What it is? A stroke is an acute violation of cerebral circulation, leading to persistent focal damage to the brain. May be ischemic or hemorrhagic. Pathology is accompanied by an acute violation of cerebral circulation, damage to blood vessels and the central nervous system. If the normal blood flow is disturbed, the nutrition of the nerve cells of the brain worsens, and this is very dangerous, since the organ works due to the constant supply of oxygen and glucose to it.
Let's look at what signs are characteristic of a stroke, why it is important to help a person in the first minutes of the onset of symptoms, and also what are the possible consequences of this condition.
What is a stroke?
A stroke is an acute violation of the blood circulation of the brain, causing damage and death of nerve cells.
During " therapeutic window”(conditionally called the first 3-6 hours after a stroke), it is possible to prevent the irreversible consequences of ischemia and cell death by medical manipulations.
Strokes occur in people in a wide age range: from 20-25 years to old age.
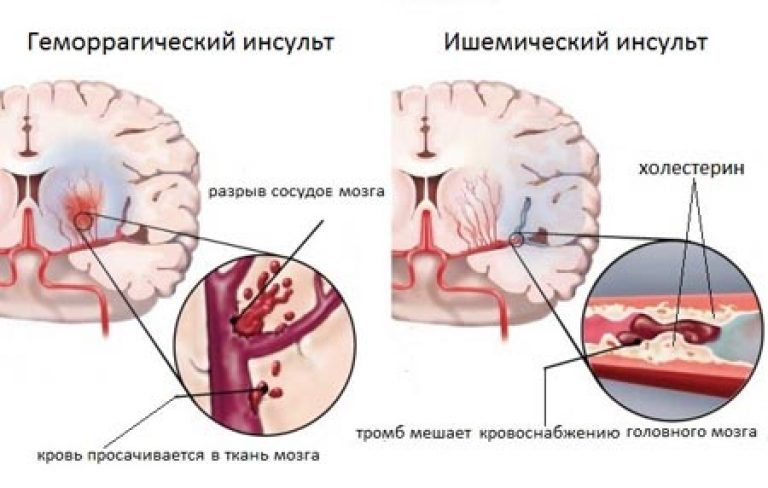
- Narrowing or blockage of blood vessels in the brain - ischemic stroke;
- Hemorrhages in the brain or in its membranes - hemorrhagic stroke.
The frequency is quite high, with age it increases significantly. Mortality (mortality) from stroke remains very high. Treatment is aimed at restoring the functional activity of neurons, reducing the influence of causative factors and preventing the re-development of vascular catastrophe in the body. After a stroke, it is very important to rehabilitate a person.
Every person needs to know the signs of the disease in order to respond in time to a brain catastrophe and call an ambulance team for themselves or their loved ones. Knowing the basic symptoms can save someone's life.
Kinds
There are 2 main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. They have a fundamentally different mechanism of development and require radically different approaches to treatment. Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes account for 80% and 20%, respectively, of the total population.
Ischemic stroke
Ischemic brain damage occurs in 8 cases out of 10. Mostly it affects the elderly, after 60 years, more often men. The main reason is the blockage of blood vessels or their prolonged spasm, which entails a cessation of blood supply and oxygen starvation. This leads to the death of brain cells.
This type of disease can develop more often at night or in the morning. There is also a connection with a previous increased emotional (stress factor) or physical activity, alcohol consumption, blood loss, or the progression of an infectious process or somatic disease.
Hemorrhagic stroke
What is this? Hemorrhagic stroke is the result of hemorrhage into the substance of the brain after damage to the walls of the vessel. Violation of functional activity and death of neurocytes in this case mainly occurs due to their compression by a hematoma.
The occurrence of hemorrhagic stroke is associated mainly with diffuse or isolated cerebral vascular pathology, due to which the vascular wall loses its elasticity and becomes thinner.
Often accompanied by loss of consciousness, more rapid development of stroke symptoms, always significant neurological disorders. This is due to the fact that in this case the cerebral circulation is disturbed due to rupture of the vascular wall with an outpouring of blood and the formation of a hematoma or as a result of impregnation of the nervous tissue with blood.
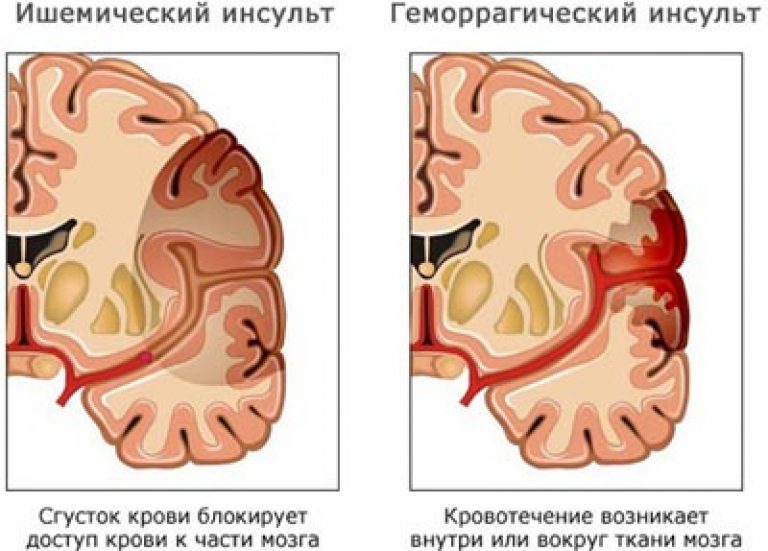
In 5% of stroke cases it is not possible to determine the type and mechanism of development. Regardless of the type of stroke, its consequences are always the same - a sharp, rapidly developing dysfunction of a part of the brain due to the death of part of its neurocyte cells.
The first signs of a stroke in an adult
Signs of a stroke should be known to all people, regardless of their medical education. These symptoms are primarily associated with a violation of the innervation of the muscles of the head and body, so if you suspect a stroke, ask the person to perform three simple actions: smile, raise their hands, say any word or sentence.
In a person who suddenly felt "lightheaded", vascular problems can be assumed by the following signs, which can be taken as the first signs of a stroke:
- Numbness of body parts (face, limbs);
- Headache;
- Loss of control over the environment;
- Double vision and other visual disturbances;
- Nausea, vomiting, dizziness;
- Motor and sensory disorders.
It happens that a stroke occurs suddenly, but more often it occurs against the background of precursors. For example, in half of the cases, ischemic stroke is preceded by.
If at least two of the following symptoms recur once a week or more often in the last three months, then an immediate visit to a doctor is required:
- Headache that does not have a specific localization and occurs with overwork or weather disasters.
- Vertigo at rest and aggravated by movement.
- The presence of tinnitus, both permanent and transient.
- "Dips" of memory for the events of the current period of time.
- Changes in the intensity of working capacity and sleep disturbances.
These symptoms should be considered as harbingers of the development of a stroke.
How to recognize a stroke?
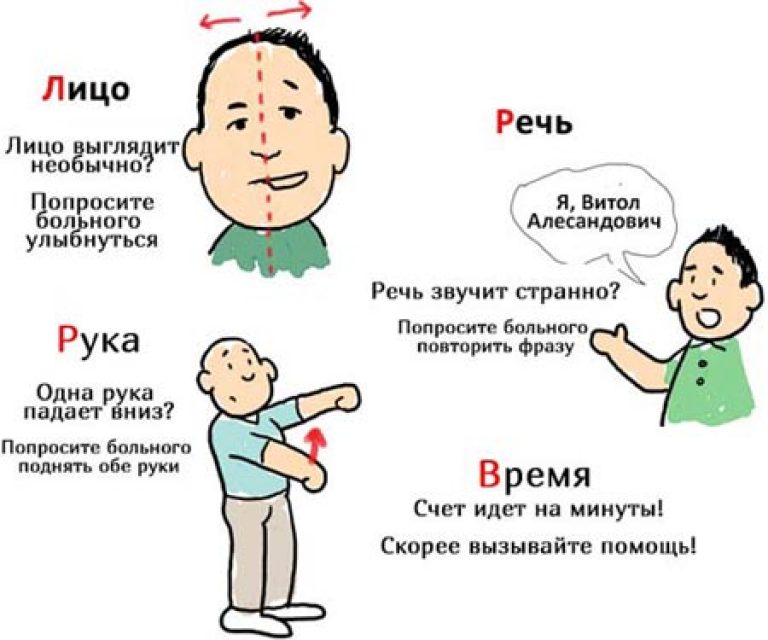
To recognize this disease, pay attention to the following points:
- Take a closer look, ask if the person needs help. A person can refuse, because. I still don't understand what is happening to him. The speech of a person with a stroke will be difficult.
- Ask for a smile if the corners of the lips are located on a different line and the smile looks strange - this is a symptom of a stroke.
- Shake the person's hand if there was a stroke, then the handshake will be weak. You can also ask to raise your hands up. One arm will spontaneously drop.
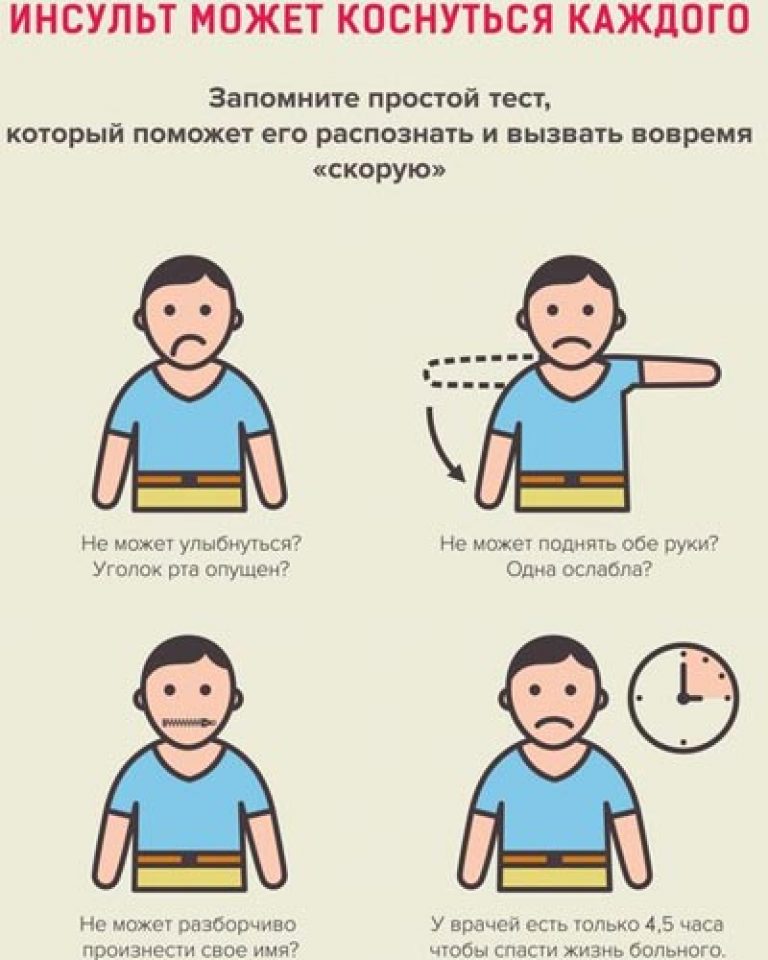
When detecting signs of a stroke in a person urgently call an ambulance!!! The sooner qualified assistance is provided, the greater the chances of eliminating the consequences of this disease!!!
Causes
Doctors identify two main causes of stroke. This is the occurrence of blood clots in the circulatory system and the presence of cholesterol plaques that can block blood vessels. An attack can happen in a healthy person, but this probability is extremely small.
Pathology develops as a complication of the underlying disease of the heart and blood vessels, as well as under the influence of adverse factors:
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- thromboembolism;
- hypertension ( arterial);
- rheumatic affections of the heart;
- myocardial infarction;
- heart surgery;
- constant stress;
- vascular tumors;
- taking certain types of drugs;
- alcoholism;
- smoking;
- cerebral artery aneurysm.
The development of complications is also possible against the background of general well-being, however, often the failure of compensation mechanisms occurs in cases where the load on the vessels exceeds a certain critical level. Such situations can be associated with everyday life, with the presence of various diseases, with external circumstances:
- a sharp transition from a lying position to a standing position (sometimes it is enough to go into a sitting position);
- dense food;
- hot bath;
- hot season;
- increased physical and mental stress;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure (most often under the influence of drugs).
But the most common cause of a stroke is high blood pressure, 7 out of 10 victims of hemorrhage are people with (pressure above 140 over 90), a violation of the heart. Even a harmless atrial fibrillation causes the formation of blood clots, which lead to impaired blood flow.
Stroke Symptoms
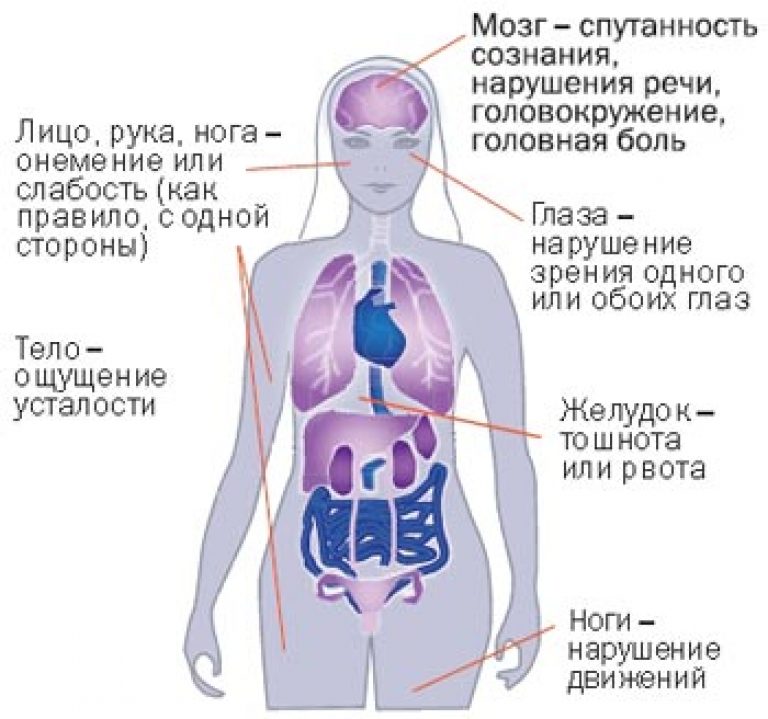
The clinical manifestations of a stroke depend on its type, location and size of the lesion.
Symptoms of a stroke in adults:
- Signs of an impending stroke begin with headaches and dizziness that are not explained by other causes. Possible loss of consciousness.
- The loss of the ability to clearly express one's thoughts in words is one of the characteristic symptoms. A person cannot say anything specific or even repeat a simple phrase.
- The patient may begin to vomit, as well as with a concussion.
- Noise in the head.
- Forgetfulness appears, a person does not know or does not remember where he was going, why he needs the objects that he holds in his hands. Outwardly, this is manifested by absent-mindedness and confusion.
- Visually, the symptoms of circulatory disorders in the brain are visible on the face of a person. The patient cannot smile, the face is distorted, possibly cannot close the eyelid.
There are seven main symptoms before a stroke, which accurately indicate this disease:
- Distorted face (asymmetric smile, slanted eye).
- Incoherent speech.
- Drowsiness (apathy).
- Focal sharp pains in the head and face.
- Violation of vision.
- Paralysis of the limbs.
- Impaired coordination.
Signs of an impending stroke can be very diverse, so you should be extremely careful about what symptoms a person has before a stroke.
| Symptoms in adults | |
| Ischemic stroke | The most pronounced symptoms of ischemic stroke are observed with embolism or thromboembolism of the large arteries of the brain. It is typical for him:
In addition, during an ischemic attack, the swallowing reflex and speech may worsen in a person. Therefore, the patient may begin to stutter, not speak clearly. Due to damage to the spinal (vertebral) column, the patient may develop a lack of coordination, so he will not be able to move independently or even sit. |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | The first signs of a stroke (hemorrhagic type):
|
It is worth considering that if there are signs of a stroke, then the time of irreversible changes in the brain has already begun its countdown. Those 3-6 hours that are available for the restoration of impaired blood circulation and the struggle to reduce the affected area are decreasing every minute.
If the symptoms of a stroke completely disappear within 24 hours from the onset of its clinical manifestations, then this is not a stroke, but a transient cerebrovascular accident (transient ischemic attack or hypertensive cerebral crisis).
First aid
With a stroke, cerebral hemorrhage requires an immediate response to its occurrence, therefore, after the onset of the first symptoms, the following steps must be performed:
- Position the patient in such a way that his head is raised by about 30 °.
- If the patient has lost consciousness and is on the floor, move him to a more comfortable position.
- If the patient has prerequisites for vomiting, turn his head to the side so that the vomit does not enter the respiratory system.
- It is necessary to understand how the pulse and blood pressure of a sick person changes. If possible, you need to check these indicators and remember them.
- When the ambulance arrives, the doctors need to indicate how the problems began, how much worse the patient felt and looked, and what pills he took.
- move a person or shift him to a bed (it is better to leave him where the attack occurred);
- use ammonia to bring the patient to consciousness;
- force to hold the limbs in the event of convulsions;
- give the patient medicines in tablets or capsules that can get stuck in the airways (especially if he has a swallowing disorder).
Consequences
The most typical problems that arise after a stroke include the following:
- Weakness or paralysis of the limbs. Paralysis of one half of the body is most often manifested. The immobilization can be complete or partial.
- Spasticity of muscles. The limb is held in one position, the joints may gradually atrophy.
- Problems of the speech apparatus: indistinctness and incoherence of speech.
- Dysphagia is a violation of swallowing functions.
- Visual impairment: partial loss of vision, double vision, reduced field of coverage.
- Violation of the functions of the intestines and bladder: urinary incontinence or, conversely, the inability to excrete it.
- Mental pathologies: depression, fear, excessive emotionality.
- Epilepsy.
| Left sided stroke | Right sided stroke |
|
|
Signs of a coma
Coma after a stroke attack develops quite quickly, acutely and has the following symptoms:
- Man suddenly lost consciousness
- His face turned crimson red.
- Breathing became loud, wheezing
- The pulse became tense, blood pressure increased
- Eyeballs deviated to the side
- Pupils narrowed or became uneven
- Pupillary reaction to light became sluggish
- Decreased muscle tone
- There is a disorder of the functions of the pelvic organs (urinary incontinence)
How many years do people live after a stroke?
There is no definite answer to this question. Death can occur immediately after a stroke. However, a long, relatively full life for decades is also possible.
Meanwhile, it has been established that mortality after strokes is:
- During the first month - 35%;
- During the first year - about 50%.
The prognosis of stroke outcome depends on many factors, including:
- The age of the patient;
- Health conditions before stroke;
- Quality of life before and after a stroke;
- Compliance with the regime of the rehabilitation period;
- Complete elimination of the causes of stroke;
- The presence of concomitant chronic diseases;
- Presence of stress factors.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures include:
- Inspection. SPL test. It is called by the letters of the first three actions that the patient must perform: smile, speak and try to raise his hand.
- Assessment of the general condition of the patient by a doctor.
- An accurate and prompt examination of the patient is prescribed, magnetic resonance therapy or computed tomography will help.
- Lumbar puncture will distinguish cerebral hemorrhage from other brain pathologies.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging are used to detect the fact of a stroke, clarify its nature (ischemic or hemorrhagic), the affected area, and also to exclude other diseases with similar symptoms.
Treatment and rehabilitation after a stroke
The optimal terms of hospitalization and initiation of therapy are considered to be the first 3 hours from the onset of clinical manifestations. Treatment in the acute period is carried out in intensive care units of specialized neurological departments, then the patient is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit. Before establishing the type of stroke, basic undifferentiated therapy is carried out, after an accurate diagnosis is made, specialized treatment is carried out, and then long-term rehabilitation.
Treatment after a stroke includes:
- conducting a course of vascular therapy,
- the use of drugs that improve brain metabolism,
- oxygen therapy,
- restorative treatment or rehabilitation (physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy, massage).
In the event of a stroke, call an ambulance immediately! If you do not provide immediate assistance, this will lead to the death of the patient!
To prevent complications, therapy is carried out using the following drugs:
- cerebroprotectors restore the structure of damaged brain cells;
- blood thinners (only indicated for ischemic stroke);
- hemostatics, or hemostatic agents (used for a clearly established stroke of hemorrhagic origin);
- antioxidants, vitamin preparations and drugs that improve metabolism and blood circulation in tissues.
Rehabilitation activities:
- are carried out from the very beginning of a stroke and continue while maintaining a neurological deficit throughout life with the participation of the patient, a team of health workers and relatives;
- proper care of the patient's body, the use of special devices;
- breathing exercises (for the prevention of pneumonia);
- as early as possible activation of the patient's motor regimen, ranging from short sitting down in bed to a full-fledged physiotherapy;
- the use of various physiotherapeutic and other methods: electroprocedures, massage, acupuncture, classes with a speech therapist.
Folk remedies to restore the body after a stroke
Before using folk remedies, be sure to consult with your doctor, because. possible contraindications.
- Rosehip cinnamon. The fruits and roots of the plant are used to prepare a decoction, which is introduced into general baths in the treatment of paralysis and paresis. The course is 25 procedures, the broth is poured into water at a temperature of 37-38 ° C.
- Bath with sage after suffering a stroke. 3 cups of sage herb pour 2 liters of boiling water. Let the product stand for 1 hour, strain and pour into a bath of warm water. Take these baths every other day.
- Very useful and such a decoction: a teaspoon of crushed dry peony roots should be poured with a glass of boiling water. After that, insist for an hour and strain. Use a tablespoon of decoction 5 times a day.
- Laurel oil. This remedy is prepared as follows: 30 g of bay leaf should be poured with a glass of vegetable oil. Infuse for 2 months, while every day you need to shake the jar. The oil must be filtered and then brought to a boil. The mixture is recommended to be rubbed into paralyzed places.
Prevention
Stroke belongs to the category of those diseases that are easier to prevent than to treat. Stroke prevention consists of:
- It can be prevented with the help of a rational organization of the work and rest regime, proper nutrition, sleep regulation, a normal psychological climate, sodium salt restriction in the diet, timely treatment of cardiovascular diseases: coronary heart disease, hypertension.
- The best way to avoid a stroke is to prevent atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. Blood pressure control and checking for are important here.
- If necessary, take medications that improve the microcirculation of cerebral vessels, and it is also possible to take drugs that prevent a lack of oxygen (hypoxia) of the brain as prescribed by a doctor.


