A similar problem occurs in many people, especially in old age. The teeth have a kind of shock absorber, the balance, the violation of which leads to wobbling and their loss. Many do not pay special attention to this, but this is a reason to see a doctor. The cause may be periodontitis, or a damaged jaw.
In these diseases, the connection between the tissues of the gums and the bone is disrupted, which leads to loosening of the tooth. Periodontitis is an inflammatory process associated directly with the patient's lack of hygiene, as well as the use of poor quality hygiene items. The bone begins to dissolve.
Along with this, the cause can be an incorrect bite with an incorrect position of the upper and lower jaw, or a grinding sound, as a result of which hard tissues wear out and become mobile.
Only a doctor can determine the cause of mobility and prescribe treatment. Strong glue for fixing will not help if the bone around the hole has completely lost its strength. In this case, there is practically no chance of saving.
Causes of mobility
Teeth become mobile when:
- deep bite;
- smoking;
- heavy load on the tooth surface;
- stress;
- diseases of the thyroid gland;
- mechanical injuries.
Symptoms include dental plaque, increased saliva viscosity, pain while eating.
Dental treatment for mobility:
If the bone tissue and gums have not atrophied, then with the help of surgical intervention, the tooth can be returned to its place. Sometimes, to strengthen it, a removable or non-removable splint is applied in the hole, which will strengthen the fallen tooth with the adjacent one, and it will soon grow together.
Today, mobility is treated well with Emdogain, a biological product that is able to return soft and hard tissues to their previous state. Emdogain promotes the formation of healthy tissue that will attach the tooth to the bone, restoring its vitality to it.
Mobility is a pathology that requires lightning-fast dental treatment. The neglected form of periodontitis makes the treatment process difficult and not always successful. An extracted tooth modifies bone tissue, leading to its partial or complete loss. All this entails loosening of adjacent healthy teeth, since the bone tissue after the loss of a diseased tooth does not receive a load, and begins to gradually dissolve.
In this case, doctors are advised to put yourself a crown, or an artificial root. Dental mobility pathology has three stages. In the first stage, the teeth can only move in two directions: back and forth. Further, a sign of the second stage - the movement of the teeth is added to the side. The third stage is difficult, the movement occurs vertically and in a circle. Determine the degree of mobility with tweezers, go with a probe, slightly pressing it in a different direction.
Thus, it is recognized how much the ligaments are destroyed and what kind of inflammation associated with periodontitis. In periodontitis, it is important to determine the depth of the clinical pocket. With the gum pocket, the gingival groove is probed, up to 3 mm deep. With a periodontal pocket, periodontal tissues are partially destroyed, while bone tissue is destructed.
The depth of the pocket is measured with a graduated probe by pressing it against the tooth surface. Depth is measured from 4 sides. If periodontitis passes into an advanced stage, and the focus of inflammation cannot be drowned out in the ear, then the tooth requires removal. In this case, it is possible to remove multi-rooted teeth leading to the development of ostiomyelitis. The measurement results in the deepest section.
Treatment is associated with the elimination of a factor that affects dental mobility. The first step is to remove deposits. It is important to remove bleeding and restore the microflora of the oral cavity. Treatment is always aimed at preserving the tooth as much as possible.
As you can see, harmless staggering cuts in itself many dangers and hidden pathological factors. Do not postpone a visit to the doctor, because modern orthopedics is equipped with the latest materials and equipment to restore dental health. You can put crowns of any complexity and from any material, this is much better than endangering the periodontium, which is devoid of a tooth.

In an adult, tooth mobility can occur for various reasons, but in any case it is not very pleasant and most of those who have such an anomaly want to eliminate it. Quite often, periodontal disease can be considered the reason that teeth begin to wobble.
If so, then the treatment of tooth mobility must be carried out. But before starting treatment for tooth mobility, you need to understand exactly what caused it and what degree of the disease. This will allow you to choose the optimal tactics for dealing with the problem and achieve good results.
Physiological and pathological tooth mobility
There is physiological and pathological tooth mobility. The emergence of a physiological form of mobility is associated with the need to evenly distribute the load on the dentoalveolar apparatus. But the pathological mobility of the teeth is an abnormal phenomenon and requires mandatory elimination.
Degrees of tooth mobility: 1, 2, 3, 4 degrees
Dentists distinguish different degrees of tooth mobility:
- Mobility of the 1st degree is manifested by the movement of the teeth in one direction and the amplitude of movement is less than 1 millimeter.
- Teeth mobility of the 2nd degree is the movement of the teeth to the sides and back and forth with an amplitude of more than 1 mm.
- The mobility of the teeth of the 3rd degree is also a movement in the vertical direction.
- Mobility of the 4th degree - the tooth can not just stagger, but also rotate.
Different degrees of tooth mobility in combination with bleeding and swelling of the gums indicate the activity and neglect of the pathological process. So if you have degree 2 teeth mobility, you must definitely see a doctor and eliminate the anomaly. If you have been diagnosed with grade 3 teeth mobility, treatment should be urgent. Otherwise, you risk losing loose teeth and involving other teeth in the pathological process.
Periodontal disease and tooth mobility
Many believe that periodontal disease can lead to loose teeth. Mobility of the teeth, however, with this disease can occur only in the most extreme stages. Most often, periodontitis can be considered the cause of pathological teeth instability!
Both periodontitis and periodontal disease are characterized by the fact that periodontal disease is affected, but a disease characterized by the development of an inflammatory process is periodontitis, and periodontal tissue damage without inflammation is periodontal disease. Mobility of teeth with periodontal disease occurs due to the fact that the ligaments that anchor the tooth in the hole are damaged.
 One of the signs of periodontitis is bleeding. Mobility of teeth in the presence of blood from the gums is a double signal that you have periodontitis. But periodontal disease is very rarely accompanied by bleeding gums.
One of the signs of periodontitis is bleeding. Mobility of teeth in the presence of blood from the gums is a double signal that you have periodontitis. But periodontal disease is very rarely accompanied by bleeding gums.
If you do not treat periodontitis, then teeth loss is possible within 2 years. Therefore, if you find bleeding, teeth mobility, swelling of the gums and a feeling of discomfort in them, you should immediately contact a periodontist and deal with the problem.
Elimination of tooth mobility
Eliminating tooth mobility can involve different treatment approaches. If the reason is the presence of periodontitis, then measures are taken to treat this disease. Gums are massaged, teeth are splinted, injections are used to eliminate bleeding and relieve inflammation, and much more.
In very difficult situations, when the elimination of tooth mobility is impossible, basal implantation or removable prosthetics may be recommended.
At the PerioCenter dentistry center you will meet highly qualified specialists who will select the most effective treatment for your ailment and help eliminate loosening of the dentition.
Even normal healthy teeth somewhat mobile. The data of the histological structure of the periodontium confirm the possibility of such mobility. Periodontium or pericment, consisting of connective tissue permeated with a dense network of numerous blood and lymphatic vessels and impregnated with tissue fluid, is a loose soft layer that allows the tooth to move under chewing pressure in different directions around the longitudinal and transverse axes.
Such micro-excursions, invisible to the naked eye and not detectable by palpation of the teeth, are confirmed by the existence of approximal facets in the tooth located in the middle of the dentition. So, for example, the 7th tooth has contact surfaces from the mesial and distal sides and the facet from the 6th and 8th teeth, the 8th tooth is in contact only with the 7th and therefore has only one facet from the mesial side. These facets are apparently formed as a result of naturally occurring micro-excursions of the teeth around the vertical axis.
Pathological tooth mobility... Examination of the patient reveals teeth with pathological mobility. DA Entin distinguishes three degrees of tooth mobility. Light rocking of the tooth with fingers or tweezers, accompanied by a visible displacement of its crown in one direction (vestibulo-oral), he defines as first degree mobility. The visible displacement of the crown in two directions - vestibulo-oral and mesio-distal - indicates the second degree of tooth mobility. The mobility of the tooth in three directions - vestibulo-oral, medio-distal and apical is assessed as the mobility of the third stele and.
Magnitude and topography dentition defects... The size of the dentition defect and its location depends, as said, on various reasons, including the anomaly in the number of erupted teeth.
Anomaly in the number of erupted teeth.
Tooth number anomaly expressed in a decrease or increase in their number. Normally, the number of teeth in a milk bite is 20, and in a permanent one - 32.
As a result of the reduction chewing apparatus the number of teeth in modern humans has decreased to 32. The dental system tends to be further reduced in the process of adapting to the new functional needs of the chewing apparatus. In this regard, the upper lateral incisors, upper and lower wisdom teeth disappear, and some authors believe that there is a reduction of the lower small molars. The transitional stages of the reduction of these teeth are expressed in the spike-like shape of the lateral incisors and the altered morphology of the wisdom teeth. A decrease in the number of teeth can be the result of pathological processes. It is sometimes caused by a developmental or eruption pathology. When developmental abnormalities are absent in the jaw, the rudiments of teeth (adentia or anodontia), with pathology of eruption, teeth are retained in the thickness of the jaw bone tissue (retention) and are detected only by palpation or X-ray examination.
Adentia can be complete and incomplete... The same can be said for retention. The upper canines and second premolars are more likely to be retentive.
Adentia and retention are rare, usually the decrease in the number of teeth is associated with their loss or removal. This fact should also be clarified through a survey. If the teeth fall out by themselves and, moreover, entirely, then in most cases they, obviously, were affected by periodontal disease. If gradually decaying teeth were removed, then we are talking about teeth affected by caries.
Tooth number anomaly it is also expressed in an increase in their number, which is also rare. Supernumerary teeth are most often in the area of \u200b\u200bthe incisors of the upper or lower jaw and more often in a permanent than in a milk bite. If there is space, supernumerary teeth are located in the dentition; in the absence of space, they erupt orally or vestibularly. Sometimes there is also the eruption of four molars instead of three. Supernumerary canines and premolars are rare (Peckert).
Etiology of supernumerary teeth is not yet clear, and there are many theories to explain this issue. Some (Osborne) explain the formation of supernumerary teeth by the proliferation of the epithelium of the dental plate, others (Valkhoff) - by the bifurcation of the normal tooth germ into parts capable of development; still others (Bolk) are atavism. Classification of dentition defects. The size of the defects and their location are determined by the dental formula. However, they vary so much that it became necessary to systematize and classify them.
According to the calculations of A. L. Grozovsky, there may be over 16,000 different combinations defects of the dentition... The classifications have been proposed by many authors.
With class I defects, it is possible use of prostheses only removable construction, and with I subclass shows a bilateral, and II - a one-sided prosthesis. In case of defects of subclass I of class II in all cases, a non-removable prosthesis design can be shown, and in subclass II, in most cases, a removable design or removable prostheses in combination with fixed ones is shown, except for a defect in the region of the anterior teeth, in which a non-removable design is shown, even in the absence four incisors.
Sure, when choosing a design the anatomical and physiological features of the teeth, the nature of the mucous membrane and the state of other elements of the prosthetic field should be taken into account.
Often, tooth mobility is a symptom of some pathology. The degrees of anomalies are of different intensity, and the methods of treatment today are so diverse that they make it possible to preserve healthy units in a complete set.
Poor hygiene, neglect of the health of teeth and gums, untimely treatment of diseases leads to active infection of the oral cavity, pathologies and premature loss of dental units. What to do and how to strengthen the root part in order to maintain a beautiful smile for as long as possible?
Causes of occurrence
What is tooth loosening? Doctors believe that it is not an independent disease, but rather a consequence of various pathologies. To begin with, it is advisable to determine why this is happening and only then you can decide by what method to prevent premature tooth loss.
Some of the most common loosening problems in individual units include:
- and - are formed as a result of an acute inflammatory process of tissues. Usually this leads to, which was left without treatment and manifests itself in the form. From the constantly accumulating bacteria, a periodontal pocket is formed, which pushes the mucous membrane away from the neck of the tooth, thereby leading to more serious complications.
- - grinding of jaws during night sleep. Such an unforeseen and uncontrolled overload can lead to the mobility of all units in the row.
- Wrong bite - a lot depends on its shape and position of the teeth. Sometimes some of them have more reliable fixation and deep roots, which makes it possible to drive out weak "neighbors".
- After braces - when changes in the position of individual units have not yet been fixed and they are trying to return to their original position.
- Injuries and various injuries - the result of a simple blow can be both a complete loss of a tooth and its strong loosening.
- Removal or loss of one of the units in a row - usually, the absence of the usual load on the bone tissue leads to its fast. And when it becomes thinner in one place, it decreases little by little in neighboring areas, which threatens the precariousness and loss of healthy teeth.
There may be other reasons for the weakening of the ligament or the separation of the gums from hard tissues in your case. So, vitamin deficiency, long-term diseases of a general nature, atherosclerosis of blood vessels, problems with the circulatory system, and even psychosomatics can lead to a similar pathology.
Teeth are loosened in a seemingly healthy gum, and in inflamed areas, under crowns or dentures, in the area of \u200b\u200ba wisdom tooth, etc. In any case, the cause must be established before starting treatment.
Degrees of mobility
There are different classifications of loosening of the teeth, but in the general formula they are reduced to varying degrees of its intensity:
- Physiological is the natural mobility of a unit, which is provided by nature for the normal functioning of a number, high-quality processing of food, etc. It is not a pathological form and does not require treatment or correction.
- The first degree of mobility - indicates that inflammatory processes have already begun or other problems with soft tissues. In this case, only slight loosening to the right and to the left is allowed, no more than 1 mm in amplitude.
- The second degree is characterized by the movement of the tooth not only to the sides, but also back and forth, and the intensity increases by more than 1 mm.
- The third degree is manifested by the mobility of the unit in almost all directions and even with an inclination to free space in any direction.
- The fourth degree is not distinguished by all scientists, but it differs from the previous one in that the tooth can be rotated a little around its axis, which indicates the close date of its independent loss.
Treatment methods
There is no need to think that if you have one tooth or several loose, then it makes no sense to go to the doctor, they say, he will fall out. Perhaps, in your case, it is still realistic to save the dentition and simply fix it in some accessible way. Moreover, modern medicine offers a number of treatment methods that are selected depending on the reasons that led to loosening.
Let's highlight the main ways to correct the pathological process:
- They clean plaque and tartar so that other methods of exposure are carried out on a clean surface.
- In case of soft tissue inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed.
- For fixing a row, sometimes it becomes a good solution, which is to fasten them on the invisible side with hooks or even full-fledged caps.
- In the case of periodontal tissue disease, the best treatment is, which is a high-quality deep cleaning of periodontal pockets.
- Flap surgery is applicable when the intensity of the gum lesion is too great and a complete dissection of tissues and their restoration by a surgical method is required.
- If the problem of bruxism became the cause of loosening of the teeth, then it is better to treat it psychotherapeutically, and put on special mouth guards at night.
- Any bite defects are corrected, for this, braces are most often used. And to fix the result, you need to additionally carry it.
- In cases of tooth loss, in order to prevent bone tissue atrophy and mobility of adjacent units, it is recommended to immediately replace it with a high-quality implant or at least a removable prosthesis.
- For the treatment of periodontal tissues and restoring their position around the neck of the tooth, methods such as ozone, laser therapy or. They promote deep cleaning of pockets and rapid tissue regeneration, which becomes an effective method in the early stages of the disease.
Video: tooth mobility, splinting.
Of course, the price for each of these methods is different and largely depends on the level of the clinic. Nevertheless, saving on health is not worth it, since replacing your teeth with artificial ones will still be more expensive.
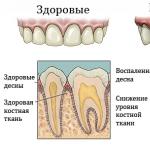
Healthy teeth appear to be completely motionless. However, in reality, they elastically displace during chewing, providing an even distribution of the load on the dentition.
But this physiological shift is so insignificant that it is not noticed by a person. In contrast, pathological mobility is clearly felt when the tooth is pressed with a finger or tongue.
Stability standards
The periodontal ligamentous apparatus is responsible for the stability of the teeth, which ensures their fixation in the alveolar socket. Its main element is collagen fibers, which are attached to the cement of the root at one end, and to the bone of the alveoli at the other.
On the one hand, they keep the tooth from significant movements in any direction, and on the other hand, they perceive the chewing load and gently transfer it to the alveolus, protecting the bone tissue from overload.
In a normal state, the periodontal gap (the space between the cement of the tooth and the bone of the alveoli) is within the physiological norm. At the apex of the root, its thickness is 0.2-0.25 mm, in the middle part - 0.15-0.2 mm, in the cervical region - 0.3 mm.
If you try to shake a healthy tooth, it will seem to be motionless. Its displacement under load can only be determined using a special test.
The surrounding tissues are pink-coral in color, there are no swellings and gingival pockets.
Reasons for loosening

Pathological teeth mobility are caused by the following reasons:
- Periodontal disease.
- Abnormal position of some units. Often this is a malocclusion that disturbs the occlusion.
- Loss of adjacent units, depriving the problem tooth of lateral support.
- Oral trauma.
- Resorption (resorption) of the jaw bone.
- Dentist mistake - accidental damage to the tooth with dental instruments or the negative effects of medication.
Most often, the mobility of the teeth is a consequence of periodontal disease, and the late one, which is in the 2nd or 3rd stage. The mobility caused by changes in the periodontium speaks of its significant damage.
The periodontium ensures the stability of the position of the teeth in the gums, protects them from infections, maintains trophism and metabolic processes in a normal state. With its defeat, the ligament ceases to perform its function, the teeth lose stability, become mobile.
Factors causing periodontitis:
- Poor oral hygieneleading to decay of food debris and the development of pathogenic microflora.
- Saliva bactericidalcausing the formation of tartar.
- Overload or underload of the periodontium. In the first case, hypertrophy (expansion) of the periodontal gap occurs with a change in the structure of the alveolar bone. Underloading is dangerous by resorption of the jawbone.
- Reduced immunity or vitamin deficiency.
- Diseases of various organs - Gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, pancreas, etc.
Clarification of the complexity of the clinical case
There are several ways to measure tooth mobility. According to the classification of D.A. Entin, there are 4 degrees of pathology:
- I degree. The movement of the top of the tooth in the oral-vestibular direction ("right-left" for lateral units, "forward-backward" - for anterior) does not exceed 1 mm. In other directions, there is no mobility.
- II degree. Mobility I degree + movement of no more than 1 mm in the palatal-distal ("back-forward" for lateral units, "right-left" - for front) direction.
- III degree. The vertical is added to the mobility of the I and II degrees.
- IV degree. The first 3 mobility + rotation of the tooth around its axis. Thus, grade IV is characterized by mobility in all possible directions.
Attention! The third and, especially, the fourth degree speaks of far-reaching and, most likely, irreversible changes in the periodontium.

Forbidden actions and diagnostics
Usually, patients see a doctor about tooth mobility when it progresses to the 3rd or 4th stage. If it is caused by periodontal disease, it means that 5-6 years have passed since the onset of the disease.
Periodontal disease usually begins with bleeding of the gums after brushing your teeth. It is at this moment that you should consult a doctor in order to prevent the development of the disease.
Late circulation makes the forecast uncertain. It is possible that the correct treatment will help avoid extraction, but this is not guaranteed.
Having found that the tooth is loose, the patient should do the following:
- Rinse your mouth with warm water.
- Eliminate any physical impact on the problem tooth - do not touch it with a brush when brushing, do not touch it with your hands and tongue.
- See a doctor as soon as possible.
The doctor determines the degree of mobility and the cause of it by examining the oral cavity, and if necessary using fluoroscopy.
If there is pronounced mobility, it is easy to establish it by swinging the tooth with tweezers or a finger set on the apex. The condition of the surrounding tissue is also determined by examination and palpation.
Bright red gums may indicate gingivitis. Gray color usually indicates its transition to the necrotic ulcerative stage. A dark red-burgundy shade speaks in favor of periodontal disease.
In this case, gingival pockets usually appear. The doctor measures their depth, evaluates the condition of the gum edge. The appearance of pockets can be accompanied by destruction of bone tissue.
Diagnostics is carried out not only with an open, but also a closed mouth - to check the occlusion, to determine the nature and depth of the bite. This is necessary to establish whether there is an anomaly in the structure and position of the teeth, which may cause mobility.
X-ray allows confirming or refuting the previously made diagnosis. Sometimes a blood test is required.
Treatment methods
In the general case, the treatment of tooth mobility is reduced to eliminating the cause that caused it and ensuring the stability of the tooth by means of its mechanical fixation. In each case, an individual decision is made, depending on the specific clinical situation.
Treatment begins with measures that eliminate the cause of the pathology. Therapeutic (medication), microsurgical and hardware methods of treatment are used.
Hardware treatment

This method of treatment involves the use of devices that work on physical principles:
- Laser treatment. A modern, low-traumatic type of treatment of lesions, which can be used for most pathologies.
It is an excellent alternative to the old drill. The laser beam destroys pathogenic microflora, sterilizes the affected area, promotes accelerated tissue regeneration. At the same time, the risk of complications is minimized.
- Ultrasound treatment. Sound impulses and water supplied by an ultrasonic scaler destroy and remove tartar, plaque, microbial films, and toxins from the enamel surface. Ultrasound can be used to clean gingival pockets up to 11 mm deep.
- Ozone therapy. Relieves inflammation and disinfects the focus of the disease with ozone generated by a special apparatus. Ozone therapy is often used in conjunction with ultrasound and laser treatments.
Curettage
Curettage is the cleaning of gum pockets from microbes, decomposed food debris and diseased tissue. After cleaning, preparations are injected into the gap between the gum and the root, which accelerate the regeneration processes.
Splinting
The main way to eliminate tooth mobility (but not its cause) is splinting - the installation of a removable or permanent splint that ties together healthy and diseased teeth, ensuring the stability of the latter.
The types of splinting are diverse:
- Semi-ring and ring tires. In the case of the latter, thin metal sleeves connected to each other are put on the teeth. Semi-ring tires are installed from the inside, remaining invisible from the front. This makes the splinting more aesthetic.
- Cap splinting. It is performed in the form of caps welded together and put on the teeth. Their difference from semicircular and annular structures is that they simultaneously cover the cutting surfaces with the side ones.
- Intradental tires. The most modern constructions are connected to dentin by inserts implanted into it.
- Insert tires. They are a metal insert installed on the edges of the teeth and connected at the edges with full crowns worn on the support units. Thus, the insert takes over the function of the common cutting edge.
- Coronal splints. They cover the teeth from all sides up to the gums. Long-lasting and aesthetic designs, but require healthy gums for their installation.
- Splinting structures made of fiberglass and aramid yarns. The link connecting the teeth is a fiberglass tape or aramid thread, which is inserted into the grooves cut into the enamel and dentin. Fastened with composite material.
- Pin tires. They are caps attached to the pins inserted into the pulped canals. These are reliable and aesthetic designs used most often from the front. A serious drawback is the need for depulpation.
- Splinting clasp prostheses. Structurally, they represent a developed metal arch, fixed from the inside of the jaw. The arc is equipped with various fasteners (clasps, claws, etc.), providing fixation of problematic units.
Removal of a mobile tooth with subsequent prosthetics is used in cases where the restoration of its function is impossible, and the delay in excretion threatens neighboring units.
This usually happens with advanced stages of periodontal disease with atrophy of the alveolar bone tissue.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Prevention
The main measures for the prevention of mobility are high-quality oral hygiene, and timely access to a doctor at the first signs of the disease - be it caries, pulpitis, periodontitis or other pathology.
When removing several adjacent units, the placement of implants helps to stop the destruction of the jawbone, which provide loading of the jaw, contributing to the preservation of the bone structure.
The cost of therapy

Prices for the treatment of tooth mobility vary greatly depending on their number, degree of damage, complexity of the work, the methods and equipment used, the location of the clinic and other conditions.
Without pretending to be particularly accurate, we provide approximate prices for some types of work.
|
Treatment type |
Estimated price, rub. |
|
| Laser treatment | Treatment of superficial and medium caries | |
| Deep caries treatment | ||
| Treatment of a periodontal pocket in the area of \u200b\u200bthe 1st tooth | ||
| Treatment for necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis | ||
| Ultrasound treatment | Removal of hard deposits from the 1st tooth | |
| Cleaning the oral cavity | ||
| Splinting |
Front row fiberglass | |
| Fiberglass premolars and molars | ||
| Metal crowns | ||
| Clasp prosthesis | Metal-ceramic crowns for 5-6 anterior units | |
| All-metal crowns for 5-6 anterior units | ||
Fixation of teeth by splinting is not such a frequent operation in comparison with drug or hardware treatment. Few people can "brag" about having a fiberglass or other splint in their mouths.