Unfortunately for doctors, the need for constant health care has not been formed in the minds of our compatriots. More often, when signs of illness appear, people think that the symptoms will disappear on their own, nothing will happen to them, and the disease will recede. It will go by itself. There are probably many reasons for this behavior. But here's what it leads to, reflects the dry language of statistics. Kazan doctors conducted a study of the causes of death in strokes.
Stroke kills a lot of people
The results were horrendous:
- Half of stroke patients are admitted to the hospital more than 6 hours after onset. What is 6 hours in ordinary life? Even for sleep is not enough. But not to save the life of the patient. This gap is called the "therapeutic window". The time at which treatment gives the maximum result and allows you to save a person from disability or save his life.
- More than half of these patients are not hospitalized! Not because they are rejected. They do not go to the hospital or refuse hospitalization offered by emergency doctors. Mortality in this group is 97%.
What can be done so as not to replenish the dry statistical lines of mortality in stroke with your life? Just to understand at what signs of a change in well-being it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. So to speak, to recognize the enemy in the face.
What is a stroke and what are the types of stroke?
The word "stroke" refers to acute interruptions in the blood supply to the brain, which develop according to the ischemic (reduction or absence of blood circulation) or hemorrhagic (hemorrhage) type. For cerebral ischemia, another short-term condition called a transient ischemic attack is distinguished. Learn more about each of these states.
Strokes are divided into 2 large groups: ischemic and hemorrhagic
Transient ischemic attack
A microstroke or transient ischemic attack is an acute transient disturbance of the blood supply to a small part of the brain that does not cause irreversible changes in the cells. But this condition is not as harmless as it might seem. In people who have undergone a TIA, in 20% of cases a full stroke develops a week later, in another 45% in the first year after the attack. This is a call that you need to be more careful about yourself, and urgently call a doctor as soon as they appear:
- Changes in sensation in the face or limbs: numbness or tingling sensation on the skin.
- Restriction of movements.
- Difficulties in understanding the speech of other people.
- Partial loss of hearing, touch or vision.
- Double vision.
- Dizziness.
- There may be a disorder of coordination of movements, gait.
- Loss of speech.
- Clouding of consciousness or short fainting.
In this case, call the doctor immediately! Despite the transience of TIA, timely examination and treatment can prevent a life-threatening condition.
Ischemic stroke
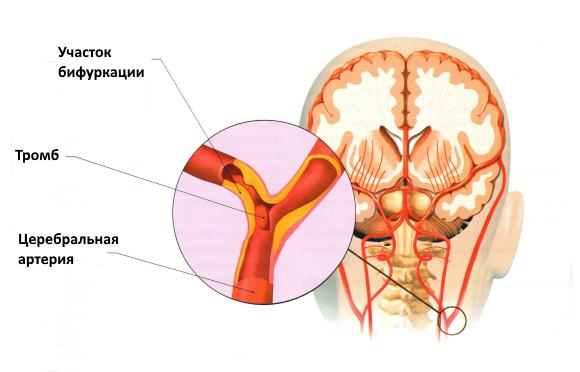
Ischemic stroke due to vascular thrombosis
#3 cause of death in the world. A disease that changes a person forever. Deprives him of speech, movements, the ability to think. A condition that confines a person to bed for months. And despite this, people continue to hope for "maybe". Say to yourself: "maybe it will pass." During ischemia, part of the neurocytes ceases to receive oxygen. If you do not return them the opportunity to "breathe", they die.
And it is possible to prevent the death of brain cells in the first 6 hours from the onset of ischemia.
It is only necessary to deliver the patient to the hospital as soon as possible. Signs of cerebral ischemia:
- There are speech disorders, difficulties in intelligible pronunciation of words.
- Violent headache, sometimes accompanied by vomiting.
- Asymmetry of the face: the corner of the mouth or eye is lowered on one side, the smile is crooked.
- Muscular weakness of the leg and arm on one side. Trying to raise both arms at the same time may fail.
- Clouding of consciousness, loss of orientation, fainting.
These symptoms signal the development of ischemia. A person needs urgent help:
- Call an ambulance. It is better to say by phone what happened, because there are specialized “stroke” teams at the stations.
- Be sure to help him lie down. Even on the floor, even on the table. Doesn't matter. The main ˗ horizontal position.
- Do not try to bring the patient back to consciousness. Doctors will take care of this.
If measures are taken to start treatment quickly, the chances of regaining health after an illness reach 50%. Not just to survive, but to restore the ability to live actively.
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhages in the brain occur 4 times less often than ischemia. Only the prognosis for their outcome is much worse. Apoplexies end in death in 45% of people in the first week from the onset of the stroke. A condition that is not worth treating on its own or waiting for it to go away on its own. The insidiousness of hemorrhages lies in the fact that the blood pouring from the vessels remains inside the skull and compresses the brain. The signs of hemorrhage are joined by symptoms of secondary ischemia from exposure to the spilled blood. Signs of apoplexy:
- The condition develops unexpectedly, against the background of high emotional or physical stress.
- May be accompanied by a rush of blood to the face.
- The head starts to hurt badly.
- Consciousness becomes confused.
- Nausea appears, vomiting may develop.
- Sometimes there are seizures.
First aid in this case is the same as for cerebral ischemia:
- Put the person down.
- Call an ambulance.



