Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease accompanied by hyperglycemia and glycosuria. Patients suffering from sweet urine disease get information on how to lower blood sugar from therapists and nutritionists, they look for it in a folk recipe.
The disease is dangerous with unpredictable changes in the indicator with large amplitudes of fluctuations and the impossibility of controlling the blood sugar content. Inexperienced patients believe they can lower their sugar levels at home and cure glycosuria.
Reasons for high blood sugar
The main source of energy is glucose. Fats and oligosaccharides broken down by digestive enzymes are absorbed into the blood. Veins from the intestines carry nutrients to the liver.
Carbohydrates continue to break down in the liver to monosaccharides. Glucose enters a cycle of biochemical transformations, the result of which is the release of energy. This process is most intense during night sleep. Part of the calories is spent directly to restore the body's strength, and the excess is polarized and deposited by the liver in the form of glycogen polysaccharide. If necessary, the polysaccharide is able to break down for glucose, satisfying the urgent energy needs of the organs.
The level of blood glucose in an adult and a child is regulated by the brain through the connection of nerve nodes with the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland sends an order to the pancreatic gland to produce the required amount of insulin.
The latter responds to changes in the body's need for energy during stressful situations, physical overload, and diseases. Calories are needed by the body to process food. Ensuring the functioning of the nervous system and other physiological functions.
Insulin does not allow the glucose concentration to fall below the threshold value, and in the event of a risk of developing hypoglycemia, it gives a signal to the liver to accelerate the consumption of deposited reserves.
The development of diabetes mellitus perverts the metabolism of glucose in the body. The result of the anomaly is the creation of excess reserves of glucose in the blood. Excess glucose is not able to be converted into energy.
High blood sugar causes many complications, so the main task of the body is to bring the concentration of blood glucose to normal.
There are the following types of diabetes:
- First. congenital pathology. The pancreas does not produce enough insulin. Diagnosed in childhood
- Second. Occurs in obese people of mature age;
- Gestational. Occurs at the end of pregnancy and disappears after childbirth.
Norm of indicators
The normal concentration of blood glucose taken from a vein is considered to be 4.80±1.30 mmol/l. Capillary blood, taken from a finger, has its own criterion for the norm of sugar - 4.40 ± 1.10 mmol / l. The latter procedure is necessary for regular self-monitoring by patients with diabetes mellitus.
Tormented by this disease, they are familiar with glucometers, which allow them to independently determine the saturation of blood with sugar within 6 seconds. An increase in the concentration of glucose in the body of an adult above 6.1 is called hyperglycemia, and a fall below 3.5 is called hypoglycemia. Both conditions are dangerous to health.
The task of the organism of a person suffering from diabetes is to bring the concentration of the main source of energy back to normal.
The state of hyperglycemia occurs as a result of a malfunction of the organs involved in the metabolism of sugars - the liver and pancreatic gland, and the pituitary gland. Therapeutic measures for diabetes mellitus are reduced to the therapy of these organs. Such diabetes mellitus, called secondary, is a symptom of diseases of these organs. Treatment of second diabetes is to eliminate the causes that caused it.
The main method of diet therapy is the inhibition of glucose formation. To do this, limit the intake of carbohydrates and fats with food. Lipids are energy-intensive nutrients, and their deficiency leads to the expenditure of energy at the expense of glucose, which is what is required.
Limit access to easily digestible carbohydrates (LPU). Sources of health care facilities are sweets, bakery products, potatoes, chocolate.

With hyperglycemia, the diet is diversified with foods that reduce blood sugar:
- Cherries, apples. They have a low glycemic index. Accelerate the uptake of glucose by tissues;
- Lemon. Sugar-burning effect has a complex of substances contained in lemon. Sugar-reducing effect has a mixture of juice of one lemon and a raw chicken egg before meals;
- Tomatoes cucumbers. Virtually no carbohydrates;
- Cabbage. Contains a complex of sugar-burning substances
The recipe for cooking was developed in accordance with the therapeutic diet No. 9.
Sweets have to resort to the use of sweeteners.
The most popular natural sweetener is fructose. This substitute for equal calories. It is permissible to use sorbitol and xylitol in diabetes. The main disadvantage of natural sweeteners is their calorie content comparable to sugar. Obesity creates the conditions for the onset of type II diabetes.
Among synthetic sweeteners, the following have found use in the treatment of diabetes:
- Cyclamate. The sweetness is equivalent to thirty times the volume of sugar. Contains no calories. In large quantities, toxic, contraindicated for pregnant women;
- aspartame 200 times sweeter than sugar. Calorie, but a small daily dosage,<3 г устраняет недостаток;
- Sukrazit. Sweetness is 600 times higher than sugar. Daily dosage for an adult is not more than 1 g;
- Acesulfame potassium. It is identical in sweetness and dosage to sucrasite. Contraindicated in heart disease and nervous disorders.
Natural and synthetic sweeteners should not be consumed uncontrollably. Side effects are digestive disorders. The dosage of drugs and natural remedies is determined by the doctor.
With the development of mild hyperglycemia, the most popular drugs are pills to lower blood sugar.
Sulfonylureas:
- (Glidiab MB, Glibenclamide, Glidanil, Gliclazide) provide a gentle decrease in concentration, excluding drops in concentration.
Biguanides:
- Glycon, Gliformin, Glyformin Prolong, Glucophage, Diaformin OD, Metfogamma, Formetin, Siofor are produced in a dosage convenient for use, have a prolonged action, and have no side effects. They do not have any effect on the production of the hormone. This treatment of high sugar is indicated for secondary type diabetes caused by a violation of sugar metabolism.
If the patient has confirmed type 1 diabetes, insulin injections are indispensable. All existing insulin preparations are administered subcutaneously. The patient from the beginning to the end of his life is forced not to part with the syringe.
The dosage is usually determined in units. It is set by an endocrinologist, taking into account the degree of hyperglycemia, the presence of glucosuria, the level of physical activity, and the patient's sensitivity to the drug. In the absence of insulin, a patient suffering from the first type of diabetes mellitus falls into an unconscious state - a diabetic coma. The removal of a patient from a coma is possible by intravenous injection of insulin by drip.
Treatment of diabetes with medicinal herbs has been practiced since ancient times. Plants supply the human body with cations that provide an alkaline reserve. An alkaline environment improves the conditions for the absorption of glucose by tissues and lowers blood sugar.
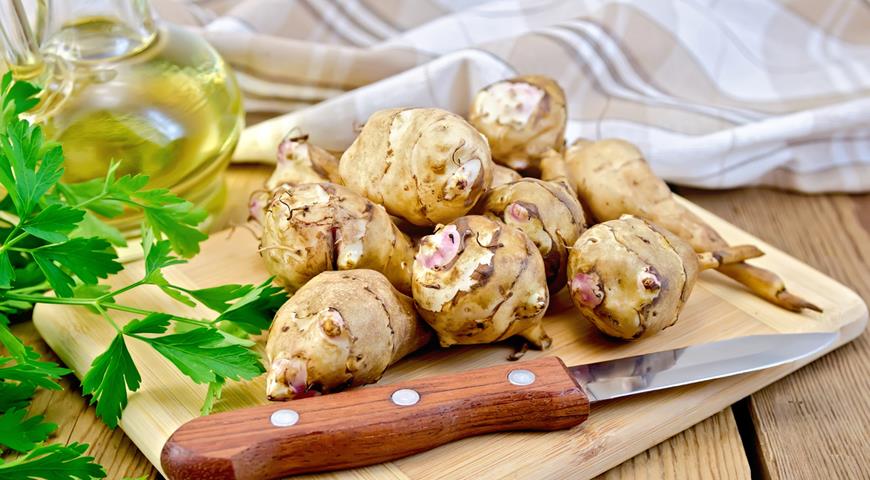
In nature, there are plants that synthesize pectins for their needs, inulin, which normalize digestion, as well as phytohormones similar in structure to human insulin. The most famous is Jerusalem artichoke. It is called artichoke, earthen pear, turnip, tuberous sunflower. The tubers are edible and ripen in autumn.

The following herbal remedies will help to reduce sugar levels at home quickly and effectively:
- Foliage of blueberries, nettles, clover;
- Dandelion root;
- birch buds;
- Above-ground part of St. John's wort;
- Beet and cabbage juices;
- Onions, garlic thermally processed;
- Berries of viburnum, mountain ash;
- Pears.
Folk remedies for diabetes have certain disadvantages:
- Non-traditional agents are effective for mild hyperglycemia;
- Phytotherapeutic agents cause an individual intolerance reaction. If a skin rash, itching or discomfort appears, the remedy must be abandoned forever;
- The doctor must be informed about the use of sugar-lowering drugs. You may need to adjust the dosage of the main drugs;
- Treatment with folk remedies can relieve the symptoms of hyperglycemia, and the patient spontaneously stops taking prescribed medications. Such behavior is dangerous to health;
- The diet when using alternative medicine should not be violated. Five times, at least, food intake cannot be violated;
- Phytotherapeutic agents can cause hunger, body tremors, dizziness. - symptoms of hypoglycemia. In this case, you need to eat, or have a snack with sweets;
A steady return of blood glucose to normal should be considered a good sign, but not the result of complete healing. If a person fears a recurrence of the disease, he must comply with dietary restrictions, do not avoid dispensary supervision and regularly monitor blood sugar levels. We hope we have helped you with your illness and now you know how to lower blood sugar at home, with the help of medicines and traditional medicine.


