Consulting a doctor for advice is the very first rule that must be followed if any pain syndrome occurs. And if the head hurts a lot (especially in young people), then making the correct diagnosis is simply vital. Stroke diagnosis is a complex, multi-step process.
Types of stroke
There are four main types of cerebral stroke:
- acute ischemic stroke of the brain;
- microstroke and transient ischemic attack;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Acute ischemic stroke occurs when one of the cerebral arteries is blocked by a thrombus. This type is one of the most common (up to 80% of all cases, occurs at any age). The symptom complex of the disease occurs within a minute after its onset. And irreversible processes in the human brain - in the fifth minute.
Transient ischemic attack and microstroke of the brain have the same cause of occurrence as acute ischemic stroke. The only difference will be that the symptoms of a microstroke pass quickly, and the body can independently affect the resorption of a blood clot. It is very important to make a correct diagnosis and start treatment immediately, since the risk of a second attack or the development of an acute ischemic stroke is very high within two days.
Intracerebral hemorrhage occurs due to the rupture of a vessel inside the brain. The prognosis for recovery is much worse than for ischemic stroke. The frequency of occurrence is up to 15% of the total.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage accompanies the rupture of the vessel (aneurysm) and the flow of blood into the space between the tissues of the brain and its membranes.
Statistics
The number of people who have suffered various types of strokes is increasing every year (especially among young people). According to medical statistics, the number of cases has approached the mark of twelve million people per year.
Out of 100% of sick people, 70% of people are in the disability group, and another 30% of people need assistants to care for life processes.
Among the causes of death, cerebral stroke firmly occupies the second line of the ranking (after coronary heart disease). 6.2 million patients are people who could not cope with this disease. Mortality directly depends on the treatment of the disease in the acute period. Men are more often ill.
The causative death of 44% (of the total number of deceased persons) of the country's population was precisely a stroke of the brain.
Primary diagnosis of stroke
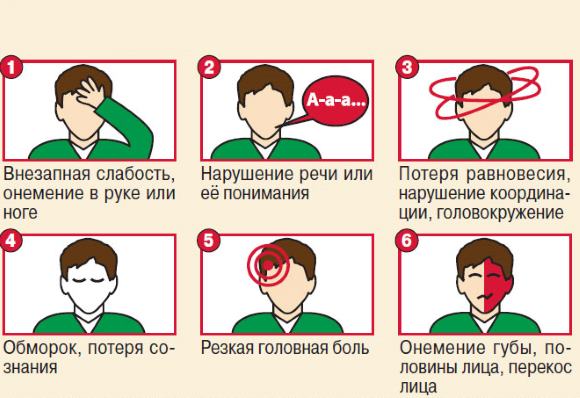
Signs of a stroke
It is very important, at the first signs of the disease (despite the young age of the patient), to call an ambulance. Only a medical professional will be able to correctly assess the situation and immediately prescribe the appropriate treatment.
The principles of primary diagnostics at the prehospital stage and upon admission to the clinic are akin to examinations at the end of the last century, when there were no such methods as MRI, CT, PET.
Anamnesis
The first thing the doctor will do is, with the help of relatives, collect an anamnesis of the disease (it is important to remember that a stroke “mows down” even young people). This will help him to suggest the development of this pathology, determine its etiology. Allows you to identify chronic diseases or suspect a number of other diseases not associated with a stroke of the brain.
Initial inspection
The initial examination is very important in making the correct diagnosis. It is worth paying attention to the following symptoms, the identification of which will help to correctly establish the pathological syndrome:
- unilateral paresis of the limbs;
- drooping corner of the mouth;

Sudden change in half of the face and impaired motor function of the limb
- it is impossible to control the tongue sticking out, it moves into one;
- unilateral paresis of the lower part of the face;
- speech is very difficult or impaired;
- slow movements, impaired coordination of movements.
If there is even the slightest suspicion of the occurrence of this disease, the patient should be sent to a medical clinic as soon as possible.
Blood analysis
Test tubes with blood for analysis
If a patient is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of "suspected stroke", he must undergo a clinical and biochemical blood test. Differential diagnosis of stroke with other diseases is also carried out using the following series of examinations:
- blood sugar is determined (the difference between a stroke and hypoglycemia);
- platelet count (you can find out the likelihood of blood clots);
- blood clotting time;
- the amount of electrolytes (potassium, magnesium, sodium).
Electrocardiogram
It is a very informative method of examination, in particular, in the diagnosis of stroke (despite the antediluvian). Cardiac pathology can also cause ischemic stroke in young people (it is detected in one case out of five, out of the total number of all sick people). The formation of blood clots may be preceded by myocardial infarction, arrhythmias.
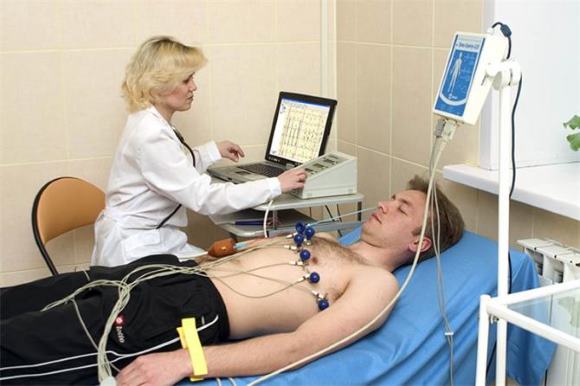
Registration of an electrocardiogram
An ECG is a mandatory part of the diagnosis, as it shows the state of the heart muscle. According to the electrocardiogram, it is possible to determine whether the pathology of the heart is the cause of the stroke (especially in young patients).
Arterial pressure
Pressure measurement is also an important part of the diagnosis. According to these data, it is possible to establish such a diagnosis as hypertension. You should know that in no case should the pressure be brought down to low numbers (maximum 10-15 mm Hg from the initial data).
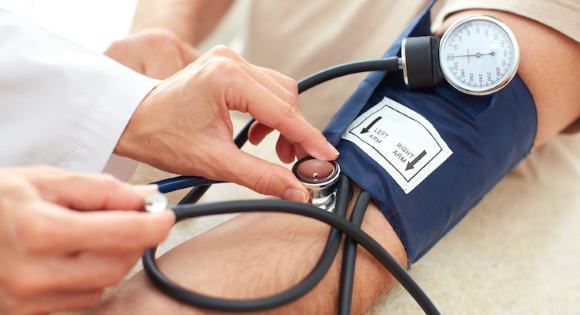
Blood pressure measurement
Lumbar puncture
With a puncture in the lumbar region, approximately 2 ml of cerebrospinal fluid is taken from the spinal canal. By appearance, it is determined whether there is blood or other impurities.
After a laboratory general analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid, it is reliably determined whether there is blood in the cerebrospinal fluid. The absence of it indicates that this is most likely not a subarachnoid hemorrhage, or not a hemorrhagic stroke.
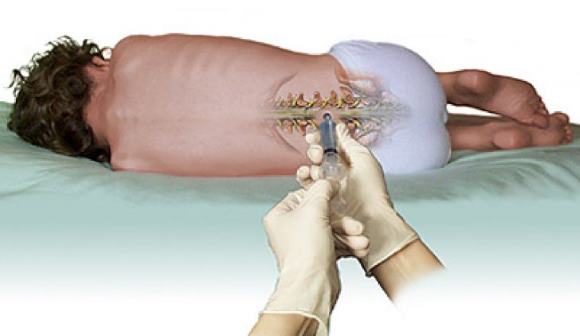
Performing a lumbar puncture
Modern methods
There are several modern methods for diagnosing stroke, which make it possible to make the correct diagnosis with 100% accuracy. These include:
- computed tomography (CT)
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- positron emission tomography (PET).
CT scan
The first in the list of measures for diagnosis is computed tomography. It is prescribed for any suspicion of a cerebral stroke. The most informative for hemorrhagic strokes, subarachnoid hemorrhages.
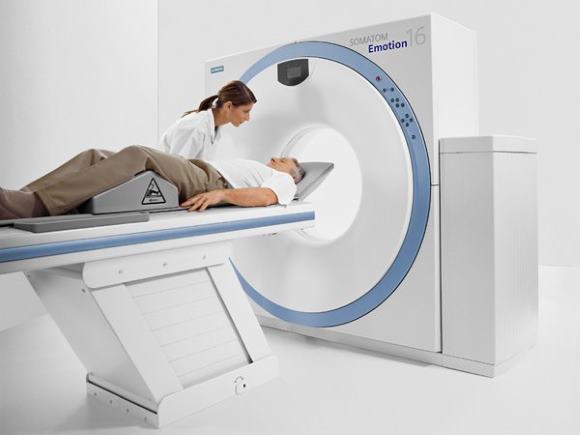
Carrying out computed tomography
This diagnostic method allows you to determine the bleeding that has just occurred (hemorrhagic stroke and the dynamics of its development). The procedure is painless, takes a minimum amount of time to carry out - up to 10 minutes.
Magnetic resonance imaging
It is prescribed as an additional diagnostic method or an independent study.
This method is most informative in ischemic strokes. Allows you to determine all types of strokes, as well as earlier ischemic lesions. Changes in brain tissues and the number of damaged cells are visible. The procedure is also painless, but it takes much more time than with CT (about an hour).
MRI is prohibited for people who have a pacemaker installed, have implanted artificial joints or organs.
Imaging should be performed as early as possible (preferably within the first 24 hours after the onset of a stroke). The findings of a tomographic study can significantly affect the treatment prescribed.
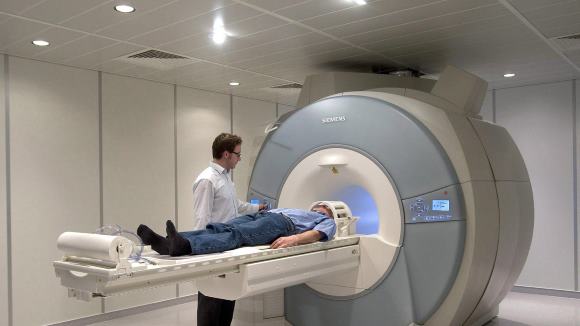
MRI is considered a more effective method of diagnosing ischemic stroke.
After the tomography, the doctor directs the patient to the following additional studies:
- Ultrasound of the heart, cerebral vessels, carotid and vertebral arteries;
- examination by an ophthalmologist;
- X-ray of the skull and chest organs;
- electroencephalogram;
- echocardiography;
- consultation with a cardiologist and endocrinologist.
Teenager's problems
A stroke of the brain, as a disease, is much younger (more often men over the age of 35 suffer). A number of reasons contribute to this. These include:
- high blood pressure;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- constant stress.

Bad habits are common causes of cerebrovascular accidents in young men
These factors contribute to the development of the disease in young people. To prevent the disability of the young population, it is necessary to diagnose stroke as soon as possible and urgently deliver such patients to a medical facility. It is imperative and immediately to conduct a full examination and prescribe treatment in accordance with the diagnosis.
In young people (with timely treatment), it is possible to fully restore working capacity. In this case, prevention of recurrence is very important.
What remedy for headaches, migraines and stress do not yet know many doctors?!
- Do you suffer from episodic or regular headaches?
- Presses and squeezes the head, eyes, or "hit with a sledgehammer" on the back of the head, knocking at the temples?
- Do you sometimes feel nauseated and dizzy when you have a headache?
- Everything starts to annoy, it becomes impossible to work!
- Throw out your irritability on loved ones and colleagues?


