Myocardial infarction is one of the most formidable diseases of the cardiovascular system. And the patient's life often depends on timely treatment. Therefore, in addition to ECG, instrumental methods of research and analysis of clinical symptoms, laboratory diagnosis of myocardial infarction plays an important role in the rapid establishment of the correct diagnosis.
Methods of differential diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction
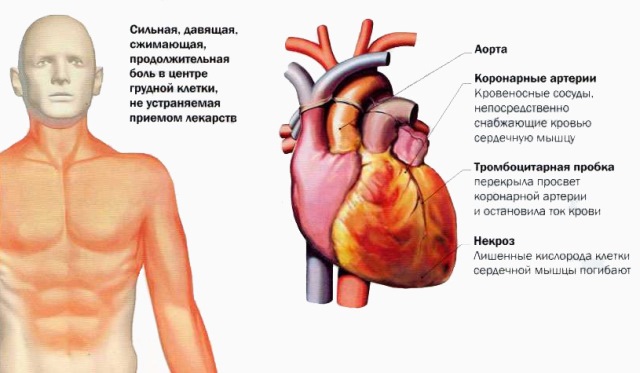
This disease is characterized by a violation of the patency of the coronary vessels, resulting in necrosis of the heart muscle. The larger the area of myocardial damage, the more severe the pathological process, and the less chance the patient has for recovery.
Timely initiation of therapy for this disease is of great importance. To do this, specialists need to make the correct diagnosis, since erroneous treatment can lead to disastrous consequences.
It is based on three main types of diagnostics. First of all, this is an assessment and correct interpretation of the patient's clinical condition, symptoms of the disease and main complaints. Equally important are the instrumental methods of examination. , Ultrasound of the heart, and other techniques allow you to quickly and with a high degree of probability establish the correct diagnosis.
Laboratory methods for studying myocardial infarction remain effective. In addition to the usual clinical blood and urine tests for most patients, special markers of damage to the tissues of the heart muscle are widely used. This includes determining the level of enzymes or troponins of CPK, AST, LDH and others.
How clinical blood and urine tests react to the development of myocardial infarction
Given that the main pathomorphological manifestation of this disease is acute necrosis of areas of the heart muscle, a general blood test for myocardial infarction will show a picture of the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. Already 4-6 hours after the onset of the acute phase of heart disease, the number of leukocytes in this study will increase by 2-3 times. The growth of white blood cells occurs mainly due to young forms of neutrophils. A similar symptom in clinical laboratory diagnostics is called a neutrophilic shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.
With the percentage of eosinophils in the blood, the following picture is observed: 24 hours after the onset of the disease, their number drops sharply and is practically not determined in the blood test. As soon as the patient's body begins to receive appropriate treatment, and the regeneration processes in the myocardium intensify, these blood elements are restored to normal values. The process can take up to 2 to 4 weeks.
ESR in myocardial infarction reacts to what is happening, as well as to any other inflammation. Immediately after the development of myocardial ischemia, ESR rises sharply and remains at a level 2–3 times higher than normal for up to 25–30 days.
As soon as the inflammatory process in the heart muscle begins to subside under the influence of specific treatment, the ESR returns to its usual numbers.
A general urine test does not carry any special semantic load in this disease. Specific changes in this study may occur if myocardial infarction is accompanied by the development of acute renal failure.
In this rather rare case, a large number of white blood cells, mucus may be present in the general urine test, and a rapid increase in specific gravity will also be characteristic.
Biochemical blood test for myocardial infarction
Most of the indicators of this analysis do not have specific values, experts assess the level of their fluctuations between the maximum and minimum numbers.
Acute myocardial infarction is characterized by a violation of the following parameters:
- The total blood protein, namely albumins and globulins, is characterized by an increase in the active phase of myocardial ischemia. This is due to violations of the metabolic process in the patient's body.
- An increase in indicators such as urea and creatinine is possible. If in the normal state these substances characterize the work of the kidneys and the urinary system, then with myocardial infarction, an increase in indicators will indicate the development of heart failure.
- An important enough symptom in acute pathology of the heart muscle will be an excess of concentration. Normally, its quantitative indicator is 3.5 - 6.5 mmol / l, and with the development of coronary artery disease, the numbers increase by 2 times.
- Absolutely necessary for the timely diagnosis of this acute process are the data of enzymes during ischemia of the heart wall. A sharp increase in ALT and AST always accompanies necrosis of the heart muscle, since the concentration of these enzymes in the myocardium exceeds their content in the blood plasma by 2000-3000 times.
- Another enzyme in myocardial infarction, amylase and phosphatase, can increase only with a pronounced necrotic process in the heart and indicate the inadequacy of the therapy.
- A few years ago, it was believed that if myoglobin was found in the patient's blood during myocardial infarction, then this indicates a pronounced severity of the pathological process. However, recent studies reject this claim and do not recommend that clinicians specifically respond to this indicator. Myoglobin is excreted from the body with urine after 1-2 hours and cannot be a 100% criterion for the presence of myocardial ischemia in a patient.
Biochemical analysis of blood in myocardial infarction is an important component in the diagnosis of this formidable disease.
Specific laboratory tests for suspected myocardial infarction
Analyzes for myocardial infarction can be divided into general and specialized studies. The latter allow doctors to diagnose and prescribe with a high degree of probability. These include:
- Analysis for C-RP or C-reactive protein. The level of this substance in the human body usually rises sharply with various inflammations. Myocardial infarction is no exception in this case. The norm of C-RB is 2.5 - 5 mg / l.
- The enzyme creatinophosphokinase or CPK refers to specific tests for necrosis of the heart muscle, it can be an indicator not only of acute myocardial infarction, but also of a major injury. For a clearer diagnosis, the CPK-MB fraction is determined, this is a direct cardiomarket for myocardial infarction.
- The most common test for diagnosing acute ischemia of the heart muscle is the determination of the tissue enzyme Tropanin. The level of this substance in the patient's blood rises within a few hours after the development of myocardial necrosis. Normally, it reaches 0.4 μg / l, any excess of this indicator indicates the development of myocardial infarction.
Instrumental methods, in particular ECG, ultrasound and radiography, remain the main methods of high-quality diagnostics for such a pathology of the heart.
However, the good old blood and urine tests cannot be completely ignored. Thanks to the introduction of new methods of laboratory examination, they remain in demand in the differential diagnosis of many diseases of the human body.


