A heart attack is a condition in which part of the heart muscle dies due to the cessation of blood supply to this area. According to the ICD, the violation was assigned the code I21.
In some cases, a heart attack is regarded as a form of ischemia, which is generally characterized by impaired blood flow to the myocardium.
Tasks of therapy
A heart attack should only be treated in a hospital setting, as it is a life-threatening emergency. If any indication of an attack occurs, the patient should be taken to the hospital as soon as possible. The patient is determined in the cardiology department according to the results and with visible violations.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes and is NOT a guide to action!
- Give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS only DOCTOR!
- We kindly ask you DO NOT self-medicate, but book an appointment with a specialist!
- Health to you and your loved ones!
After treatment in a hospital, a long one is expected. Such patients are shown sanatorium treatment and regular examination by a cardiologist.
Treatment of myocardial infarction is focused on eliminating or minimizing the disease processes that provoked an attack. The prognosis depends on how quickly the doctors manage to solve the problems that have arisen.
The main tasks of therapy:
| Restoration of normal blood circulation |
|
| Minimizing the area of necrosis |
|
| Relief of painful syndrome | This is an essential event, since the patient may simply die due to intense pain. |
| Prevention | An attack threatens with dangerous complications, the risk of which can be reduced through timely treatment. |
Medical treatment of acute myocardial infarction
Treatments can be divided into two categories:
At the initial stage of a heart attack are assigned:
- analgesics;
- tranquilizers;
- thrombolytics;
- antiplatelet agents;
- blood-thinning;
- beta blockers;
- nitrates;
Treatment regimen for acute myocardial infarction
Analgesics
They are used by the ambulance team or in the hospital if the person was not delivered by an ambulance. The pain is so severe that it may require opioid-class narcotic drugs to relieve it.
To reduce the pain syndrome, the following means are used:
Strong drugs eliminate pain within three to five minutes. In stationary conditions, if necessary, they are administered repeatedly.
tranquilizers
They are used infrequently and only at the peak of an attack.
Tranquilizers relieve psychomotor agitation, if this is noted (against the background of pain).
Diazepam is preferred (intravenous administration, dose - up to 10 mg).
Thrombolytics
The purpose of using thrombolytics is to destroy a blood clot in a vessel and normalize blood circulation. Such treatment of myocardial infarction cannot restore dead cells, but prevents an increase in the affected area. This is extremely important for the prevention of dangerous consequences and improvement of the prognosis.
The main indication for treatment with thrombolytics is ST elevation on the ECG. The drug in this case should be given as soon as possible.
The greatest therapeutic effect is provided by the introduction of the drug within an hour after the development of an attack. However, in practice, it is difficult to provide such assistance quickly - the real time limit is usually three hours.
The most effective thrombolytics:
All drugs from this group have certain adverse reactions. Their use increases the likelihood of spontaneous bleeding. For this reason, there are some contraindications that preclude the use of thrombolytics.
Thrombolytic therapy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- postoperative period;
- oncology;
- bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system.
Antiplatelet agents
Means of this group affect blood cells (mainly platelets, which do not merge well and do not “stick” to the vessel membrane). Due to this effect, the likelihood of thrombosis is reduced.
Also, antiplatelet agents affect the membranes of red blood cells and facilitate their passage through the capillaries. This allows blood to pass through the narrowed areas more quickly and easily. The blood flow to the myocardium is normalized, and the necrotic process is inhibited.
In the treatment of a heart attack, the use of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is preferable. At the peak of an attack, the therapeutic dose is up to 325 mg. The drug is taken orally. Further, the dose is up to 160 mg once a day.
Duration of admission is determined by the doctor based on the patient's condition. The use of aspirin in the acute or subacute stage of a heart attack reduces the risk of developing dangerous complications by 30%. The indication for taking aspirin is the rise of the ST sector on the ECG.
Contraindication to admission - peptic ulcer of the gastrointestinal tract, since acetylsalicylic acid aggressively affects the mucous membrane.
Anticoagulants
Such funds are prescribed to increase the effectiveness of thrombolytic therapy. The expediency of their reception is determined by the doctor based on the results of the anamnesis. Such agents also reduce the risk of thrombosis. In the acute stage of myocardial infarction, anticoagulants reduce the likelihood of thromboembolism.
However, there is a possibility of adverse reactions from taking thrombolytics. Co-administration of urokinase and anticoagulants is not practiced.
Most often, with a heart attack, they are prescribed:
The therapeutic dose is determined individually based on what kind of thrombolytics it is supposed to be taken with. When choosing a dose, the results of laboratory tests should be taken into account.
Beta blockers
They are prescribed to reduce the load on the heart and reduce the need for oxygen. Such drugs lower and weaken the heart rate.
Due to this, the myocardium experiences less stress, and the necrotic process stops. Taking beta-blockers is a mandatory element of the treatment regimen.
They are prescribed at all stages of a heart attack, if there are no contraindications.
Beta-blockers for the treatment of heart attack:
| Atenolol |
|
| metoprolol |
|
| propranolol |
|
These drugs lower the heart rate to 60 beats per minute, so they are not used if the patient has this rate already low or if there are severe symptoms of heart failure.
If you focus on the electrocardiogram, a contraindication to admission is the lengthening of the P-Q interval to 0.24 or more. A side effect of taking beta-blockers is expressed in the form of narrowing of small-caliber bronchi, so another contraindication is asthma or an asthmatic form of a heart attack.
Contraindications are usually temporary - after the restoration of normal breathing and the normalization of the heart, these funds are still included in the therapeutic course. Reception begins with small doses, gradually increasing them until the desired effect occurs.
The use of beta-blockers minimizes the likelihood of a recurrence of an attack, expansion of the heart cavity and dangerous rhythm failures. Some patients are prescribed long-term medication (for months or years).
Nitrates
In the first few days after the attack, it is desirable to take significant doses of nitrates:
In stationary conditions, a 1% solution of nitroglycerin is administered intravenously through a catheter. A daily dose of up to 12 ml is diluted with 400 ml of isotonic solution. The drug is administered for three to four days, then oral administration is prescribed.
Intensive nitrate therapy (especially continuous intravenous nitroglycerin) reduces the workload on the heart by reducing oxygen demand. The intake of nitrates improves coronary blood flow, limits the area of necrosis, and minimizes the risk of ventricular fibrillation.
Intravenous administration of nitroglycerin reduces the incidence of sudden cardiac arrest, prevents the development of cardiac asthma.
According to the severity of the positive effect, the combination of nitrates and beta-blockers is most preferable. As practice shows, replacing the combination with other schemes leads to a deterioration in the results of treatment.
ACE
ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) are used for severe heart failure, which was the result of a massive heart attack.
The drugs have a vasodilating, hypotensive effect. Their reception is contraindicated in patients with systolic pressure up to 100 mm Hg / s, in persons with renal insufficiency and during pregnancy.
Therapy begins with short-acting drugs (captopril). If the agent is well tolerated, analogues of prolonged action are prescribed.
ACE inhibitors for the treatment of heart attack:
Many people continue drug therapy for an extended period of time (months or years). This measure is caused by an increased risk of complications or recurrence of the disease.
Among the complications, cardiac aneurysm, chronic heart failure are possible, which require the use of certain drugs throughout life.
Therapeutic regimens are determined individually based on the patient's condition. If the exact cause of the heart attack is identified, an additional course may be needed to eliminate it.
Surgical intervention
In addition to drug therapy, surgical methods are sometimes used to treat a heart attack and its complications. Such measures are resorted to on special indications.
In the treatment of a heart attack, the following types of interventions are used:
| Percutaneous coronary intervention |
|
|
|
| Excision of a heart aneurysm |
|
| Implantation of pacemakers |
|
Effective treatment is evaluated by the results of the electrocardiogram and clinical observations. If the ECG shows a rapid decrease in the ST sector, it can be concluded that blood flow has been restored.
Coronary angiography
The procedure of coronary angiography is necessary to identify the affected vessels. 12 hours before the intervention, the patient does not eat anything, his inguinal region is shaved. The procedure is carried out according to emergency indications or in a planned manner.
The intervention is performed in the X-ray operating room. The patient is put into a state of semi-sleep. Under x-ray control, a long catheter is inserted through the femoral vein, which is passed to the aortic valve. Next, the mouths of two arteries are alternately located, a contrast agent is injected.
As a result, the cardiac surgeon obtains a picture of the coronary vessels, in which one can see narrowed areas and places where blood flow has stopped. The procedure is recorded on a disk, after which the doctor draws up a conclusion and evaluates the possibility of further surgical intervention.
A pressure bandage is applied to the puncture site, cold is provided for one hour, and a load is placed for a day. The patient must observe bed rest for 24 hours and limit the mobility of the injured limb.
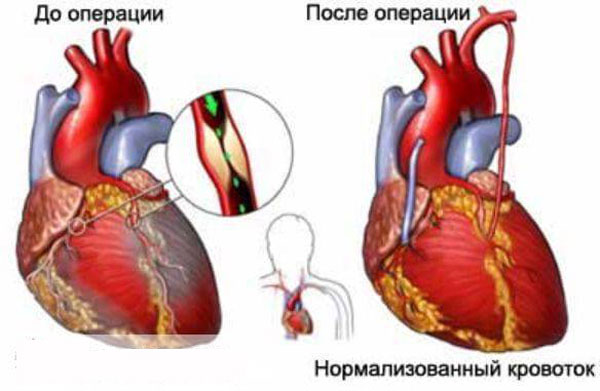
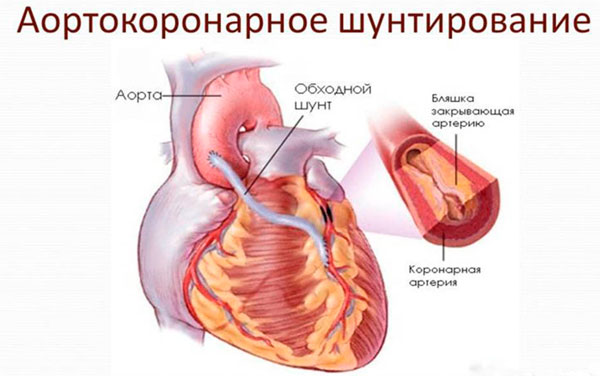
Aortocoronary and mammary coronary bypass grafting
The intervention allows you to restore blood flow by bypassing the narrowed place with the help of shunts. The operation is performed with the connection of a heart-lung machine and artificial lung ventilation. In some cases, the intervention is performed on a beating heart.
Indications:
- blood ejection by the left ventricle less than 30%;
- damage to the trunk of the left coronary artery;
- the presence of a single intact coronary artery;
- combination of left ventricular dysfunction with three-vessel injury.
The intervention is carried out if, along with damage to the coronary arteries, the heart valves are affected. In this case, the valves are first prosthetized, then the shunts are sewn. Shunting is also performed in case of complete obstruction of the vessel, when it is impossible to install a stent.
Shunting is often performed with isolated damage to the coronary arteries. The operation is traumatic and does not exclude the risk of death during the intervention. After surgery, patients are shown taking blood-thinning agents.
In some cases, mammary coronary bypass surgery is performed. If in the previous version a vein from the leg or an artery from the arm is used, then with this technique the distal end of the internal mammary artery is taken. The choice remains with the cardiac surgeon, since the use of the internal artery is not always possible.
The effectiveness of folk remedies
Not allowed. Medicinal plants cannot act as quickly as medicines. In addition, many drugs require intravenous administration to accelerate the therapeutic effect.
However, in the post-infarction period, the use of folk remedies is allowed. At this stage, medicinal plants contribute to the stabilization of cardiac activity, improve blood flow and rapid recovery.
How to treat a heart attack with folk remedies:
| lemon zest | It is recommended to chew it in the post-infarction period to improve blood circulation and reduce pain. |
| Freshly squeezed onion juice | It is stirred in equal parts with honey. The remedy stabilizes the heart rhythm, improves the work of the heart in general. |
| Ginseng infusion | Mixed crushed ginseng root and honey (1:25). After five days, the product is ready for use. |
| Carrot juice + vegetable oil | The tool accelerates the formation of connective tissue in the area of necrosis. |
| Heart collection (clover inflorescences, meadowsweet, marsh cudweed, sage, celandine) | 10 g of the collection is poured with half a liter of boiling water, insisted for four hours. The infusion accelerates rehabilitation in the post-infarction period. |
It should be remembered that not a single folk remedy can replace medications and qualified medical care. Before using this or that means it is necessary to consult with the doctor.


