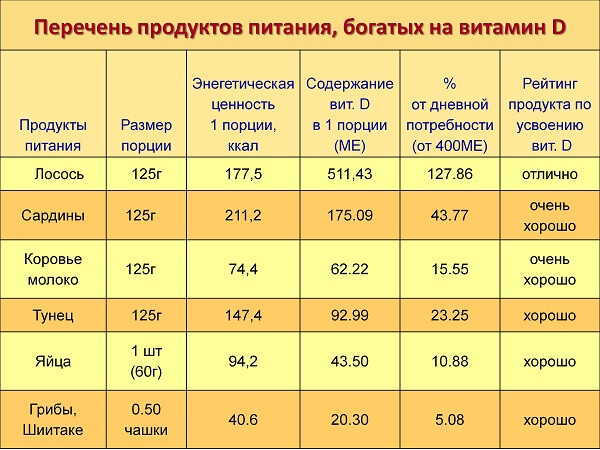
What is the danger of deficiency and excess?
Many begin the course without knowing how to take vitamin D correctly. This approach is fraught with various consequences for the body due to an excess or lack of a substance.
Deficiency symptoms are as follows:
- weakening of skeletal muscles;
- decreased calcium levels in vital body fluids;
- osteomalacia, which is characterized by a decrease in the level of phosphorus in the body.
An overdose is also dangerous, which manifests itself:
- muscle tremor;
- difficulty breathing;
- headache;
- skin itching;
- general weakness;
- loss of appetite;
- stool problems;
- jumps in blood pressure;
- vomiting and so on.



