The effect of a drug is largely determined by its dose. Depending on it (concentration), the speed of development of the effect, its severity, duration and character changes.
Types of doses of medicinal substances
It is known that the effect of a drug on the body depends on its chemical structure, physicochemical properties and dose. The latter may differ in their characteristics, purpose and effect.
In fact, they replace insufficient dopamine and directly stimulate the corresponding receptors, which makes it easier to carry out nerve impulses. The first studies showed the positive effect of this group of drugs. Dopamine agonists should be administered very slowly and carefully to avoid nausea and vomiting. In some 10% of cases arterial pressure may also be significantly reduced. But these side effects usually decreases or can be relieved with temporary additional medication.
IN Lately other non-ergoline agonists are also available with fairly similar beneficial and secondary effects, but also have a greater tendency to increase daytime sleepiness or even promote sleep. For apomorphine, the specific methods required to cause important and immediate liver destruction when ingested make it a backup and backup when all other treatments fail to provide adequate quality of life. Numerous evidence was also provided by animal experiments.
The smallest dose of a drug, after taking which a minimal therapeutic effect occurs, is called the threshold or minimum therapeutic dose. In medical practice, the so-called average therapeutic (medicinal) dose is used to treat patients, after taking which a stable therapeutic effect is observed in most patients.
Side effects include possible dyskinesia, late diarrhea and moderate change colors in urine. Only entacapone remains in Europe because talcapone was suspended after some suspected cases of liver failure. Physiotherapy Despite all medical and surgical therapeutic advances, physical treatment remains a necessity throughout the patient's life. They are considered complementary drug treatment. Sometimes they are intended to improve symptoms that are relatively resistant to drug treatment, such as postural disorders.
In some cases, this dose has an insufficient therapeutic effect and it is necessary to resort to higher doses, which is unsafe for the body. That is why for most drugs there are maximum permissible doses for one dose and for daily use - the highest single dose(HRD) and highest daily dose (HDD).
WFD medicinal substance- maximum permissible dose allowed for one dose. After its use, the greatest therapeutic effect is observed.
Considered: physical therapy, including exercise, physical therapy, occupational therapy, swimming, as well as speech therapy and sometimes relaxation. Concerning physical exercise, some preliminary remarks are necessary. Movement is necessary for a person. Healthy image life includes regular physical activity, which is essential for overall well-being, but also has beneficial effects on mood and even physical symptoms, including constipation. Lack of exercise leads to physical deconstruction, muscle weakness, joint stiffness and even retractions.
VSD is the maximum permissible dose of a medicinal substance allowed to be taken during the day.
Typically, the VRD and VSD are established for drugs of list “A” (poisonous and narcotic substances) and “B” (potent substances).
The range of drug doses from the minimum therapeutic to the highest single dose is called the breadth of the therapeutic effect of the substance. The larger it is, the less toxic the drug is, and vice versa.
This is especially true when the patient is old. In Parkinson's disease, patients experience movement difficulties that tend to isolate them and therefore reduce their physical activity. It is therefore especially important that these patients insist on the need to practice regular physical activity in order to maintain their best performance. physical state in general, but also to take an active part in their treatment and come out of their isolation. If the patient regularly practices one or more sports, he should definitely be encouraged to continue this practice.
In addition to the above, other doses of drugs are known.
Toxic dose- a dose of a medicinal substance that causes poisoning without death.
Lethal (lethal) dose- a dose of a drug that leads to death.
Course dose- a dose of a medicinal substance intended for a course of treatment.
The pleasure he gets from this is beneficial, including motor, the condition of the patient's thymus gland can have a direct impact on his motor symptoms. Swimming is definitely a great sport in general. This promotes coordination and balance. Movement in water requires reduced effort; therefore, some active mobilization activities can be intensified. Benefits may be felt within hours. Patients experiencing motor hesitation problems should always be accompanied in the water as they may unexpectedly find themselves in trouble.
In clinical practice, the following types of doses are most often used:
single (single) dose- amount of medicinal substance per dose;
daily dose- the dose with which it is possible to maintain the therapeutic concentration of the drug in the blood plasma during the day;
test dose- the dose of the drug with which treatment is started, taking into account that in some cases unforeseen reactions of pharmacodynamic (for example, the effect of the first dose when using prazosin - a sharp decrease in blood pressure when standing) or allergic types develop when taking certain drugs;
Physical exercise should be done regularly, in principle, daily. Frequent sessions, even if short and moderate, are preferable to occasional sessions of exaggerated intensity that are too tiring. The exercise should cover the entire body, but sometimes also regions more specifically related to the specific difficulties of the patients. Initial instructions from the physical therapist are helpful. Some patients, especially in the early years, can then reproduce these exercises on their own at home. In later stages of the disease or in older patients, or when postural disturbances with a risk of falling are important, systematic assistance from a physical therapist may be useful.
saturating dose- the dose with which it is possible to create the required concentration of drugs in the tissues (for example, during treatment with amiodarone, cardiac glycosides);
loading dose- a dose that allows you to create the optimal tissue (plasma) concentration of the drug necessary for its competition with a certain endogenous substrate (for example, a loading dose of sulfonamides necessary to compete with para-aminobenzoic acid for a place in the structure of the folic acid molecule at the stage of synthesis of the latter).
Private rehabilitation physiotherapy is often necessary, at least in patients with obvious akinetic-hypertensive symptoms. Massages can be beneficial due to their effect on muscle tension. Group exercise may be suitable for patients with moderate symptoms. This is an individual choice.
In Belgium, patients with Parkinson's disease can receive, at the request of a neurologist, compensation for physical therapy for severe pathology before the daily session. A rule that should be followed for all patients: do not want to succeed during the exercises, but work in such a way that they provide a feeling of overall well-being at the end of the session.
Dose regimen- dose size (single or daily) and frequency of drug administration during the day. The dosage regimen depends on many factors, but the most important of them is the period
half-life. A rational PT plan involves the administration of an initial therapeutic dose followed by the use of the same dose at intervals corresponding to the half-life of the drug. For drugs with a very short (benzylpenicillin - 30 min) or long (digitoxin - 9 days) half-life, these regimens are not suitable, since too frequent administrations are burdensome, and rare ones cause significant fluctuations in the plasma concentration of the drug. This reduces the pharmacological effect and increases the toxicity of the drug. In such cases, resort to other dosage regimens. If the half-life is short, the initial dose is increased so that it remains effective until the end of the dosage interval. This regimen is the most rational when using benzylpenicillin, since its high initial concentrations are low-toxic and only 0.3% of the drug dose remains in the body at the end of the usual 4-hour dosing interval. Drugs with a low therapeutic index (the ratio of therapeutic to toxic dose) and a short half-life (for example, norepinephrine) are usually prescribed intravenously.
Cassette o practical exercises at home can be obtained from the head office of the French-speaking Parkinson's Association. Occupational therapy finds its place in a functional perspective. It aims to improve motor and mental functions by encouraging specific work related to daily activities. Pathological movement can be corrected by asking the patient to perform gestures that require the affected movement to be performed. It is not what the patient does that is important, but the way in which the necessary movements are performed.
In addition, during occupational therapy sessions, the patient can practice everyday activities that are difficult for him: writing using his cutlery, manipulating a key, writing. Finally, we will advise the patient to use objects adapted to his difficulties. For example, a larger pen or gadgets that fit around its pencil, allowing for a better grip, often make writing easier. Speech therapy takes responsibility for motor difficulties in the ortho-laryngeal area.
The dose regimen is significantly influenced by the functional state of the elimination organs (liver, kidneys) and blood circulation. A study of the PK of antibiotics in patients with renal failure showed that the elimination of chloramphenicol and erythromycin remains almost unchanged, while gentamicin and streptomycin are eliminated much more slowly, so the frequency of their administration must be reduced. In liver diseases, drug metabolism slows down and drugs are administered less frequently.
Therefore, it can be indicated for articulation and sound recording disorders, as well as for swallowing disorders. If you want to speech exercises were effective, it is advisable to be conscientious and regular. Sometimes it is also helpful to simply practice reading the text out loud under the supervision of one of the entourage members. Here again, the exercise tape available from the Association can help patients. Swallowing disorders require additional help from a professional.
What is Parkinson's disease? Indeed, over time, side effects appear and effectiveness decreases; Despite the development of new drugs, these complications remain inevitable, since currently no treatment has a real impact on the evolution of the disease. It is these long-term limitations of drug treatment that are the basis of the indications for surgery in Parkinson's disease. Neurosurgical treatment methods of two types. Treatments that, either by damaging or stimulating the deep brain nuclei, will weaken electrical activity some areas of the brain.
Principles of dosing of medicinal substances depending on age and body weight
The effect of drugs on the body depends on age. It is known that children and people over 60 years of age are more sensitive to the effects of drugs. That is why, when determining drug doses, the age of patients must be taken into account. The IRR and IRR of toxic and potent substances for patients of different age groups are given in the corresponding tables of the State Pharmacopoeia. For other drugs, doses (depending on age) are calculated based on the dose for an adult (over 25 years old), which is taken as a unit (Table 3).
They are very effective for the symptoms of the disease and are being used more and more often. Cell replacement and neuroprotective treatments are designed to intervene in the progressive loss of dopamine neurons. Although they were already an item clinical trials, as with transplants, they remain experimental methods that are still in the field of research, but offer very promising prospects. Among the methods currently used, thalamotomy is the oldest.
To achieve precisely small targets in the brain, not only stereotactic imaging techniques are used, but also recording techniques and electrical engineering during the procedure. Thalamotomy has an excellent effect on tremor but has very little effect on rigidity, akinesia, or dyskinesia. Thus, thalamotomy may be an option for parkinsonian jerk as well as for other forms of tremor when they are resistant to drug treatment, especially in cases of significant tremor.
For persons over 60 years of age, the dose of the drug (except for antibiotics, vitamins and sulfonamides) is reduced to 2/3 or 1/2 the adult dose.
Features of drug dosing in newborns
The imperfection of the receptor apparatus of newborns, expressed in its different functional activity, leads to large individual fluctuations in the response of the child’s body to the administration of standard doses of drugs. For example, unexpected reactions to drugs in newborns are recorded 3-5 times more often than in adults.
Recently, some centers have proposed an alternative method for performing thalamotomy: radiosurgery. The big advantage of this technique is its lazy and non-traumatic nature as it does not require any brain surgery. The stereotactic approach remains the same, but the radiation is administered to an awake patient and conveniently placed in the machine without trephination. Therefore, this method is an interesting alternative for elderly patients or patients with significant surgical risk. However, radiosurgery does not allow end-target control through performance testing, and therefore this approach should only be performed with high-throughput, very high-precision radiosystems.
Thus, the incomplete development of the body of newborns leads to the fact that their risk of side effects from taking drugs is significantly higher than in adults.
Currently, the following mechanisms are identified that are responsible for the formation of side effects of PT in newborns.
Toxic effects of drugs due to the immaturity of enzyme systems that provide detoxification of the body (for example, the toxic effect of vitamin K associated with low activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in erythrocytes).
Thalamic stimulation is a method that focuses on the same target and has the same features as thalamotomy. Instead of performing a lesion, an electrode is placed that is connected to a programmable stimulator, like heartbeat, and which will stimulate the thalamus steadily. The advantage of thalamic stimulation is that it is non-destructive and reversible. The electrode contains multiple electrical contacts that can be individually programmed to obtain the best clinical response.
In addition, the risk of complications is very low in case of bilateral stimulation. Pallidotomies, such as thalamotomy, are usually performed on one side because there is increased risk speech disorders, intellectual or cognitive disorders in bilateral interventions. Pallidotomy causes lesions close to the optic pathways, and if the lesions are excessive there is a significant risk of visual impairment. Like thalamic stimulation, pallidate stimulation has the advantage that it is reversible and can be performed bilaterally.
Toxic effects associated with the peculiarities of the interaction of drugs with proteins in the blood plasma of newborns (for example, nitrofuran derivatives displace bilirubin from binding with proteins, which leads to an increase in the concentration of the latter in the blood plasma and the development of jaundice).
Toxic effects of drugs caused by imperfect renal excretory function in newborns.
IN last years pallor stimulation has been replaced by subthalamic stimulation, which is the most effective surgical method currently. Subthalamic stimulation involves placing an electrode in a very small nucleus of the brain stem, the subthalamic nucleus, to suppress its abnormally high activity in Parkinson's disease. The first patient using this technique worked in Grenoble, France. Currently, several European centers have gained extensive experience in the field of subthalamic stimulation, and in Belgium several teams are successfully using this method.
Toxic effects of drugs caused by genetically determined defects of enzyme systems in newborns.
Toxic effects of drugs caused by a perverted reaction of the newborn’s body to the drug. The frequency of their occurrence in patients of this age group reaches 24.5%, in adults it ranges from 6-17%.
Due to significant differences in the PD of drugs in children (especially the first year of life) and adults, a simple dose reduction proportional to age when calculating a safe and effective dose of drugs for a child is unacceptable, as it can lead to unpredictable consequences (Table 4).
This method raises certain objections, since in many children (especially the younger age group) the volume of fluid in the body is unstable and can contribute to a decrease or increase in body weight. That is why a drug dose calculated only on the basis of a child’s body weight may be both ineffective and toxic.
Domestic scientists have developed several schemes for calculating drug doses for a child, taking into account his body weight, age, functional state, etc.
For example, it is necessary to calculate a single dose acetylsalicylic acid for a child aged 8 years with a body weight of 22 kg, i.e. child with malnutrition. The average single dose of acetylsalicylic acid is 0.5 g. It is necessary to calculate the amount of the drug for adults: 0.5 ÷ 70 = 0.0071. As can be seen from the table, the dose factor for a child aged 8 years is 1.4. We multiply the calculated dose of the drug by the dosis factor: 0.0071 × 1.4 = 0.0099 g. Thus, the dose of acetylsalicylic acid for a malnourished child aged 8 years is 0.0099 × 22 kg = 0.22 g.
When prescribing potent and toxic drugs belonging to list “A” and “B” to children of different ages, a medical worker must be guided by the drug dosage table published in the X State Pharmacopoeia of the USSR. The dose of other drugs not included in lists “A” and “B” for children is calculated as follows: a child of the first year of life is prescribed 1/24-1/12 adult doses, at the age of one year - 1/12 adult doses, 2- 3 years - 1/8, 4-6 years - 1/6 dose, 6 years - 1/4 dose, 7 years - 1/3 dose, 8-14 years - 1/2 dose, 15-16 years - 3/4 adult doses.
It should be understood that the selection of the dose of drugs should be carried out strictly individually for each child. In this case, it is necessary to take into account both the features of its functional development and the degree of severity pathological process, as well as the characteristics of the PD and PK of specific drugs. It should also be remembered that the dose of drugs for a child, calculated by any method, should not exceed that for adults.
The influence of individual characteristics of the body on the effect of drugs
In an experiment on animals, it was shown that males are less sensitive to a number of substances (nicotine, strychnine) than females. In addition, differences in the metabolism of a number of substances were noted, but clinically the problem of the dependence of the action of drugs on the patient’s gender has not been sufficiently studied.
Women, especially during pregnancy, may be more sensitive to medications.
Dose They call the amount of medicine that enters the body. The amount of drug introduced into the body is one of the important factors that determines the speed, nature, strength and duration of action of the drug.
Doses of drugs that can serve for treatment and do not cause pathological abnormalities in the body’s vital functions are called therapeutic or therapeutic . The therapeutic dose is divided into single, daily, course. One-time and daily dose are divided by the threshold. average, maximum and one-time for universities, higher daily allowance.
Minimum therapeutic dose (threshold) causes a minimal therapeutic effect, it is 2-3 times less than the average therapeutic dose.
Average therapeutic dose causes a moderate therapeutic effect. Most often it is used in medical practice. The pharmaceutical industry produces the average therapeutic dose of drugs, usually in one unit dosage form(in ampoule, tablet). This is convenient because it provides conditions for less drug overdose. .
Maximum therapeutic dose causes the greatest effect of limited therapeutic action. For poisonous and potent drugs, the State Pharmacological Center of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine sets the maximum therapeutic dose (single and daily). The maximum therapeutic dose is used in severe cases of poisoning. For example, in case of barbiturate poisoning, it is prescribed maximum doses analeptics.
In addition to medicinal ones, there are toxic doses at which pathological phenomena are observed. Minimum doses cause side effects, are called minimal toxic . Minimum dose which causes death is called minimum lethal dose (lethal).
Rice. 1. Types of doses: 1 - threshold (small) doses 2 - medium doses 3 - higher doses 4 - threshold lethal; 5 - LD И00.
Toxicology studies the toxic effects of substances on the body, the importance of which is increasing due to widespread chemicalization.
It is quite clear that in medical practice only those doses of medicinal substances that lie in the range of the minimum therapeutic and minimum toxic doses can be used. This range is called breadth of therapeutic action of drugs , (Fig. 1). The greater the therapeutic breadth of action, the safer the drugs. To characterize the safety of the drug, it is also used therapeutic index (TI), which is also determined by dose. The therapeutic index is the ratio of the average lethal dose to the average therapeutic dose.
where DC 50 is the dose that causes the death of 50% of animals.
ED 50 is a dose that causes a pharmacological effect in 50% of animals.
The annotations for the drugs indicate course, daily and single doses.
A single dose is prescribed in one dose, a daily dose is prescribed for the whole day, a course dose is prescribed for several days. As a rule, higher daily doses are three times higher than single doses. For example, the highest single dose of analgin for an adult is 1.0, the maximum daily dose is 3.0.
The decisive factor for an intense pharmacological effect is not the absolute value of the dose of the drug taken, but its concentration in the blood. The dose is expressed in grams or fractions of a gram. For more accurate dosing, the amount of substance is calculated per 1 kg of body weight. Some medicines(antibiotics, hormones, etc.) are usually dosed in Action Units (AU).
The individual choice of dose (adequate for a particular patient) depends on the severity and nature of the disease. General rule boils down to the fact that when lung diseases or moderate degree, a threshold dose is first administered, then it is increased until the desired therapeutic effect. Individual selection of doses is especially necessary for poisonous and potent drugs.
Child dose (A) is calculated using the formula:
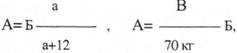
where B is the adult dose
a - child’s age
B - child’s weight
Dosing of chemotherapy drugs differs from dosing of other drugs. This group of drugs is administered in maximum tolerated doses, when the drugs act on the microorganism but are not toxic to the human body. Start with loading dose in order to create a high concentration of the drug in the blood and tissues to obtain a rapid therapeutic effect. Then the drug administration mode is set maintenance dose .
It should be remembered that the most important quality drugs are not the “strength” of their action, but the effectiveness of a safe dose. The reason for many therapeutic failures lies in the difficulty of predicting the individual difference between the dose of drugs and the concentration they reach in the blood.


