Lack of calcium in children - hypocalcemia - reduced, compared with the norm, the content of the calcium element in the child's body. Calcium is one of the most important substances necessary for the normal development of the baby, namely: the bone-ligamentous apparatus, the normal development of the dentofacial system, for the coordinated and well-coordinated work of the muscular system. Its lack can lead to serious diseases of the above systems, which will delay the development and growth of the child.
In the normal course of six months of a child's life up to a year, he receives calcium from his natural food source - from his mother's breast milk. It is possible to use special infant formulas, which also contain this macroelement in their composition. After six months, the child can be given - cereals, vegetables and fruits.
Starting from eight months, the baby can consume dairy products - this is milk, kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, cheese. It is these foods that are essential for the baby to get a normal amount of calcium.
It is also important, along with these products, the child's consumption of food rich in vitamins D and C. These are vegetable oil, herbs, berries, vegetables, fruits. Then not only the intake, but also the absorption of calcium will be sufficient for the child.
Normal calcium levels in a child:
- 400-500 mg per day in babies up to 6 months;
- 500-700 mg per day in children under one year old;
- 700-1000 mg in children under ten years of age.
How does it develop
The above vitamin D is the main substance necessary for the normal absorption of calcium in those cells of the body for which it is important. The synthesis of this vitamin is possible if there is sufficient sunlight in the life of the baby, and in the autumn-winter period it is necessary to give the child up to a year a water-soluble version of this vitamin.
Children of the older age group may experience hypocalcemia in various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Among them, the most common are enteritis, and all kinds, accompanied by dysbacteriosis. And since the place of absorption of calcium into the blood is the intestinal mucosa, a violation of its absorption is natural.
In the body of each person there are parathyroid glands - they take part in the regulation of the level of the macroelement through parathyroid hormone. Gland or hormone abnormalities can also contribute to calcium deficiency.
Thus, the three most important causes of hypocalcemia are disturbances in the digestive system and. First of all, you should pay attention to these factors if you notice a lack of calcium in your child's body.
How does it manifest
Symptoms of hypocalcemia are fully manifested in children, but in babies they have some features. Since babies cannot move and speak on their own, cannot complain of any discomfort, only a pediatrician can identify the diagnosis of hypocalcemia.
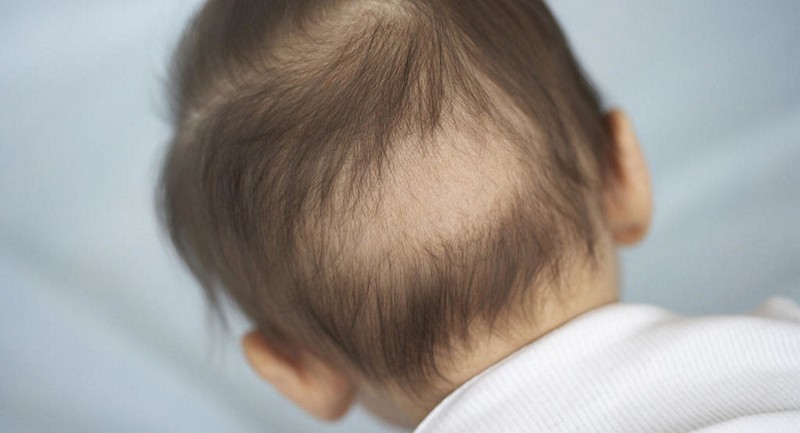
The leading signs of calcium deficiency in babies are:
- Profuse sweat on the skin, and especially on the occipital region;
- Rolling out of the hairline at the points of contact of the child's head with the pillow;
- Trembling of chin during crying;
- Trembling with loud stimuli - sound, flashes.
The baby may develop a curvature of the skeleton of the extremities, the spine. becomes pathological. The older the child becomes, the higher the likelihood of fractures, dislocations, joint mobility. Anemia is observed in the blood.
From the side of the muscular system, a macronutrient deficiency threatens with very formidable manifestations - these are spasms, seizures. Since calcium is responsible for the transmission of the neuromuscular impulse, when it is deficient, the coordinated work of nerves and muscles is disrupted. This pathology is dangerous for the life of the child.
In addition to all of the above, the most common manifestation of calcium deficiency is.
Rickets can be divided into early and late stages. In the early stage, all the symptoms of a trace element deficiency are visible - sweating, increased excitability with external stimuli. At this stage, manifestations from the bone apparatus are not observed.
It is important to notice these symptoms in a timely manner and show the child to a pediatrician in order to begin treatment. Otherwise, the early stage will quickly move into a more formidable later one, where rickets will play out in full force.
First of all, dyspeptic disorders begin - loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting. are observed. Calcium deficiency has a bad effect on.
In this stage, the main symptoms of rickets appear - asymmetry in the development of the skull, malocclusion of the jaws, the formation of bone tubercles on the forehead and crown, and curvature of the lower extremities. From the side of the sternum and spine - deformation and curvature, the so-called "chicken breast".
Treatment
Delayed treatment leads to the progression of the disease. This can lead to serious consequences and disability.
Preparations
Medical therapy is prevalent. The pediatrician prescribes drugs, taking into account the causes, symptoms and degree of development of the disease. All drugs can be divided into three groups:
- calcium supplements,
- preparations of a combination of calcium and vitamin D necessary for its absorption,
- multivitamin complexes.

Among the drugs of the first and second groups, the following have been used:
- Chloride, lactate, produced in the form of tablets for oral administration, with various additives; in addition, such a drug is available in the form of solutions, so calcium injections for children also exist;
- The well-known Calcium D3 Nycomed and Calcium Complivit D3 are good drugs used in both children and adults, both in the prevention of hypocalcemia and in the treatment of this disease;
- Calcinova containing various vitamins of groups A, D, B;
- Dolomite, Berocca and others.
Multivitamin complexes are prescribed as the main, and as a secondary means. For example, if a child takes calcium in preparations without vitamin D, then such complexes are indispensable. Vitamins with a lack of calcium are,. Regardless of whether these vitamin preparations contain calcium supplements, they are needed in the treatment of hypocalcemia.
Diet
With a lack of calcium in a child, it is necessary to correct his nutrition - in other words, introduce a diet. When choosing foods for a child's diet, one should consider which of them are most favorable in replenishing the macronutrient.
First of all, it is recommended to provide the child with dairy products - milk and its derivatives, cheeses, cottage cheese, ayran, curdled milk. You should also not forget about fruits and vegetables - and try to serve fresh herbs with dishes.
Nuts, dried fruits, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds are other calcium-rich foods that can be consumed in the diet of a growing organism.
Egg yolks, seafood and fish are a real storehouse of useful elements and substances, including calcium.
Rational nutrition of a growing organism, taking into account the choice of these products, will help to fill the lack of this element, eliminate unpleasant symptoms and provide a preventive effect.
Other Methods
In addition to the above methods of getting rid of the problem, there is a restriction in the child's diet of acidic foods and chocolate - they can interfere with the absorption of calcium. If children live in areas with insufficient sunlight, it is necessary to provide it to them through tanning beds and physiotherapy. Monitor your child's activity and sleep.
Prevention
Pregnant women are shown the use of vitamin D so that the bone skeleton, dentofacial system and the muscular apparatus of the fetus develop normally.



